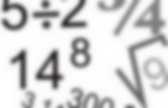
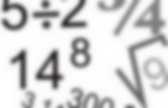
1.3.3.26.11. Scatterplot Matrix. Data analysis on the Web. Wolfram MathWorld: The Web's Most Extensive Mathematics Resource. SOCR: Statistics Online Computational Resource. SOCR: Statistics Online Computational Resource. SOCR: Statistics Online Computational Resource. Basic Statistics - Part 1. Statistical Analysis Handbook. Outline of statistics. The following outline is provided as an overview and guide to the variety of topics included within the subject of statistics: Statistics pertains to the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data.
It is applicable to a wide variety of academic disciplines, from the physical and social sciences to the humanities; it is also used and misused for making informed decisions in all areas of business and government. Basic Statistics. This section describes basic (and not so basic) statistics.
It includes code for obtaining descriptive statistics, frequency counts and crosstabulations (including tests of independence), correlations (pearson, spearman, kendall, polychoric), t-tests (with equal and unequal variances), nonparametric tests of group differences (Mann Whitney U, Wilcoxon Signed Rank, Kruskall Wallis Test, Friedman Test), multiple linear regression (including diagnostics, cross-validation and variable selection), analysis of variance (including ANCOVA and MANOVA), and statistics based on resampling.
Since modern data analyses almost always involve graphical assessments of relationships and assumptions, links to appropriate graphical methods are provided throughout. It is always important to check model assumptions before making statistical inferences. Power analysis provides methods of statistical power analysis and sample size estimation for a variety of designs. Statistics Help for Journalists. Numbers can't "talk," but they can tell you as much as your human sources can.

But as with human sources, you have to ask! So what should you ask a number? Well, mathematicians have developed an entire field — statistics — dedicated to getting answers out of numbers. Now, you don't have to have a degree in statistics in order to conduct an effective "interview" with your data. But you do need to know a few basics. In 1996, I first published Statistics Every Writer Should Know, an online tutorial for math-phobic journalists. Running a business demands at least a basic knowledge of math and math concepts, so I'm including this tutorial as an appendix my 2012 book, How to Make Money Publishing Community News Online. 6 BASIC STATISTICAL TOOLS. There are lies, damn lies, and statistics......

(Anon.) 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Definitions 6.3 Basic Statistics 6.4 Statistical tests 6.1 Introduction In the preceding chapters basic elements for the proper execution of analytical work such as personnel, laboratory facilities, equipment, and reagents were discussed. Before embarking upon the actual analytical work, however, one more tool for the quality assurance of the work must be dealt with: the statistical operations necessary to control and verify the analytical procedures (Chapter 7) as well as the resulting data (Chapter 8). It was stated before that making mistakes in analytical work is unavoidable.
Data analysis. Basic statistics: mean, median, average, standard deviation, z-scores, and p-value - ControlsWiki. From ControlsWiki Note: Video lecture available for this section!
Authors: Andrew MacMillan, David Preston, Jessica Wolfe, Sandy Yu Stewards: Jeff Byrd, Khek Ping Chia, John Cruz, Natalie Duchene, Samantha Lyu Date Presented: 11/21/06; Revised: 11/5/07 Introduction Statistics is a field of mathematics that pertains to data analysis. Average value (mean) Most frequently occurring value (mode) On average, how much each measurement deviates from the mean (standard deviation of the mean) Span of values over which your data set occurs (range), and Midpoint between the lowest and highest value of the set (median) Statistics is important in the field of engineering by it provides tools to analyze collected data.
What is a Statistic? In the mind of a statistician, the world consists of populations and samples. Parameters are to populations as statistics are to samples. A parameter is a property of a population. Statistics take on many forms. What are Basic Statistics. Descriptive Statistics "True" Mean and Confidence Interval.
Probably the most often used descriptive statistic is the mean. The mean is a particularly informative measure of the "central tendency" of the variable if it is reported along with its confidence intervals. As mentioned earlier, usually we are interested in statistics (such as the mean) from our sample only to the extent to which they can infer information about the population. The confidence intervals for the mean give us a range of values around the mean where we expect the "true" (population) mean is located (with a given level of certainty, see also Elementary Concepts). Shape of the Distribution, Normality. More precise information can be obtained by performing one of the tests of normality to determine the probability that the sample came from a normally distributed population of observations (e.g., the so-called Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, or the Shapiro-Wilks' W test.
Correlations Purpose (What is Correlation?) Outliers. Basic Statistics Home Page. Statistics.com. Free Statistical Software - FreeStatistics.info.