Age of Enlightenment. The Age of Enlightenment (or simply the Enlightenment, or Age of Reason) is an era from the 1650s to the 1780s in which cultural and intellectual forces in Western Europe emphasized reason, analysis and individualism rather than traditional lines of authority.
It was promoted by philosophes and local thinkers in urban coffeehouses, salons and masonic lodges. It challenged the authority of institutions that were deeply rooted in society, such as the Catholic Church; there was much talk of ways to reform society with toleration, science and skepticism. New ideas and beliefs spread around the continent and were fostered by an increase in literacy due to a departure from solely religious texts. Publications include Encyclopédie (1751–72) that was edited by Denis Diderot and (until 1759) Jean le Rond d'Alembert. The Book of THOTH - The complete guide to the Tarot, Magick and. Magick. One must find out for oneself, and make sure beyond doubt, who one is, what one is, why one is ...Being thus conscious of the proper course to pursue, the next thing is to understand the conditions necessary to following it out.
After that, one must eliminate from oneself every element alien or hostile to success, and develop those parts of oneself which are specially needed to control the aforesaid conditions. (Crowley, Magick, Book 4 p.134) Crowley defined Magick as "the science and art of causing change to occur in conformity with will. "[4] He goes on to elaborate on this, in one postulate, and twenty eight theorems. Anemia. Anemia is the most common disorder of the blood. The several kinds of anemia are produced by a variety of underlying causes. It can be classified in a variety of ways, based on the morphology of RBCs, underlying etiologic mechanisms, and discernible clinical spectra, to mention a few.
The three main classes include excessive blood loss (acutely such as a hemorrhage or chronically through low-volume loss), excessive blood cell destruction (hemolysis) or deficient red blood cell production (ineffective hematopoiesis). Of the two major approaches to diagnosis, the "kinetic" approach involves evaluating production, destruction and loss,[3] and the "morphologic" approach groups anemia by red blood cell size. Signs and symptoms[edit] Main symptoms that may appear in anemia[5] Anemia goes undetected in many people, and symptoms can be minor or vague. Illuminati. History The Owl of Minerva perched on a book was an emblem used by the Bavarian Illuminati in their "Minerval" degree.
Secret society. "Secret Society Buildings at Yale College", by Alice Donlevy[1] ca. 1880.
Pictured are: Psi Upsilon (Beta Chapter), 120 High Street. Left center: Skull & Bones (Russell Trust Association), 64 High Street. Right center: Delta Kappa Epsilon (Phi Chapter), east side of York Street, south of Elm Street. Bottom: Scroll and Key (Kingsley Trust Association), 490 College Street. A secret society is a club or organization whose activities, events, and inner functioning are concealed from non-members.
Occult. Three Books of Occult Philosophy. De Occulta Philosophia, Libri tres Three Books of Occult Philosophy (De Occulta Philosophia libri III) is Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa's study of occult philosophy, acknowledged as a significant contribution to the Renaissance philosophical discussion concerning the powers of ritual magic and its relationship with religion.
Ordo Templi Orientis. Ordo Templi Orientis (O.T.O.) ('Order of the Temple of the East' or 'Order of Oriental Templars') is an international fraternal and religious organization founded at the beginning of the 20th century.
English author and occultist Aleister Crowley has become the best-known member of the order. Originally it was intended to be modelled after and associated with European Freemasonry,[1] such as Masonic Templar organizations, but under the leadership of Aleister Crowley, O.T.O. was reorganized around the Law of Thelema as its central religious principle. Ritual. A priest elevates the Host during a Catholic Mass, one of the mostly widely performed rituals in the world.
A ritual "is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, and objects, performed in a sequestered place, and performed according to set sequence. The Light of Egypt or the Science of the Soul and the Stars. Phoenixmasonry, Inc. Devil. The Devil (from Greek: διάβολος or diábolos = slanderer or accuser)[1] is believed in many religions, myths and cultures to be a supernatural entity that is the personification of evil and the enemy of God and humankind.
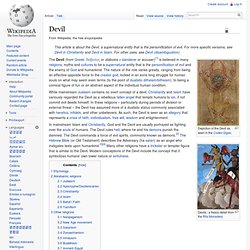
The nature of the role varies greatly, ranging from being an effective opposite force to the creator god, locked in an eons long struggle for human souls on what may seem even terms (to the point of dualistic ditheism/bitheism), to being a comical figure of fun or an abstract aspect of the individual human condition. While mainstream Judaism contains no overt concept of a devil, Christianity and Islam have variously regarded the Devil as a rebellious fallen angel that tempts humans to sin, if not commit evil deeds himself. In these religions – particularly during periods of division or external threat – the Devil has assumed more of a dualistic status commonly associated with heretics, infidels, and other unbelievers.
Etymology Abrahamic religions Judaism Christianity Islam. Scrying. Scrying (also called seeing or peeping) is the practice of looking into a translucent ball or other material with the belief that things can be seen, such as spiritual visions, and less often for purposes of divination or fortune-telling.