

Oxygen mystery: How marine mammals hold their breath. 13 June 2013Last updated at 21:24 ET By Victoria Gill Science reporter, BBC News Dr Michael Berenbrink from the University of Liverpool explains how marine mammals are able to hold their breath for so long.
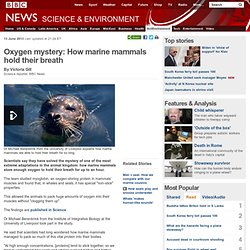
Scientists say they have solved the mystery of one of the most extreme adaptations in the animal kingdom: how marine mammals store enough oxygen to hold their breath for up to an hour. The team studied myoglobin, an oxygen-storing protein in mammals' muscles and found that, in whales and seals, it has special "non-stick" properties. This allowed the animals to pack huge amounts of oxygen into their muscles without "clogging them up". The findings are published in Science. CFCUL - Bem-vindo. Eukaryotes. The oldest eukaryotic fossil is approximately 1.5 billion years old.

The origin of the eukaryotes must have appeared before because the fossil is of a relative complex single-celled organism. There is no fossil record recording the evolution of the eukaryotes. So most hypotheses have been inferred from studying the biology of modern organisms. Perhaps the most significant difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, if we want to understand the origin of the later, is that prokaryotes are inclosed in a rigid cell wall, whereas eukaryotes usually are not and can change their cell shape easily. The absence of the cell wall does, however, mean that the eukaryote needs some other way of supporting and strengthening the cell surface (a wall-less naked cell membrane is very fragile). CIENTIC. Evolução biológica – Unicelularidade e multicelularidade. Can you name the stages of human evolution in this circle of skulls?
Human Family Tree.