

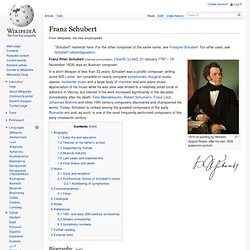
Hector Berlioz. Symphonie fantastique. Symphonie Fantastique: Épisode de la vie d'un artiste ... en cinq parties (Fantastic Symphony: An Episode in the Life of an Artist, in Five Parts) Op. 14 is a program symphony written by the French composer Hector Berlioz in 1830. It is an important piece of the early Romantic period, and is popular with concert audiences worldwide. The first performance was at the Paris Conservatoire in December 1830. The work was repeatedly revived between 1831 and 1845 and subsequently became a favourite in Paris. Instrumentation[edit] Franz Schubert. 1875 oil painting by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait Franz Peter Schubert (German pronunciation: [ˈfʁant͡s ˈʃuːbɐt]; 31 January 1797 – 19 November 1828) was an Austrian composer.
In a short lifespan of less than 32 years, Schubert was a prolific composer, writing some 600 Lieder, ten complete or nearly complete symphonies, liturgical music, operas, incidental music and a large body of chamber and solo piano music. Appreciation of his music while he was alive was limited to a relatively small circle of admirers in Vienna, but interest in his work increased significantly in the decades immediately after his death. Felix Mendelssohn, Robert Schumann, Franz Liszt, Johannes Brahms and other 19th-century composers discovered and championed his works. Today, Schubert is ranked among the greatest composers of the early Romantic era and, as such, is one of the most frequently performed composers of the early nineteenth century. Symphony No. 8 (Schubert) The Unfinished, third movement, facsimile, 1885, in J. R. von Herbeck's biography Schubert’s Eighth is sometimes called the first Romantic symphony due to its emphasis on expressive melody, vivid harmony and creative combinations of orchestral tone color despite the architecturally imposing Classical structures of its two completed movements highlighted by the dramatically climactic development section of the first movement based solely on its quietly sinister opening theme.
To this day, musicologists still disagree as to why Schubert failed to complete the symphony; or even whether he did fail to complete it.[4] Some have speculated that he stopped working on it in the middle of the scherzo in the fall of 1822 because it was associated in his mind with the initial outbreak of syphilis, or simply that he was distracted by the inspiration for his Wanderer Fantasy for solo piano which occupied his time and energy immediately afterward; or perhaps a combination of both factors. Ludwig van Beethoven. Ludwig van Beethoven ( i/ˈlʊdvɪɡ væn ˈbeɪ.toʊvən/; German: [ˈluːtvɪç fan ˈbeːt.hoːfən] ( Born in Bonn, then the capital of the Electorate of Cologne and part of the Holy Roman Empire, Beethoven displayed his musical talents at an early age and was taught by his father Johann van Beethoven and Christian Gottlob Neefe.
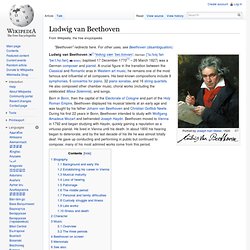
During his first 22 years in Bonn, Beethoven intended to study with Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and befriended Joseph Haydn. Beethoven moved to Vienna in 1792 and began studying with Haydn, quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. He lived in Vienna until his death. Biography Background and early life Prince-Elector's Palace (Kurfürstliches Schloss) in Bonn, where the Beethoven family had been active since the 1730s. List of compositions by Ludwig van Beethoven.
The musical works of Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827) are listed below.
Two overlapping lists of Beethoven's works are presented here. The first is a listing of his best-known works classified by genre. The second is a larger list of works, classified by various numbering systems. Years in parentheses denote dates of composition or publication. The listings that follow include all of these relevant identifiers. List of works by genre[edit] Beethoven, caricatured by J. Orchestral music[edit] Symphonies[edit] Concertos[edit] Other works for soloist and orchestra[edit] Overtures and incidental music[edit] Chamber music[edit] Beethoven wrote 16 string quartets and numerous other forms of chamber music, including piano trios, string trios, and sonatas for violin and cello with piano, as well as works with wind instruments.
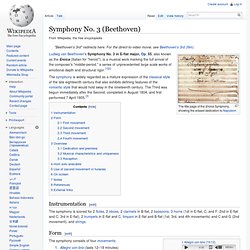
Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven) Symphony No. 6 (Beethoven) Part of a sketch by Beethoven for his Symphony No. 6 The Symphony No. 6 in F major, Op. 68, also known as the Pastoral Symphony (German Pastoral-Sinfonie[1]), is a symphony composed by Ludwig van Beethoven, and completed in 1808. One of Beethoven's few works containing explicitly programmatic content,[2] the symphony was first performed in the Theater an der Wien on 22 December 1808[3] in a four hour concert.[4] The work has become one of the central works of the symphonic repertoire. It is frequently performed, and has been often recorded. Portrait of Beethoven in 1804, when he had been working on the Sixth Symphony for two years. Symphony No. 3 (Beethoven) The title page of the Eroica Symphony, showing the erased dedication to Napoleon Ludwig van Beethoven's Symphony No. 3 in E-flat major, Op. 55, also known as the Eroica (Italian for "heroic"), is a musical work marking the full arrival of the composer's "middle-period," a series of unprecedented large scale works of emotional depth and structural rigor.[1][2] Allegro con brio (lasts 12–18 minutes)Marcia funebre: Adagio assai in C minor (14–18 minutes)Scherzo: Allegro vivace (5–6 minutes)Finale: Allegro molto (10–14 minutes) The performance time is approximately 50 minutes.
Although the first movement's typical performance is around 12–18 minutes, only one recording of the first movement lasted 20 minutes. It was performed by conductor Carlo Maria Giulini and the Los Angeles Philharmonic, and released in 1996. The third movement is a lively scherzo.