

Équipementier aéronautique. Wikipedia wellcamp airport wagner global services. Beauvais–Tillé Airport. Despite its official name Aéroport de Beauvais-Tillé and its location 85 km (53 mi) north of Paris, some low-cost airlines serving the airport refer to it as Paris–Beauvais for marketing purposes.
History[edit] This airport was built in the 1930s and seized by the Germans in June 1940 during the Battle of France. German use during World War II[edit] Beauvais was used as a Luftwaffe military airfield during the occupation. Known units assigned (all from Luftflotte 3, Fliegerkorps IV):[3][4] Kampfgeschwader 76 (KG 76) June – 24 October 1940 Dornier Do 17Z-2 (Fuselage Code: F1+)Sturzkampfgeschwader 1 (SKG 1) July 1940 Junkers Ju 87B Stuka The initial German use of the airport was as a bomber base. kg 76 and SKG 1 both took part in the Battle of Britain. kg 76 was reduced to 19 out of 29 serviceable machines by 18 August 1940. kg 76 raided London on 7 and 15 September 1940. American use[edit] It was liberated by Allied ground forces about 3 September 1944 during the Northern France Campaign.
Châlons Vatry Airport. History[edit] Châlons Vatry Airport's origins began in 1950 when, with the Cold War, NATO faced several problems while attempting to solve the air power survival equation.
Planning for first strike survival in both conventional and nuclear wars had to be considered. Construction began in 1953, and Vatry Air Base was designed for 50 fighters with three large hangars constructed. With the French withdrawal from the integrated NATO military structure in 1967, the American forces left Vatry Air Base and it was closed. For many years, Vatry Air Base was under the control of the French Air Force and used for a training facility. Airbus selected this airport to do some aircraft tests, like the A350 Velocity Minimum Unstick tests. Paris–Le Bourget Airport. Paris–Le Bourget Airport (French: Aéroport de Paris-Le Bourget) (IATA: LBG, ICAO: LFPB) is an airport located within portions of the communes of Le Bourget, Bonneuil-en-France, Dugny and Gonesse, 6 NM (11 km; 6.9 mi) north-northeast[2] (NNE) of Paris, France.
It is now used only for general aviation including business jet operations and air shows, most notably the Paris Air Show. History[edit] The airport started commercial operations in 1919 and was Paris's only airport until the construction of Orly Airport in 1932. It is famous as the landing site for Charles Lindbergh's historic solo transatlantic crossing in 1927 and as the departure point two weeks earlier for the French biplane The White Bird (L'Oiseau Blanc), which took off in its own attempt at a transatlantic flight but then mysteriously disappeared. Orly Airport. For the World War I and NATO military use of this facility, see Orly Air Base.
Paris Orly Airport (French: Aéroport de Paris-Orly) (IATA: ORY, ICAO: LFPO) is an international airport located partially in Orly and partially in Villeneuve-le-Roi, 7 NM (13 km; 8.1 mi) south[2] of Paris, France. It serves as a secondary hub for domestic and overseas territories flights of Air France and as the homebase for Transavia France and features flights to destinations in Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Caribbean, North America and Southeast Asia. Etihad Airways. The airline operates more than 1,000 flights per week to over 120 passenger and cargo destinations in the Middle East, Africa, Europe, Asia, Australia and the Americas, with a fleet of 119 Airbus and Boeing aircraft as of August 2015.
In 2012, Etihad carried 10.3 million passengers, a 23% increase from the previous year,[6] delivering revenues of US$4.8 billion and net profits of US$42 million.[7] Etihad Airways is the third largest airline in the Middle East and it is the second largest airline in the UAE, after the Dubai-based airline Emirates. Its main base is Abu Dhabi International Airport.[8] History[edit] Etihad Airways was established as the second flag carrier of the United Arab Emirates in July 2003 by Royal (Amiri) Decree issued by Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan. It started with an initial paid-up capital of AED500 million. Emirates. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Asiana Airlines. Asiana Airlines logo, 1988–2006 Asiana Airlines Inc.
(Hangul: 아시아나 항공; RR: Asiana Hanggong; KRX: 020560; formerly Seoul Airlines) is one of South Korea's two major airlines, along with Korean Air. Asiana has its headquarters in Asiana Town building in Seoul.[2] The airline has its domestic hub at Gimpo International Airport and its international hub at Incheon International Airport (70 kilometres (43 mi) from central Seoul). As a member of Star Alliance, it operates 14 domestic and 90 international passenger routes, and 27 cargo routes throughout Asia, Europe, North America, and Oceania.[3] As of December 2014, the company employs 10,183 people. The majority of Asiana's pilots, ground staff, and flight attendants are based in Seoul. History[edit] Founding[edit] American Airlines. American Airlines, Inc.
(AA) is a major United States-based airline, operating an extensive international and domestic network, and is the world's largest airline by fleet size and revenue, and the second-most by number of destinations, only after United Airlines. It operates from its main hub at Dallas/Fort Worth, and its hubs at Charlotte, Los Angeles, New York-JFK, Miami, Chicago-O'Hare, Philadelphia, Phoenix, and Washington, D.C., while its primary maintenance base is at Tulsa International Airport. The company, which is headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, also has a significant presence in Atlanta, Boston, London-Heathrow, New York-LaGuardia, Raleigh-Durham, San Antonio, and San Francisco.[8] The airline primarily competes with Delta, United, and Southwest.
History[edit] Predecessors[edit] American Airlines has merged with several carriers since its formation in 1930 (which itself happened by a merger of 80 carriers). Early history[edit] Air Canada. Air Canada (TSX: AC) is the flag carrier and largest airline of Canada.
The airline, founded in 1937, provides scheduled and charter air transport for passengers and cargo to 178 destinations worldwide. It is the world's ninth-largest passenger airline by fleet size, and is a founding member of the Star Alliance.[7] Air Canada's corporate headquarters are located in Montreal, Quebec,[8] while its largest hub is Toronto Pearson International Airport, located in Mississauga, Ontario. Air Canada had passenger revenues of CA$13.27 billion in 2014.[5] The airline's regional service is Air Canada Express. Canada's national airline originated from the Canadian federal government's 1936 creation of Trans-Canada Airlines (TCA), which began operating their first transcontinental flight routes in 1938. In 1965, TCA was renamed Air Canada following government approval. Heathrow Airport. Heathrow Airport (IATA: LHR, ICAO: EGLL) is a major international airport in west London, England.
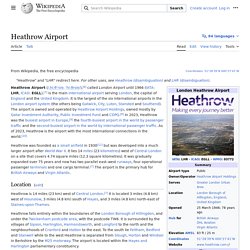
Heathrow is the busiest airport in the United Kingdom, busiest airport in Europe by passenger traffic, third busiest airport in the world by total passenger traffic. In 2014, it handled a record 73.4 million passengers, a 1.4 percent increase from 2013.[4] Heathrow lies 12 nautical miles (22 km; 14 mi) west of Central London,[2] and has two parallel east–west runways along with four operational terminals on a site that covers 12.14 square kilometres (4.69 sq mi). The airport is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings, which itself is owned by FGP TopCo Limited, an international consortium led by the Spanish Ferrovial Group that includes Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec and Government of Singapore Investment Corporation.[5] Heathrow is the primary hub for British Airways and the primary operating base for Virgin Atlantic.
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. Amsterdam Airport Schiphol (Dutch: Luchthaven Schiphol, Dutch pronunciation: [ˈlʏxtˌɦaːvə(n) ˈsxɪˌpɦɔɤˤ]) (IATA: AMS, ICAO: EHAM) is the main international airport of the Netherlands, located 4.9 nautical miles (9.1 km; 5.6 mi)[5] southwest of Amsterdam, in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer, province of North Holland. It is the fifth busiest airport in Europe in terms of passengers. The airport is built as one large terminal (a single-terminal concept), split into three large departure halls. Adelaide Airport. Adelaide Airport (IATA: ADL, ICAO: YPAD) is the principal airport of Adelaide, South Australia and the fifth busiest airport in Australia, servicing 7,696,000 passengers in the financial year ending 30 June 2014.[1] Located adjacent to West Beach, it is approximately 6 km (3.7 mi) west of the city-centre. It has been operated privately by Adelaide Airport Limited under a long-term lease from the Commonwealth Government since 29 May 1998.[2]:p 25.
Delta Air Lines. Delta Air Lines, Inc. ("Delta"; NYSE: DAL) is a major American airline, with its headquarters and largest hub at Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Atlanta, Georgia.[11] The airline along with its subsidiaries operate over 5,400 flights daily and serve an extensive domestic and international network that includes 334 destinations in 64 countries on six continents, as of June 2015.[5] Delta is one of the four founding members of the SkyTeam airline alliance, and operates joint ventures with: Air France-KLM and Alitalia; Virgin Atlantic; and Virgin Australia.[5] Regional service is operated under the brand name Delta Connection. Delta is the sixth-oldest operating airline by foundation date, and the oldest airline still operating in the United States. The company's history can be traced back to Huff Daland Dusters, founded in 1924 in Macon, Georgia as a crop dusting operation.
History Restored Huff-Daland Duster. KLM. KLM, legally Koninklijke Luchtvaart Maatschappij N.V. (Royal Dutch Airlines), is the flag carrier airline of the Netherlands.[4] It is headquartered in Amstelveen, with its hub at nearby Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. KLM was founded in 1919; it is the oldest airline in the world still operating under its original name and had 32,505 employees as of 2013[update].[5] KLM operates scheduled passenger and cargo services to approximately 130 destinations. Passenger aircraft are configured in a three-class layout, including business class, Economy Comfort, and economy class.
KLM has a reputation as one of the world's safest airlines, and has a large social media presence. Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. KLM Cityhopper. KLM Cityhopper is the regional subsidiary of KLM Royal Dutch Airlines (part of the Air France-KLM group). The airline's head office, the Convair Building, is on the grounds of Amsterdam Airport Schiphol in Schiphol-Oost, Haarlemmermeer. It operates short haul services in Europe on behalf of its parent company, KLM. Therefore, the ICAO code 'KLM' is used by air traffic control and the IATA code 'KL' are used on tickets and flight information displays et cetera. Flights are scheduled to approximately 44 destinations, but this can vary on the time of year, and the carrier takes up differing routes when directed to do so by its parent company KLM.
Air France–KLM. Air France–KLM S.A., also known as Air France–KLM Group, is a Franco-Dutch airline holding company incorporated under French law with its headquarters at Charles de Gaulle Airport in Tremblay-en-France, near Paris. The group has offices in Montreuil, Seine-Saint-Denis, Paris, and in Amstelveen, Netherlands.[3][4] Air France–KLM is the result of the merger in 2004 between Air France and KLM. Both Air France and KLM are members of the SkyTeam airline alliance. The company's namesake airlines rely on two major hubs, Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol respectively. Air France–KLM Airlines transported 87.3 million passengers in 2014. Nice Côte d'Azur Airport. Lyon–Saint-Exupéry Airport. Marseille Provence Airport. Orly Airport. Air France. Auckland Airport. Charles de Gaulle Airport. Brisbane Airport. Cairo International Airport.
Cairo International Airport (IATA: CAI, ICAO: HECA) (Arabic: مطار القاهرة الدولي; Maṭār al-Qāhirah al-Duwaliyy) is the international airport of Cairo and the busiest in Egypt and serves as the primary hub for EgyptAir and EgyptAir Express as well as several other airlines. The airport is located to the northeast of the city around 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from the business area of the city and has an area of approximately 37 square kilometres (14 sq mi). Darwin International Airport. Frankfurt Airport. Germanwings. Charles de Gaulle Airport. List of the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic. List of the world's busiest airports by cargo traffic. List of the world's busiest airports by cargo traffic. Frankfurt Airport. Frankfurt Airport. Sydney Airport. Avalon Airport. Moorabbin Airport. Melbourne Airport. Air Hong Kong. HK Express.
Hong Kong Airlines. Dragonair. Hong Kong International Airport. File:HongKongAirportlogo.svg. Manchester Airport. Essendon Airport. Essendon Airport. Kobe Airport. Kansai International Airport. List of airports in Japan. Osaka International Airport. Perth Airport. Jeju International Airport. Gimpo International Airport. Air New Zealand. Qantas. Croydon Airport. Wikipedia ansett australia. Wikipedia trans australian airlines. Wikipedia australian airlines. Wikipedia tasman empire airways limited. Wikipedia deregulation airlines australia. Birmingham Airport. AirRail Link. London Southend Airport. Newcastle Airport. Manchester Airport. Expansion of Gatwick Airport.
Liverpool John Lennon Airport. Norwich International Airport. Airports Commission. Glasgow Airport. Gatwick Airport. Birmingham Airport. List of the busiest airports in Germany. George Best Belfast City Airport. Heathrow Airport. Belfast International Airport. City of Derry Airport. Kerry Airport. British Airways plans unveiled for Dreamliner and A380. Newcastle Airport. Charters Towers Airport. Archerfield Airport. Darwin International Airport. Batchelor Airfield. Canberra International Airport. List of airports in Greater Sydney.
List of airports in New South Wales. Bankstown Airport. Federal Airports Corporation. Essendon Airport. Avalon Airport. Essendon Airport. Moorabbin Airport. Trans Australia Airlines. World's busiest passenger air routes.