

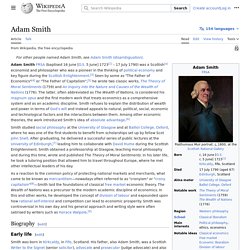
Adam Smith. 18th-century Scottish moral philosopher and political economist Adam Smith FRSA (16 June [O.S. 5 June] 1723[4] – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist, philosopher and author as well as a moral philosopher, a pioneer of political economy and a key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment,[5] also known as ''The Father of Economics''[6] or ''The Father of Capitalism''.[7] Smith wrote two classic works, The Theory of Moral Sentiments (1759) and An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776).
The latter, often abbreviated as The Wealth of Nations, is considered his magnum opus and the first modern work of economics. In his work, Adam Smith introduced his theory of absolute advantage.[8] Classical liberalism. Capitalism. The degree of competition, role of intervention and regulation, and scope of state ownership varies across different models of capitalism.[5] Economists, political economists, and historians have taken different perspectives in their analysis of capitalism and recognized various forms of it in practice.
These include laissez-faire capitalism, welfare capitalism, crony capitalism and state capitalism; each highlighting varying degrees of dependency on markets, public ownership, and inclusion of social policies. The extent to which different markets are free, as well as the rules defining private property, is a matter of politics and policy. Many states have what are termed capitalist mixed economies, referring to a mix between planned and market-driven elements.[6] Capitalism has existed under many forms of government, in many different times, places, and cultures.[7] Following the demise of feudalism, capitalism became the dominant economic system in the Western world.
Etymology[edit] Negative income tax. In economics, a negative income tax (NIT) is a progressive income tax system where people earning below a certain amount receive supplemental pay from the government instead of paying taxes to the government.
Such a system has been discussed by economists but never fully implemented. It was developed by British politician Juliet Rhys-Williams in the 1940s[1] and later by United States economist Milton Friedman.[2][3][4]