

Compte-rendu.1.-Atelier-Cultures-associées.pdf. Cycles. Psophocarpus tetragonolobus. Description The winged bean plant looks pretty much like a typical green bean plant.
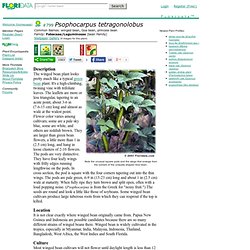
It's a high-climbing, twining vine with trifoliate leaves. The leaflets are more or less triangular, tapering to an acute point, about 3-6 in (7.6-15 cm) long and almost as wide at the widest point. Flower color varies among cultivars; some are a pale sky blue, some are white, and others are reddish brown. They are larger than green bean flowers, a little more than 1 in (2.5 cm) long, and hang in loose clusters of 2-10 flowers.
The pods are very distinctive. Location It is not clear exactly where winged bean originally came from. Culture Most winged bean cultivars will not flower until daylight length is less than 12 hours, yet they are sensitive to frost. Usage The leaves, flowers, pods, green seeds, dried seeds, and (in some varieties) tuberous roots of winged bean are all edible and nutritious. Features The dried seeds of winged beans are about 35% protein, which is higher than that of soybeans. Rotação de Culturas. 2.1 Informações gerais A rotação de culturas, processo de cultivo para a preservação ambiental, influi positivamente na recuperação, manutenção e melhoria dos recursos naturais.

Esta viabiliza produtividades mais elevadas, com mínima alteração ambiental. Outras vantagens do uso contínuo da rotação de culturas é a de preservar ou melhorar as características físicas, químicas e biológicas do solo, além de auxiliar no controle de plantas daninhas, doenças e pragas. A rotação repõe restos orgânicos e protege o solo da ação dos agentes climáticos, ajuda a viabilização da semeadura direta e diversifica a produção agropecuária. Neste capítulo são indicadas várias seqüência de culturas, objetivando compor sistemas de rotação com soja e trigo ou cevada, destinadas a explorações agrícolas com uma adequada adoção de tecnologias. 2.2 Conceito A rotação de culturas consistem em alternar espécies vegetais, no correr do tempo, numa mesma área agrícola. 2.3.
. * calagem e adubação; * semeadura direta; Langage des fleurs. Second bite - Landline - Interview. ANNE KRUGER, PRESENTER: One of the key questions for an exporting country like Australia is how to produce more grain to take advantage of growing markets and higher prices.
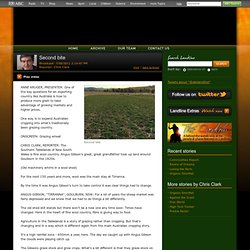
One way is to expand Australian cropping into what's traditionally been grazing country. ONSCREEN: Grazing wheat CHRIS CLARK, REPORTER: The Southern Tablelands of New South Wales is fine wool country. Angus Gibson's great, great grandfather took up land around Goulburn in the 1820s. (Old machinery whirrs in a wool shed) For the next 150 years and more, wool was the main stay at Tirranna. By the time it was Angus Gibson's turn to take control it was clear things had to change. ANGUS GIBSON, "TIRRANNA", GOULBURN, NSW: For a lot of years the sheep market was fairly depressed and we knew that we had to do things a bit differently.
The old shed still stands but there won't be a new one any time soon. Agriculture in the Tablelands is a story of grazing rather than cropping. It's a high rainfall zone - 650mm a year, here. Polyculture Guilds.
Companion Planting.