

Paleoclimatology. History of the Earth. The history of the Earth concerns the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.[1][2] Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's past.
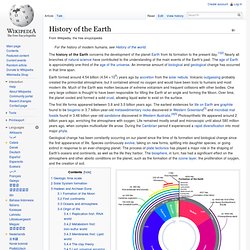
The age of Earth is approximately one-third of the age of the universe. An immense amount of biological and geological change has occurred in that time span. The first life forms appeared between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years ago. The earliest evidences for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland[3] and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia.[4][5] Photosynthetic life appeared around 2 billion years ago, enriching the atmosphere with oxygen.
Life remained mostly small and microscopic until about 580 million years ago, when complex multicellular life arose. Atmosphere of Earth. Composition of Earth's atmosphere by volume.
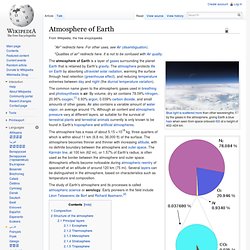
The lower pie represents the trace gases which together compose 0.038% of the atmosphere. The numbers are from a variety of years (mainly 1987, with CO2 and methane from 2009) and do not represent any single source. The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen,[1] 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases.
Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1%.