

BBC iWonder - How did we become the United Kingdom? History - Emmeline Pankhurst. Emmeline Pankhurst. Emmeline Pankhurst. British Union of Fascists. Homework: Who were the suffragettes? CBBC Newsround. About the 15th, 19th and 26th Amendments. The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any on account of sex.

Passed by Congress: 6/4/1919 Ratified & took effect: 8/18/1920. The Tiffany Story. X Tiffany opens its doors on September 14, 1837 at 259 Broadway in New York.
The first day’s sales total is $4.98. View More. Untitled. Research Starters: Immigration. INCORE: Conflict Data Service: Internet Country Guides: Russia Thorough guide to resources on conflicts and ethnicity within the Russian Federation (chiefly in the Caucasus).
Includes databases, news media, papers, and more. From INCORE project on conflict research maintained by the UN Univ. and the Univ. of Ulster. A Walk Around Brooklyn – Thirteen This virtual tour of Brooklyn includes historic information on its role in American immigrant experience, an interactive map, panoramic views, and a selection of links to related resources. Web companion to a Thirteen/WNET public television series. Heart of Darkness. Heart of Darkness. Scramble for Africa. Areas controlled by European colonial powers on the African continent in 1913, shown along with current national boundaries.
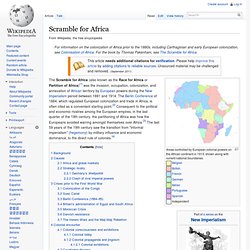
Independent The Scramble for Africa (also known as the Race for Africa or Partition of Africa)[1] was the invasion, occupation, colonization, and annexation of African territory by European powers during the New Imperialism period between 1881 and 1914. The Berlin Conference of 1884, which regulated European colonization and trade in Africa, is often cited as a convenient starting point.[2] Consequent to the political and economic rivalries among the European empires, in the last quarter of the 19th century, the partitioning of Africa was how the Europeans avoided warring amongst themselves over Africa.[3] The last 59 years of the 19th century saw the transition from "informal imperialism" (hegemony) by military influence and economic dominance, to the direct rule of colonies.[4] Background[edit] Technological advancement facilitated overseas expansionism.
Second wave of European colonisation. The New Imperialism (sometimes Neoimperialism or Neo-imperialism) was a period of colonial expansion—and its accompanying ideologies—by the European powers, the United States and the Empire of Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
By some accounts, it began as early as 1830, and may have lasted until the Second World War (1939–45). The period is distinguished by an unprecedented pursuit of overseas territorial acquisitions. At this time, countries focused on building their empire with new technological advances and developments, making their country bigger through conquest, and exploiting their resources. Rise[edit] Second wave of European colonisation. IL COLONIALISMO INGLESE. Il colonialismo inglese ebbe la sua massima espansione dal XVII al XIX secolo, nel nord America, in India, in Africa e in Australia.

I coloni inglesi si insediarono nelle Indie Occidentali e tutte queste colonie svilupparono ben presto forme di governo semi-autonome, soggette solamente alla superiore autorit della corona britannica. La colonizzazione britannica fu nelle mani della East India Company che favor la domanda di t di qualit, di seta e di cotone. Come conseguenze al colonialismo inglese ci fu una rivolta in Nord- America: i francesi si impossessarono dei territori dell ’attuale est del Canada. Scoppi la guerra dei sette che fin con il trattato di Parigi nel 1753. Il colonialismo port anche ricchezza e benessere all’interno dell’Inghilterra: gli insediamenti del Canada, dell ’Australia e della Nuova Zelanda ebbero un auto governo. Il colonialismo in America In genere nell’America settentrionale le guerre contro gli Indiani precedettero quelle con le colonie. Alla fine del XVII sec. IL COLONIALISMO INGLESE. Liberal Italy (1861–1922) United States history [1920-1933]
1920's Prohibition. During Prohibition, the manufacture, transportation, import, export, and sale of alcoholic beverages were restricted or illegal.

Prohibition was supposed to lower crime and corruption, reduce social problems, lower taxes needed to support prisons and poorhouses, and improve health and hygiene in America. Instead, Alcohol became more dangerous to consume; organized crime blossomed; courts and prisons systems became overloaded; and endemic corruption of police and public officials occurred. GCSE Bitesize: Prohibition summary. Research Starters: Immigration. Immigration: Stories of Yesterday and Today and Ellis Island.
World War II and the Postwar Period The United States entered World War II in 1942.

Ellis Island - FREE Port of New York Passenger Records Search. From 1892 to 1954, over twelve million immigrants entered the United States through the portal of Ellis Island, a small island in New York Harbor.

Ellis Island is located in the upper bay just off the New Jersey coast, within the shadow of the Statue of Liberty. Through the years, this gateway to the new world was enlarged from its original 3.3 acres to 27.5 acres mostly by landfill obtained from ship ballast and possibly excess earth from the construction of the New York City subway system. Before being designated as the site of the first Federal immigration station by President Benjamin Harrison in 1890, Ellis Island had a varied history. The local Indian tribes had called it "Kioshk" or Gull Island.
Due to its rich and abundant oyster beds and plentiful and profitable shad runs, it was known as Oyster Island for many generations during the Dutch and English colonial periods. This scenario was far different for "steerage" or third class passengers. Ellis Island - FREE Port of New York Passenger Records Search. How Churchill Led Britain To Victory In The Second World War. Winston Churchill became Britain's prime minister on 10 May 1940.
As he was later to write: 'I felt...that all my past life had been but a preparation for this hour and for this trial'. On the very day that Churchill fulfilled his life's ambition, Germany had, that morning, invaded France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Britain faced its supreme test. History of Sir Winston Churchill. Winston Churchill was an inspirational statesman, writer, orator and leader who led Britain to victory in the Second World War. He served as Conservative Prime Minister twice - from 1940 to 1945 (before being defeated in the 1945 general election by the Labour leader Clement Attlee) and from 1951 to 1955.
Accessible Media Player by Nomensa. Winston Churchill. The Right Honourable Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (1874-1965), the son of Lord Randolph Churchill and his American wife Jennie Jerome, was educated at Harrow and Sandhurst. Winston Churchill: greatest British hero or a warmongering villain? Sir Winston Churchill, a journalist, a soldier, and a war-time leader, was a maverick who divided opinion throughout his lengthy political career. As the 50th anniversary of his death approaches, historians and journalists appear no closer to agreeing on his legacy. We weigh up the leading arguments on both sides.
1607-1776 Colonial America. American History.