

Authentication. Authentication (from Greek: αὐθεντικός authentikos, "real, genuine," from αὐθέντης authentes, "author") is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a single piece of data (datum) or entity.
In contrast with identification which refers to the act of stating or otherwise indicating a claim purportedly attesting to a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of actually confirming that identity. It might involve confirming the identity of a person by validating their identity documents, verifying the validity of a Website with a digital certificate, tracing the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product is what its packaging and labeling claim to be. Authorization. Authorization or authorisation is the function of specifying access rights to resources related to information security and computer security in general and to access control in particular.
More formally, "to authorize" is to define an access policy. For example, human resources staff are normally authorized to access employee records and this policy is usually formalized as access control rules in a computer system. During operation, the system uses the access control rules to decide whether access requests from (authenticated) consumers shall be approved (granted) or disapproved (rejected). Resources include individual files or an item's data, computer programs, computer devices and functionality provided by computer applications. Examples of consumers are computer users, computer programs and other devices on the computer. Overview[edit] Access control in computer systems and networks rely on access policies. Authorize v authorise[edit] Related interpretations[edit] Public policy[edit] Lucene - Apache Solr. Load balancing (computing) For Internet services, the load balancer is usually a software program that is listening on the port where external clients connect to access services.
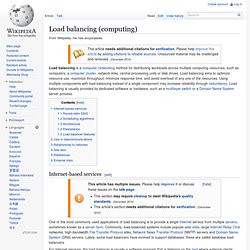
The load balancer forwards requests to one of the "backend" servers, which usually replies to the load balancer. This allows the load balancer to reply to the client without the client ever knowing about the internal separation of functions. It also prevents clients from contacting back-end servers directly, which may have security benefits by hiding the structure of the internal network and preventing attacks on the kernel's network stack or unrelated services running on other ports. Some load balancers provide a mechanism for doing something special in the event that all backend servers are unavailable. This might include forwarding to a backup load balancer, or displaying a message regarding the outage. It is also important that the load balancer itself does not become a single point of failure.
. @ in a 192.0.2.1 @ in a 203.0.113.2. Staged event-driven architecture. SEDA employs dynamic control to automatically tune runtime parameters (such as the scheduling parameters of each stage) as well as to manage load (like performing adaptive load shedding).
Decomposing services into a set of stages also enables modularity and code reuse, as well as the development of debugging tools for complex event-driven applications. See also[edit] References[edit] Bibliography[edit] External links[edit] Apache ServiceMix provides a Java SEDA wrapper, combining it with related message architectures (JMS, JCA & straight-through flow).Criticism about how SEDA premises (threads are expensive) are no longer validJCyclone: Java open source implementation of SEDAMule ESB is another open-source Java implementationSEDA: An Architecture for Highly Concurrent Server Applications describing the PhD thesis by Matt Welsh from Harvard UniversityA Retrospective on SEDA by Matt Welsh, July 26, 2010. AVL tree. Example AVL tree In computer science, an AVL tree (Adelson-Velskii and Landis' tree, named after the inventors) is a self-balancing binary search tree.
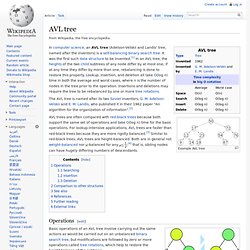
It was the first such data structure to be invented.[1] In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Lookup, insertion, and deletion all take O(log n) time in both the average and worst cases, where n is the number of nodes in the tree prior to the operation.
Business process. Overview[edit] There are three types of business processes: Management processes, the processes that govern the operation of a system.
Typical management processes include "corporate governance" and "strategic management".Operational processes, processes that constitute the core business and create the primary value stream. Typical operational processes are purchasing, manufacturing, advertising and marketing, and sales.Supporting processes, which support the core processes. Examples include accounting, recruitment, call center, technical support. A business process begins with a mission objective and ends with achievement of the business objective. A business process can be decomposed into several sub-processes,[1] which have their own attributes, but also contribute to achieving the goal of the super-process. Business Processes are designed to add value for the customer and should not include unnecessary activities.
History[edit] Adam Smith[edit] Other definitions[edit] Standard operating procedure. The term standard operating procedure, or SOP, is used in a variety of different contexts, including healthcare, aviation, engineering, education, industry, and military.
The U.S. military sometimes uses the term Standing — rather than Standard — Operating Procedure, because a military SOP refers to a unit's unique procedures, which are not necessarily standard to another unit. "Standard" could imply that there is one (standard) procedure to be used across all units. Clinical research and practice[edit] In clinical research, the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) defines SOPs as "detailed, written instructions to achieve uniformity of the performance of a specific function". SOPs get usually applied in pharmaceutical processing and for related clinical studies. SOP's can also provide employees with a reference to common business practices, activities, or tasks.