

- Electrostatics § Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations. Magnetic field in a solenoid. Electromagnetic Radiation - The Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation. Visible light is a complex phenomenon that is classically explained with a simple model based on propagating rays and wavefronts, a concept first proposed in the late 1600s by Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens.

Electromagnetic radiation, the larger family of wave-like phenomena to which visible light belongs (also known as radiant energy), is the primary vehicle transporting energy through the vast reaches of the universe. The mechanisms by which visible light is emitted or absorbed by substances, and how it predictably reacts under varying conditions as it travels through space and the atmosphere, form the basis of the existence of color in our universe. Basic Electromagnetic Wave Properties - Java Tutorial. Electromagnetic radiation is characterized by a broad range of wavelengths and frequencies, each associated with a specific intensity (or amplitude) and quantity of energy.
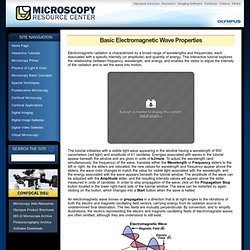
This interactive tutorial explores the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy, and enables the visitor to adjust the intensity of the radiation and to set the wave into motion. The tutorial initializes with a visible light wave appearing in the window having a wavelength of 650 nanometers (red light) and amplitude of 61 candelas. Energies associated with waves in the tutorial appear beneath the window and are given in units of kJ/mole. Electromagnetic Radiation - Java Tutorial.
Magnetism. Light waves.