

Cola nitida. It is a tree native to the rainforests of tropical West Africa.
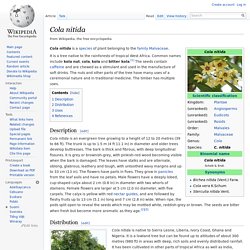
Common names include kola nut, cola, kola and bitter kola.[1] The seeds contain caffeine and are chewed as a stimulant and used in the manufacture of soft drinks. The nuts and other parts of the tree have many uses of a ceremonial nature and in traditional medicine. The timber has multiple uses. Catharanthus roseus. Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as the Madagascar periwinkle or rosy periwinkle, is a species of Catharanthus native and endemic to Madagascar.
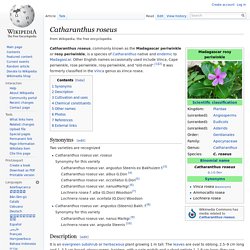
Other English names occasionally used include Vinca, Cape periwinkle, rose periwinkle, rosy periwinkle, and "old-maid".[1][2] It was formerly classified in the Vinca genus as Vinca rosea. Synonyms[edit] Two varieties are recognized Catharanthus roseus var. roseus Synonymy for this variety. Cascabela thevetia. Cascabela thevetia (syn: Thevetia peruviana) is a poisonous plant of central and southern Mexico and Central America.
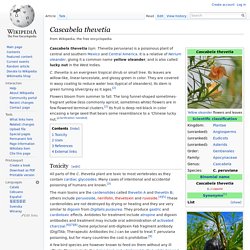
It is a relative of Nerium oleander, giving it a common name yellow oleander, and is also called lucky nut in the West Indies. C. thevetia is an evergreen tropical shrub or small tree. Its leaves are willow-like, linear-lanceolate, and glossy green in color. Caesalpinia pulcherrima. Caesalpinia pulcherrima is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is native to the tropics and subtropics of the Americas.
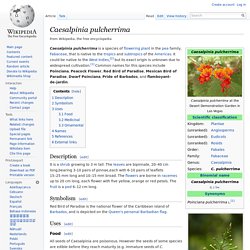
It could be native to the West Indies,[2] but its exact origin is unknown due to widespread cultivation.[1] Common names for this species include Poinciana, Peacock Flower, Red Bird of Paradise, Mexican Bird of Paradise, Dwarf Poinciana, Pride of Barbados, and flamboyant-de-jardin. Description[edit] Buds of Peacock Flower at Kerala It is a shrub growing to 3 m tall. The leaves are bipinnate, 20–40 cm long,bearing 3-10 pairs of pinnae,each with 6-10 pairs of leaflets 15–25 mm long and 10–15 mm broad.
Bougainvillea spectabilis. Bougainvillea spectabilis, also known as great bougainvillea,[1] is a species of flowering plant.
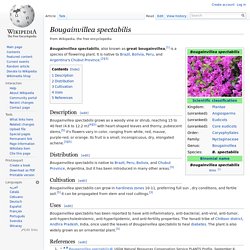
It is native to Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, and Argentina's Chubut Province.[2][3] Description[edit] Bougainvillea spectabilis grows as a woody vine or shrub, reaching 15 to 40 feet (4.6 to 12.2 m)[4][5] with heart-shaped leaves and thorny, pubescent stems,[5] it's flowers vary in color, ranging from white, red, mauve, purple-red, or orange. Its fruit is a small, inconspicuous, dry, elongated achene.[3][5] Distribution[edit] Bougainvillea glabra. Bougainvillea glabra, lesser bougainvillea or paperflower,[2] is the most common species of bougainvillea used for bonsai.[3] Description[edit] It is an evergreen, climbing shrub with thorny stems.
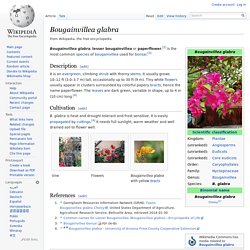
It usually grows 10–12 ft (3.0–3.7 m) tall, occasionally up to 30 ft (9 m). Tiny white flowers usually appear in clusters surrounded by colorful papery bracts, hence the name paperflower. The leaves are dark green, variable in shape, up to 4 in (10 cm) long.[4] Phanera purpurea. Phanera purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to South China (which includes Hong Kong) and Southeast Asia.
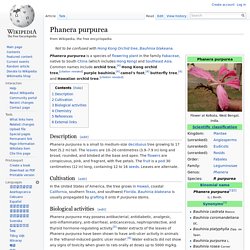
Common names include orchid tree,[4] Hong Kong orchid tree,[citation needed] purple bauhinia,[4] camel's foot,[4] butterfly tree,[4] and Hawaiian orchid tree. [citation needed] Description[edit] Phanera purpurea flower (Kaniar) in Hyderabad, India. Barleria lupulina. Averrhoa carambola. Averrhoa carambola is a species of woody plant in the family Oxalidaceae; it has a number of common names including carambola and starfruit.[1] This evergreen tree is native to Southeast Asia and the Indian Subcontinent.[2][3] A. carambola is a small tree or shrub that grows 5–12 metres tall, with rose to red-purple flowers.
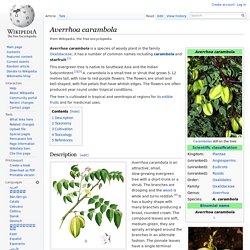
The flowers are small and bell-shaped, with five petals that have whitish edges. The flowers are often produced year round under tropical conditions. The tree is cultivated in tropical and semitropical regions for its edible fruits and for medicinal uses. Description[edit] Asystasia gangetica. Asystasia gangetica is a species of plant in the Acanthaceae family.
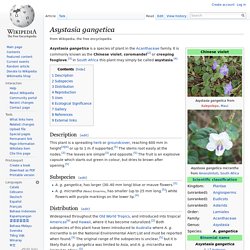
It is commonly known as the Chinese violet, coromandel[2] or creeping foxglove.[3] In South Africa this plant may simply be called asystasia.[4] Description[edit] This plant is a spreading herb or groundcover, reaching 600 mm in height[3][4] or up to 1 m if supported.[5] The stems root easily at the nodes.[3] The leaves are simple[3] and opposite.[5] The fruit is an explosive capsule which starts out green in colour, but dries to brown after opening.[5] Asclepias curassavica. Asclepias curassavica, commonly known as tropical milkweed,[4] is a flowering plant species of the milkweed genus, Asclepias.[2] It is native to the American tropics[5] and has a pantropical distribution as an introduced species.
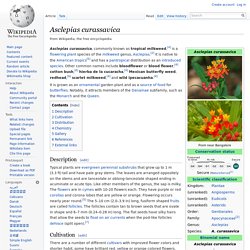
Other common names include bloodflower or blood flower,[4] cotton bush,[6] hierba de la cucaracha,[4] Mexican butterfly weed, redhead,[6] scarlet milkweed,[4] and wild ipecacuanha.[4] Description[edit] Cultivation[edit] There are a number of different cultivars with improved flower colors and shorter habit, some have brilliant red, yellow or orange colored flowers. Asclepias curassavica is excellent in butterfly gardens or as a cut flower.
Argemone mexicana. Chemical constituents[edit] A. mexicana seeds contain 22–36% of a pale yellow non-edible oil, called argemone oil or katkar oil, which contains the toxic alkaloids sanguinarine and dihydrosanguinarine. Four quaternary isoquinoline alkaloids, dehydrocorydalmine, jatrorrhizine, columbamine, and oxyberberine, have been isolated from the whole plant of Argemone mexicana.[4] The seed pods secrete a pale yellow latex when cut open. This argemone resin contains berberine and protopine. Pineapple. The pineapple (Ananas comosus) is a tropical plant with edible multiple fruit consisting of coalesced berries,[2][3] and the most economically significant plant in the Bromeliaceae family.[4] Pineapples may be cultivated from a crown cutting of the fruit,[2][5] possibly flowering in 20–24 months and fruiting in the following six months.[5][6] Pineapple does not ripen significantly post-harvest.[7] Pineapples can be consumed fresh, cooked, juiced, and preserved, and are found in a wide array of cuisines.
In addition to consumption, the pineapple leaves are used to produce the textile fiber piña in the Philippines, commonly used as the material for the men's Barong Tagalog and women's Baro't saya formal wear in the country. The fiber is also used as a component for wallpaper and other furnishings.[8] §Etymology.
Cashew. The cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale) is a tropical evergreen that produces the cashew nut and the cashew apple. It can grow as high as 14 metres (46 ft), but the dwarf cashew, growing up to 6 metres (20 ft), has proved more profitable, with earlier maturity and higher yields. The shell of the cashew nut yields derivatives that can be used in many applications from lubricants to paints, and other parts of the tree have traditionally been used for snake-bites and other folk remedies. Allamanda cathartica. Allamanda cathartica, commonly called golden trumpet,[2] common trumpetvine,[2] and yellow allamanda,[2] is a species of flowering plant of the genus Allamanda in the family Apocynaceae.
It is native to Brazil. This plant is cited in Flora Brasiliensis by Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant for its large, fragrant flowers. It is a vine that requires a trellis or a fence for support. Abutilon indicum. Abutilon indicum (Indian Abutilon, Indian Mallow; is a small shrub in the Malvaceae family, native to tropic and subtropical regions and sometimes cultivated as an ornamental.[2] This plant is often used as a medicinal plant and is considered invasive on certain tropical islands.[1] Tamil name: துத்தி "thuthi"Sanskrit name: अतिबला AtibalaaTelugu name: Duvvena Kayalu Distribution[edit] The species occurs in a number of tropical and subtropical zones.
An example occurrence is within parts of the Great Barrier Reef islands of the Coral Sea.[3] Vachellia nilotica. Acmella uliginosa. Acalypha hispida.