

Ten Amazing Rainforest Plants. Our surroundings are sometimes taken for granted.
Even something as unique as the rainforest is forgotten. It seems a little bit of knowledge and a shove in the right direction can get people to appreciate the environment. So, why not start with the wonder that is the rainforest? Even though rainforests only cover less than two percent of the Earth’s entire surface area, they are home to 50 percent of the plants and animals. They are also found on every continent, except Antarctica. You’re probably thinking “I know all there is to know about bananas; I eat them for breakfast and can make delicious banana bread.” Habitation: Found in Central America, South America, Africa, Southeast Asia and non-tropical regions like the United States thanks to modern agricultural technologies. Rainforest Animals. Animals Often Seen. Advertisement.
EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.Click here to learn more. (Already a member? Click here.) Rainforests are tremendously rich in animal life. Different animals live in different strata of the rainforest. Many species of rainforest animals are endangered and many other have gone extinct as the number of acres of rainforests on Earth decreases. Protection from Predators Animals are always in danger of being eaten and have developed many methods of protecting themselves from hungry animals.
Hiding: Some animals simply hide from predators, concealing themselves in burrows, under rocks or leaves, in tree hollows, or in other niches where they are hard to find. How Animals Help. Medical Plants. Rainforest Remedies Daniel Mowrey, Ph.D.

Undiscovered Riches The number of potentially useful medicinal plants growing in the world's rainforests is estimated to be in the thousands. Certainly, mankind would benefit from the application of these plants. In future years, we might witness the discovery of cures for many serious diseases in rainforest plants. But there are serious questions about how we should go about achieving these goals. As much as we would like to see immediate results from rainforest exploration, the rule of thumb must be to go slowly. The only currently obvious trend in rainforest development is the phenomenon of drug companies rushing to South America and South Pacific Islands, usually under sponsorship of the National Cancer Institute, in search of novel compounds.
Climate. Worldwide zones of Tropical rainforest climate (Af).
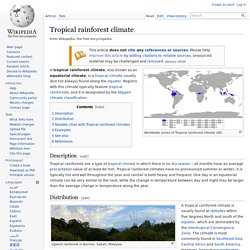
A tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate, is a tropical climate usually (but not always) found along the equator. Regions with this climate typically feature tropical rainforests, and it is designated by the Köppen climate classification. Description[edit] Distribution[edit] Upland rainforest in Borneo. A tropical rainforest climate is usually found at latitudes within five degrees North and south of the equator, which are dominated by the Intertropical Convergence Zone. Some of the places that have this climate are indeed uniformly and monotonously wet throughout the year (e.g., the northwest Pacific coast of South and Central America, from Ecuador to Costa Rica, see for instance, Andagoya, Colombia), but in many cases the period of higher sun and longer days is distinctly driest (as at Palembang, Indonesia) or the time of lower sun and shorter days may have more rain (as at Sitiawan, Malaysia). Examples[edit] Helpful Plants. Tropical Rainforest Resources Edible Rainforest Plants Allspice: (Pimenta dioica) Berries-- shaped like peppercorns-- of an evergreen tree which can grow up to 100' in height in height in the Latin American Rainforest.

The small, aromatic fruits have a subtle flavor like a mixture of clove, cinnamon, and nutmeg, hence the name "allspice. " Banana: (Musa paradisiaca) This is the most common Musa, but there are 21 species and subspecies which are edible. Black Pepper: (Piper nigrum) A vine native to the East Indies. Caspicum annum: Cayenne pepper, sweet pepper, paprika, and jalapenos are just four of the many cultivars of this plant.
Cardamom: (Elleteria cardamom) Native to India, the third most expensive spice after saffron and vanilla. Cashews: (Anarcardium occidental) Originally from Tropical America, a valuable nut and vitamin rich fruit from the tree. Chocolate/Cocoa: (Theobroma cacao) Native to lowland tropical America, probably first domesticated in Mexico. Cinnamon: (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) Dangerous Plants. Types of Plants in Tropical Rainforest. Rainforest Plants. A tropical greenhouse More than two thirds of the world's plant species are found in the tropical rainforests: plants that provide shelter and food for rainforest animals as well as taking part in the gas exchanges which provide much of the world's oxygen supply.
Rainforest plants live in a warm humid environment that allows an enormous variation rare in more temperate climates: some like the orchids have beautiful flowers adapted to attract the profusion of forest insects. Competition at ground level for light and food has lead to evolution of plants which live on the branches of other plants, or even strangle large trees to fight for survival. The aerial plants often gather nourishment from the air itself using so-called 'air roots';.