

Coconut Research Center Home Page.
Political Science. Neuroscience of free will. Neuroscience of free will is the part of neurophilosophy that studies the interconnections between free will and neuroscience.
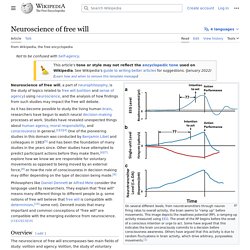
As it has become possible to study the living brain, researchers have begun to watch decision making processes at work. Findings could carry implications for our sense of agency and for moral responsibility and the role of consciousness in general.[1][2][3] Relevant findings include the pioneering study by Benjamin Libet and its subsequent redesigns; these studies were able to detect activity related to a decision to move, and the activity appears to begin briefly before people become conscious of it.[4] Other studies try to predict activity before overt action occurs.[5] Taken together, these various findings show that at least some actions - like moving a finger - are initiated unconsciously at first, and enter consciousness afterward.[6]
Willful ignorance. Willful ignorance is the state and practice of ignoring any sensory input that appears to contradict one’s inner model of reality.
At heart, it is almost certainly driven by confirmation bias. It differs from the standard definition of “ignorance“ — which just means that one is unaware of something — in that willfully ignorant people are fully aware of facts, resources and sources, but refuse to acknowledge them. Indeed, calling someone "ignorant" shouldn’t really be a pejorative, but intentional and willful ignorance is an entirely different matter. In practice though, the word "ignorance" has often come to mean "willful ignorance", and indeed, in many non-English languages, the word based on the same stem actually carries that meaning.