

Johannes Kepler. Johannes Kepler (German: [ˈkʰɛplɐ]; December 27, 1571 – November 15, 1630) was a German mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer.
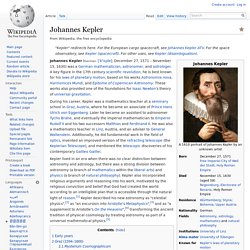
A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his laws of planetary motion, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican Astronomy. These works also provided one of the foundations for Isaac Newton's theory of universal gravitation. During his career, Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, Austria, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel. The birthplace of Hegel in Stuttgart, which now houses The Hegel Museum Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (German: [ˈɡeɔɐ̯k ˈvɪlhɛlm ˈfʁiːdʁɪç ˈheːɡəl]; August 27, 1770 – November 14, 1831) was a German philosopher, and a major figure in German Idealism.
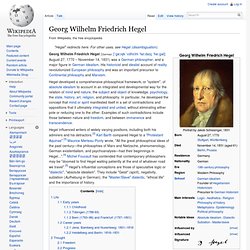
His historicist and idealist account of reality revolutionized European philosophy and was an important precursor to Continental philosophy and Marxism. Life[edit] Early years[edit] Childhood[edit] Hegel was born on August 27, 1770 in Stuttgart, in the Duchy of Württemberg in southwestern Germany. Philosophy-of-Mind. Friedrich Nietzsche. Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (/ˈniːtʃə/[1] or /ˈniːtʃi/;[2] German: [ˈfʁiːdʁɪç ˈvɪlhɛlm ˈniːt͡sʃə]; 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, cultural critic, poet, composer and Latin and Greek scholar.
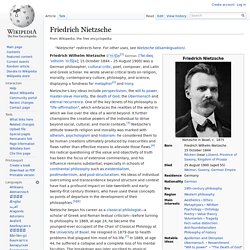
He wrote several critical texts on religion, morality, contemporary culture, philosophy and science, displaying a fondness for metaphor[3] and irony. Nietzsche's key ideas include perspectivism, the will to power, the death of God, the Übermensch and eternal recurrence. One of the key tenets of his philosophy is "life-affirmation", which embraces the realities of the world in which we live over the idea of a world beyond. Nietzsche began his career as a classical philologist—a scholar of Greek and Roman textual criticism—before turning to philosophy. In 1869, at age 24, he became the youngest-ever occupant of the Chair of Classical Philology at the University of Basel.
As his caretaker, his sister assumed the roles of curator and editor of Nietzsche's manuscripts. Arthur Schopenhauer. Life[edit] Schopenhauer's birthplace house, ul.
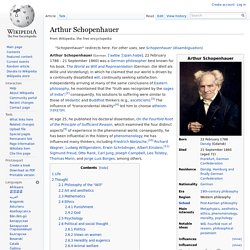
Św. Ducha (formerly Heiligegeistgasse) In 1814, Schopenhauer began his seminal work The World as Will and Representation (Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung). He finished it in 1818 and published it the following year. While in Berlin, Schopenhauer was named as a defendant in a lawsuit initiated by a woman named Caroline Marquet.[18] She asked for damages, alleging that Schopenhauer had pushed her. In 1821, he fell in love with nineteen-year old opera singer, Caroline Richter (called Medon), and had a relationship with her for several years. Schopenhauer had a notably strained relationship with his mother Johanna Schopenhauer.
Grave at Frankfurt Hauptfriedhof Schopenhauer had a robust constitution, but in 1860 his health began to deteriorate. Thought[edit] Philosophy of the "Will"[edit] Schopenhauer in 1815, second of the critical five years of the initial composition of Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung Art and aesthetics[edit] Ethics[edit] Jakob Böhme. Jakob Böhme (/ˈbeɪmə, ˈboʊ-/;[1] 1575 – November 17, 1624) was a German Christian mystic and theologian.
He is considered an original thinker within the Lutheran tradition, and his first book, commonly known as Aurora, caused a great scandal. In contemporary English, his name may be spelled Jacob Boehme; in seventeenth-century England it was also spelled Behmen, approximating the contemporary English pronunciation of the German Böhme. Biography[edit] Jakob Böhme (anonymous portrait) Böhme was born in March 8, 1575, at Alt Seidenberg (now Stary Zawidów, Poland), a village near Görlitz in Upper Lusatia, a territory of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1610 Böhme experienced another inner vision in which he further understood the unity of the cosmos and that he had received a special vocation from God.
Kierkegaard. Daniel Dennett.