

The Brick Testament. When was the Bible written and who wrote it. Apollodorus of Athens. Apollodorus of Athens (Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ὁ Ἀθηναῖος; born c. 180 BC, died after 120 BC) son of Asclepiades, was a Greek scholar, historian and grammarian.
He was a pupil of Diogenes of Babylon, Panaetius the Stoic, and the grammarian Aristarchus of Samothrace. He left, or fled, Alexandria around 146 BC, most likely for Pergamon, and eventually settled in Athens. Literary works[edit] References[edit] Hornblower, Simon (1996). External links[edit] Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus) The Bibliotheca (Ancient Greek: Βιβλιοθήκη, Bibliothēkē, "library") is a compendium of myths and heroic legends, arranged in three books, generally dated to the first or second centuries AD.[1] It was known traditionally as the Library of Apollodorus, but the attribution is now regarded as false.
The Bibliotheca has been called "the most valuable mythographical work that has come down from ancient times".[2] An epigram recorded by Photius expressed its purpose: It has the following not ungraceful epigram: 'Draw your knowledge of the past from me and read the ancient tales of learned lore. Look neither at the page of Homer, nor of elegy, nor tragic muse, nor epic strain.
Seek not the vaunted verse of the cycle; but look in me and you will find in me all that the world contains'.[3] The brief and unadorned accounts of myth in the Bibliotheca have led some commentators to suggest that even its complete sections are an epitome of a lost work. The first mention of the work is by Photius. DIONYSUS : Greek God of Wine & Festivity. Family tree of the Greek gods.
Key: The essential Olympians' names are given in bold font.
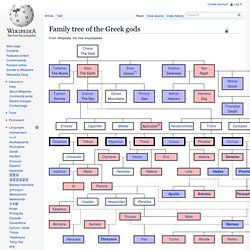
See also List of Greek mythological figures Notes External links Media related to Family trees of Greek mythology at Wikimedia Commons. About this. Gods and Goddesses. Ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt.
It is one of six civilizations globally to arise independently. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology)[1] with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh.[2] The history of ancient Egypt occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. History Map of ancient Egypt, showing major cities and sites of the Dynastic period (c. 3150 BC to 30 BC) Predynastic period A typical Naqada II jar decorated with gazelles. In Predynastic and Early Dynastic times, the Egyptian climate was much less arid than it is today. Early Dynastic Period (c. 3050 –2686 BC) Parallels between the lives of Jesus and Horus, an Egyptian God. Jesus-Pagan links Menu Sponsored link.

Quotations: