

Walrus.wr.usgs.gov/reports/reprints/Bruns_CPC_12.pdf. The Arabian plate. The Mighty Forces of Earth. Plate tectonics (geology. Plate tectonics, theory dealing with the dynamics of Earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere, that revolutionized Earth sciences by providing a uniform context for understanding mountain-building processes, volcanoes, and earthquakes, as well as understanding the evolution of Earth’s surface and reconstructing its past continental and oceanic configurations.
The concept of plate tectonics was formulated in the 1960s. According to the theory, Earth has a rigid outer layer, known as the lithosphere, which is typically about 100 km (60 miles) thick and overlies a plastic layer called the asthenosphere. The lithosphere is broken up into about a dozen large plates and several small ones.
These plates move relative to each other, typically at rates of 5 to 10 cm (2 to 4 inches) per year, and interact along their boundaries, where they converge, diverge, or slip past one another. Convergent plate boundary (geology. Plate Tectonics : Subduction Zones. When two oceanic plates collide, the younger of the two plates, because it is less dense,* will ride over the edge of the older plate.
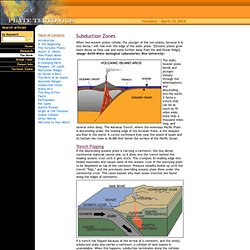
*[Oceanic plates grow more dense as they cool and move further away from the Mid-Ocean Ridge]. (Image: Keith-Wiess Geological Laboratories; Rice University) The older, heavier plate bends and plunges steeply through the athenosphere, and descending into the earth, it forms a trench that can be as much as 70 miles wide, more than a thousand miles long, and several miles deep. The Marianas Trench, where the enormous Pacific Plate is descending under the leading edge of the Eurasian Plate, is the deepest sea floor in the world. It curves northward from near the island of Guam and its bottom lies close to 36,000 feet below the surface of the Pacific Ocean. Trench Flipping If the descending oceanic plate is carrying a continent, the less dense continental material cannot sink, so it dives into the trench behind the leading oceanic crust until it gets stuck.
People.rses.anu.edu.au/lambeck_k/pdf/189.pdf. Accretion and Erosion in Subduction Zones: The Role of Fluids - Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 21(1):307. Convergent Zones in Plate Tectonics. Subduction (geology. Subduction Zone in Action. Glaucophane (mineral. Orogeny (geology. Petrogenesis of the Largest Intraplate Volcanic Field on the Arabian Plate (Jordan): a Mixed Lithosphere-Asthenosphere Source Activated by Lithospheric Extension - Science & Technology - ProQuest. Alfred Wegener and the concept of continental drift.
Dynamic Earth . Plates & Boundaries. Plate Tectonics : Plate Boundaries. How do Earth’s tectonic plates interact? Divergent and Convergent Plate Boundaries For background on this animation series, download Background from the Resources box.Animations are available for preview in embedded YouTube.

To download, right click the 'Quicktime Animation' link and choose 'Save Target As' (PC) or 'Download Linked File' (Mac).Send us feedback. Divergent Boundary Spreading mid-ocean ridges form the longest mountain ranges in the world. New oceanic crust is created at this boundary when basalt magma, formed in the mantle, rises into fractures in the crust and solidifies. Convergent Boundary In this animation, we are showing an ocean/continent convergent boundary. Strike-Slip Fault Simple example of a strike slip fault. Quicktime (116 kB) Animación Quicktime (120 kB) Video Lecture Video lecture by Dr. Quicktime (2.5 MB) Animations and videos are made in partnership with Earthscope, USGS, and Volcano Video & Graphics.
Please send feedback to Jenda Johnson. Britannica Online Encyclopedia.