

DFS Replication. DFS Questions and Answers. I have been looking at the Search Terms that have led people to here.
I noticed that my DFS stuff was getting some hits, and I decided to write a part FAQ and part HOWTO on some DFS stuff. Here it goes.Why is my DFS replication so slow? This one has two possible answers, and most likely, it is a little bit of both. The first is that the replication priority is too low. The second is that there is not enough space for the replication staging, which is causing replication to either die out, or try to only replicate smaller files. Non Server 2003R2 machines You will use the older Distributed File System to manage priority, and editing the registry to change the staging space. Priority Staging Space Run RegeditOpen HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NtFrs\ParametersEdit Staging Space Limit in KB for all DFS shares on that serverClose RegeditEither restart the File Replication Service on the server, or reboot.This needs to be edited on each server.
Bandwidth Usage Staging Quota. Kendal Van Dyke: Things You Need To Know If You Use DFS Replication. In addition to being a SQL DBA I'm also a network administrator, or at least I pretend to be.

This is a bit off-topic from my usual SQL Server fare, but I figured my pain is your gain. Today, July 31, is System Administrator Appreciation Day. If you use DFS Replication in your company, give your sysadmin a gift by forwarding this on to him\her. DFS (and DFS replication) is really nifty when it works. My company uses it to keep content synchronized on servers across multiple datacenters. Lesson #1 – Be Very Careful When Removing And Re-Adding Members To A DFS Replication Group Let's pretend you've got DFS Replication set up and you want to add a server (referred to as a member) into your group.
It turns out that when you delete a member from a DFS replication group information about the member isn't actually deleted from the DFS replication database. This "feature" and 3 workarounds are documented in Microsoft KB article 961655. How do you fix that? Jeroen van Lieshout. DFS Replication (DFSR) health reports are an excellent mechanism for monitoring replication status.
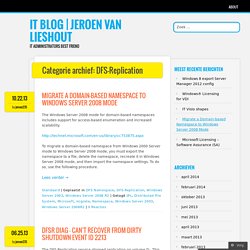
Health reports can be generated by the DfsrAdmin.exe command line utility or via the DFS Management UI. The command-line interface makes DfsrAdmin.exe the better tool for health report automation. Where’s my file? Root cause analysis of FRS and DFSR data deletion - Ask the Directory Services Team. Hi, Ned here.
In the Directory Services support space here at Microsoft, we are often contacted by customers for disaster recovery scenarios. We’re also brought in for deeper forensic analysis of what lead to a problem. Today we’re going to talk about a situation that covers both: A customer has seen some critical data go missing.That data was replicated via the File Replication Service (FRS) or the Distributed File System Replication (DFSR) Service.Before they restore the data with their backup copy, they want to have root cause on who deleted what and where it started. We can’t do this after restoring data because our whole audit trail will of course be destroyed within the respective JET databases. FRS Deletion Forensics – The Where and When You need to start by determining the name of some folder or file that has been deleted.
Install FRSDIAG on any server that participated in the FRS content set where data was deleted. Open a CMD prompt and navigate to the FRSDIAG directory. Done! Tuning replication performance in DFSR (especially on Win2008 R2) - Ask the Directory Services Team. Hi all, Ned here again.
There are a number of ways that DFSR can be tuned for better performance. This article will go through these configurations and explain the caveats. Even if you cannot deploy Windows Server 2008 R2 - for the absolute best performance - you can at least remove common bottlenecks from your older environments. If you are really serious about performance in higher node count DFSR environments though, Win2008 R2’s 3rd generation DFSR is the answer. But there’s more you can do, especially in 2008 R2. Registry tuning All registry values are REG_DWORD (and in the explanations below, are always in decimal). HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DFSR\Parameters\Settings A restart of the DFSR service is required for the settings to take effect, but a reboot is not required. Important Note: None of these registry settings apply to Windows Server 2003 R2. Introduction to DFS Replication. Updated: August 22, 2005 Applies To: Windows Server 2003 R2 DFS Replication, the successor to the File Replication service (FRS) introduced in Windows 2000 Server operating systems, is a new, state-based, multimaster replication engine that supports replication scheduling and bandwidth throttling.

DFS Replication uses a new compression algorithm known as remote differential compression (RDC). RDC is a "diff-over-the wire" client-server protocol that can be used to efficiently update files over a limited-bandwidth network. RDC detects insertions, removals, and re-arrangements of data in files, enabling DFS Replication to replicate only the changed file blocks when files are updated.