

I am epic and can find awesome revision games!
Venus - Sun Transit. The Shadow. Space.com.
Planet simulation game. What Would Happen If You Shot a Gun In Space? Diversity of Exploding Stars Provides Cosmic Yardstick. In universe spanning more than a billion light-years, distance can't be measured with a ruler.

To judge how far away objects are, astronomers must rely on other objects whose properties are already known — such as certain kinds of exploding stars called supernova. New research is shedding light on the identity of one of these "standard candles," so-called because their brightness is standard enough that their true distance can be deduced from it. Astronomers are hoping that analyzing one specific type of supernova explosion will give them a better understanding of how frequently it differs from another type. That, in turn, should allow for even more precise measurements of distance in the universe. One dwarf or two When a compact, dying star known as a white dwarf orbits another star closely enough, its strong gravitational pull can ultimately rip its partner apart. Space.com. Giant Sunspot Unleashes Massive Solar Flare. A powerful solar flare that erupted Thursday (Nov. 3) from a huge blemish on the sun's surface has been classified as an X1.9 flare, ranking it among the most powerful types of storms our star can unleash.
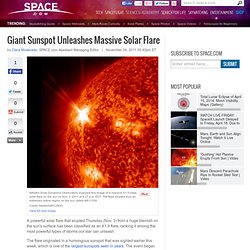
The flare originated in a humongous sunspot that was sighted earlier this week, which is one of the largest sunspots seen in years. The event began at 4:27 p.m. ET (2027 GMT). The flare "triggered some disruption to radio communications on Earth beginning about 45 minutes later," NASA officials wrote in a statement. NASA Probe Discovers 'Alien' Matter From Beyond Our Solar System. This story was updated at 2:26 p.m.

EST. For the very first time, a NASA spacecraft has detected matter from outside our solar system — material that came from elsewhere in the galaxy, researchers announced today (Jan. 31). This so-called interstellar material was spotted by NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX), a spacecraft that is studying the edge of the solar system from its orbit about 200,000 miles (322,000 kilometers) above Earth.
"This alien interstellar material is really the stuff that stars and planets and people are made of — it's really important to be measuring it," David McComas, IBEX principal investigator and assistant vice president of the Space Science and Engineering Division at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, said in a news briefing today from NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C. Weird World! 'Oozing' Alien Planet Is a Super-Earth Wonder. A new look at an alien planet that orbits extremely close to its parent star suggests that the rocky world might not be a scorching hot wasteland, as was thought.

In fact, the planet may actually be stranger and wetter than astronomers ever imagined. The exotic planet 55 Cancri e is a relatively close alien planet, just 40 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Cancer (The Crab). Alien Life May Depend on Planetary Tilt. Although winter now grips the Northern Hemisphere, those who dislike the cold weather can rest assured that warmer months shall return.
This familiar pattern of spring, summer, fall and winter does more than merely provide variety, however. Transhuman. Tiny Invisible Galaxy May Be Made Completely of Dark Matter. Astronomers have discovered a small galaxy that is invisible to telescopes and may be completely composed of dark matter, which reflects no light.

Northern Lights Mystery May Be Solved. Scientists may have solved a longstanding mystery about the origin of the energetic particles that cause Earth's dramatic aurora displays.

The electrons responsible for the auroras — also known as the northern and southern lights — are likely accelerated to incredible speeds in an active region of Earth's magnetosphere, according to a new study. This region is 1,000 times larger than scientists had thought possible, providing enough volume to generate lots of the fast-moving electrons, the study reports. "People have been thinking this region is tiny," lead author Jan Egedal, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, said in a statement. But now, he added, "we’ve shown it can be very large, and can accelerate many electrons. " Egedal and his colleagues analyzed data gathered by various spacecraft, including the European Space Agency's four Cluster probes. Kraken has 112,000 processors working in parallel.
Venus - Sun Transit. Astronomy picture of the day. Brightest Galaxy Ever Seen With Gravity Lens Shines in Hubble Photo. A fluke of astrophysics has revealed what scientists are calling the brightest galaxy ever seen through a cosmic "zoom lens," NASA officials say.

The distant galaxy is 10 billion light-years from Earth and was spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope using a so-called gravitational lens created by a massive cluster of closer galaxies located about 5 billion light-years away. The distant galaxy is three times brighter than any other seen through a gravity lens, researchers said. "This observation provides a unique opportunity to study the physical properties of a galaxy vigorously forming stars when the universe was only one-third its present age," NASA officials explained in a statement released Thursday (Feb. 2).
The universe is currently about 13.7 billion years old. New Theory Saves Universe from Accelerating Expansion, Big Rip. In 1929, cosmologists discovered that the universe is expanding that space-time, the fabric of the cosmos, is stretching.
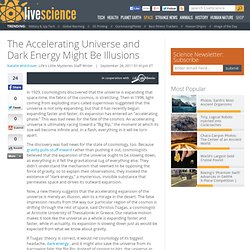
Then in 1998, light coming from exploding stars called supernovas suggested that the universe is not only expanding, but that it has recently begun expanding faster and faster; its expansion has entered an "accelerating phase. " This was bad news for the fate of the cosmos: An accelerating universe is ultimately racing toward a "Big Rip," the moment at which its size will become infinite and, in a flash, everything in it will be torn apart.
The discovery was bad news for the state of cosmology, too. Because gravity pulls stuff inward rather than pushing it out, cosmologists believed that the expansion of the universe ought to be slowing down, as everything in it felt the gravitational tug of everything else. Now, a new theory suggests that the accelerating expansion of the universe is merely an illusion, akin to a mirage in the desert. How Cold Is a Y Dwarf Star? Even You Are Warmer. Scientists have discovered the coldest type of star-like bodies known, which at times can be cooler than the human body.

Astronomers had unsuccessfully pursued these dark entities, called Y dwarfs, ever since their existence was theorized more than a decade ago. They are nearly impossible to see relying on visible light, but with the infrared vision of NASA's WISE space telescope, researchers finally detected the faint glow of six Y dwarfs relatively close to our sun, within a distance of about 40 light-years.
Y dwarfs are the coldest members of star-like bodies known as brown dwarfs, which are odd objects sometimes known as failed stars. Brown dwarfs are too puny to force atoms to fuse together and release nuclear energy, and so they have only the little heat they were born with. This heat fades over time until all the light they do emit is at infrared wavelengths. Big Bang, Expanding & Accelerating Universe. Comets Created Earth's Oceans, Study Concludes.
The dirty snowballs known as comets might be the sources of Earth's water after all, scientists say. Water is critical to life on Earth — life is found virtually wherever there is water on our planet. Researchers have spent decades debating where Earth's water and other key ingredients of life came from. Prior studies had suggested that early Earth was dry, lacking water and other so-called volatile materials. Could Blasts from Cosmic Collisions Destroy Life on Earth? The persistence of life on Earth may depend on massive explosions on the other side of the galaxy, according to a new theory that suggests powerful bursts of space radiation could have played a part in some of our planet's major extinction events. The explosions — gamma-ray bursts thought to occur when two stars collide — can release tons of high-energy gamma-ray radiation into space. Solar Magnetic Activity Cycles & Sun Weather. Our sun is apparently a happy star according to the latest video from a NASA observatory.
The video shows a pattern of sunspots that, when viewed from afar, forms a vast happy face smiling across face of the sun. Sunspots are darker, cooler patches on the sun caused when intense magnetic activity blocks heat convection. These spots are normal, but they don't usually align to give the sun's face such character. The smile on the sun is visible through 11 photographs taken by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which images the sun from Earth orbit.
Earth Magnetic Field. Planetary Transits Page. Transit of Mercury on 1973 Nov 10. Exoplanets & Extrasolar Planets, Solar System & Universe Space Exploration. Physics Simulation Game. [POWDER] : Standard powder. Bose–Einstein condensate. What Is a Black Hole? Earth Magnetic Field. Black hole. Super Smash Bros. Pokemon. Kirby. Metroid. Mario. The Legend Of Zelda. Quantum mechanics/physics/theory. The Higgs boson. Dark Matter & Dark Energy.
Gasland/Fracking. Nikola Tesla. GMO FOODS. Google Search 3T. Lasers. LEGO NXT.