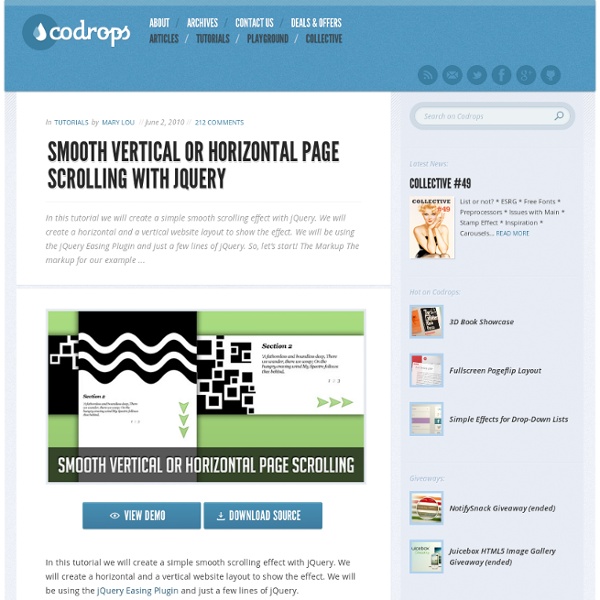
Smooth Vertical or Horizontal Page Scrolling with jQuery
Implementing Off-Canvas Navigation For A Responsive Website
Site of the Month | Showcase
Site of the Month proposes you to find the best creative work of the month in order to discover new ideas for your inspiration and in order to realize all the possible artistic achievements you can reach using modern techniques and tendencies. Site of the Month -it is a productive result of long-lasting searching and finally found creative godsends and solutions based on the laborious work and reliable experience of previous tasks and ideas. Memorable and outstanding works that open new horizons of creativity are proposed for your kind consideration as a Site of the Month, involving you to another world of materialised dreams that are waiting for your active participation. Site of the Month April 2014 Usability of the Month January 2012 HatBox HatBox is another excellent webpage and I especially like that it\'s responsive without any loss of content. Report Dead Link Animation of the Month
Related:
Related:



