


Jean-Jacques Rousseau Jean-Jacques Rousseau (/ruːˈsoʊ/;[1] French: [ʒɑ̃ʒak ʁuso]; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer of the 18th century. His political philosophy influenced the French Revolution as well as the overall development of modern political, sociological, and educational thought. Biography[edit] Youth[edit] Rousseau was born in Geneva, which was at the time a city-state and a Protestant associate of the Swiss Confederacy. Rousseau was proud that his family, of the moyen order (or middle-class), had voting rights in the city. Geneva, in theory, was governed democratically by its male voting "citizens". There was much political debate within Geneva, extending down to the tradespeople. The house where Rousseau was born at number 40, Grand-Rue. The trade of watchmaking had become a family tradition by the time of Rousseau's father, Isaac Rousseau. He and his older brother François were brought up by their father and a paternal aunt, also named Suzanne.
Classical republicanism Classical republicanism (also known as civic humanism)[1] is a form of republicanism developed in the Renaissance inspired by the governmental forms and writings of classical antiquity, especially such classical writers as Aristotle, Polybius, and Cicero. Classical republicanism is built around concepts such as civil society, civic virtue and mixed government. Development[edit] In the classical period itself the term republicanism did not exist, but the term res publica, which translates literally as "the public thing" or "the public affair," was in usage. Variant of classical republicanism is known as civic humanism, a term first employed by the German scholar of late medieval and early modern Italian history, Hans Baron.[6] And although in certain cases and with certain scholars there is a subtle distinction between the two, they are for all intents and purposes interchangeable. Since Thomas Hobbes, at the core of republicanism is the concept of the social contract. See also[edit]
Jack Kerouac Jean-Louis "Jack" Kérouac (/ˈkɛruːæk/ or /ˈkɛrɵæk/; March 12, 1922 – October 21, 1969) was an American novelist and poet. He is considered a literary iconoclast and, alongside William S. Burroughs and Allen Ginsberg, a pioneer of the Beat Generation.[2] Kerouac is recognized for his method of spontaneous prose. Biography[edit] Early life and adolescence[edit] Jack Kerouac was born on 9 Lupine Road in the West Centralville section of Lowell Massachusetts, 2nd floor. Jack Kerouac was born in Lowell, Massachusetts, to French-Canadian parents, Léo-Alcide Kéroack and Gabrielle-Ange Lévesque, of St-Hubert-de-Rivière-du-Loup in the province of Quebec, Canada. His third of several homes growing up in the West Centralville section of Lowell, Jack Kerouac later referred to 34 Beaulieu Street as "sad Beaulieu". There were few black people in Lowell,[19] so the young Kerouac did not encounter much of the racism that was common in other parts of the United States. Early adulthood[edit]
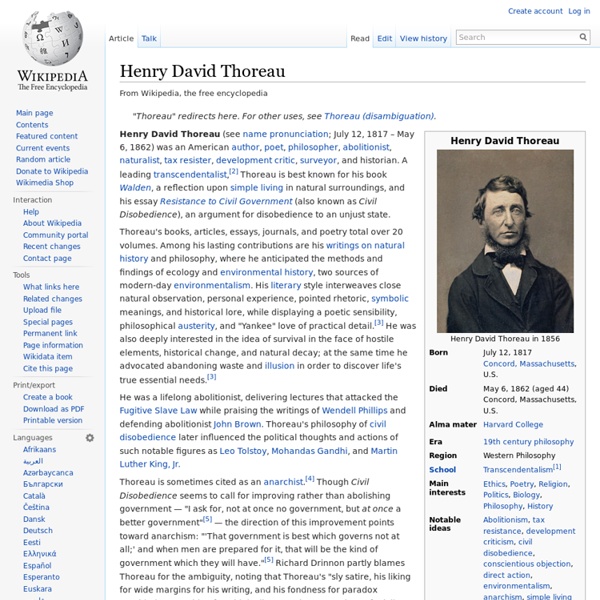
The Writings of Henry D. Thoreau By Elizabeth Witherell, with Elizabeth Dubrulle When I wrote the following pages, or rather the bulk of them, I lived alone, in the woods, a mile from any neighbor, in a house which I had built myself, on the shore of Walden Pond, in Concord, Massachusetts, and earned my living by the labor of my hands only. I lived there two years and two months. (Walden, 3) With these words, Henry David Thoreau began the tale of his experiment of simple living at Walden Pond. In the years following Thoreau's death in 1862, his sister and his friends undertook the responsibility of editing his work. In late March 1845 Thoreau went to Walden Pond, a sixty-two acre body of water a few miles from his parents' home in Concord, Massachusetts, and selected a spot to build a house. I went to the woods because I wished to live deliberately, to front only the essential facts of life, and see if I could not learn what it had to teach, and not, when I came to die, discover that I had not lived.
Conspicuous consumption The sociologist and economist Thorstein Veblen coined the term “conspicuous consumption”, and was a co-founder of the institutional economics movement. Conspicuous consumption is the spending of money on and the acquiring of luxury goods and services to publicly display economic power—either the buyer's income or the buyer's accumulated wealth. Sociologically, to the conspicuous consumer, such a public display of discretionary economic power is a means either of attaining or of maintaining a given social status. Moreover, invidious consumption, a more specialized sociologic term, denotes the deliberate conspicuous consumption of goods and services intended to provoke the envy of other people, as a means of displaying the buyer’s superior socio-economic status. History and evolution[edit] Sociologically, conspicuous consumption was previously thought to comprise social and economic behaviours primarily practiced by rich people. Distinctions of type[edit] Consumerism theory[edit]
Social contract In moral and political philosophy, the social contract or political contract is a theory or model, originating during the Age of Enlightenment, that typically addresses the questions of the origin of society and the legitimacy of the authority of the state over the individual.[1] Social contract arguments typically posit that individuals have consented, either explicitly or tacitly, to surrender some of their freedoms and submit to the authority of the ruler or magistrate (or to the decision of a majority), in exchange for protection of their remaining rights. The question of the relation between natural and legal rights, therefore, is often an aspect of social contract theory. The Social Contract (Du contrat social ou Principes du droit politique) is also the title of a 1762 book by Jean-Jacques Rousseau on this topic. Overview[edit] Thomas Hobbes famously said that in a "state of nature" human life would be "solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short". History[edit] 31.
Andrea Gibson Andrea Gibson (born August 13, 1975) is an award-winning poet and activist who lives in Boulder, Colorado. Her poetry focuses on gender norms, politics, social reform and the struggles LGBTQ people face in today's society. On top of using poetry to express what she feels and provide social and political commentary on real issues, she is involved with many activist groups. She often performs at Take Back the Night events, LGBTQ events, pride events, trans* events, anti-war rallies, peace rallies, organizations against the occupation of Palestine, and groups focused on examining the wrongs of capitalism, patriarchy and white supremacy. She also works with a group called Vox Feminista whose model is to "comfort the disturbed and disturb the comfortable" on all these issues. Gibson grew up in Calais, Maine. In 2011, Write Bloody Publishing published Andrea Gibson's 6th book, "The Madness Vase". Discography[edit] References[edit] External links[edit]
‘Walden’ for the 21st century Can a man who once refused the gift of a doormat — because, as he wrote, “It’s best to avoid the beginnings of evil” — continue to inspire people in how to live simply? The answer is yes, but with stipulations, said scholar Lawrence Buell at a Harvard lecture last week (March 25). Buell, Powell M. Buell referenced examples of literature on voluntary simplicity from the past, including Thoreau contemporary Lydia Maria Child, whose 1829 book “The American Frugal Housewife” promoted “frugal efficiency as moral imperative.” The scholar also included examples of current authors who promote the simple life, including Duane Elgin and his work “Voluntary Simplicity,” and Colin Beavan, a New York City author who recounted his efforts to limit drastically his environmental impact in the book “No Impact Man: The Adventures of a Guilty Liberal Who Attempts to Save the Planet, and the Discoveries He Makes About Himself and Our Way of Life in the Process.” Next in the series is “What’s Enough?
Simple living Poverty is general scarcity or dearth, or the state of one who lacks a certain amount of material possessions or money.[1] Absolute poverty or destitution refers to the deprivation of basic human needs, which commonly includes food, water, sanitation, clothing, shelter, health care and education. Relative poverty is defined contextually as economic inequality in the location or society in which people live.[2][3] After the industrial revolution, mass production in factories made production goods increasingly less expensive and more accessible. Of more importance is the modernization of agriculture, such as fertilizers, to provide enough yield to feed the population.[4] The supply of basic needs can be restricted by constraints on government services such as corruption, tax avoidance, debt and loan conditionalities and by the brain drain of health care and educational professionals. Etymology The English word "poverty" via Anglo-Norman povert. Measuring poverty Definitions Absolute poverty
Real freedom Real freedom is a term coined by the political philosopher and economist Philippe Van Parijs. It expands upon notions of negative freedom by incorporating not simply institutional or other constraints on a person's choices, but also the requirements of physical reality, resources and personal capacity. To have real freedom, according to Van Parjis, an individual must: 1. not be prevented from acting on their will (i.e. they must have traditional negative freedom); and 2. possess the resources or capacities actually to carry out their will. Under this conception, a moral agent could be negatively free to take a holiday in Miami, because no-one is forcing them not to (condition 1 is met); but not really free to do so, because they cannot afford the flight (condition 2 is not met). Van Parijs uses the concept of real freedom as part of his influential argument for a universal basic income.[1] See also[edit] References[edit] Jump up ^ Van Parijs, Philippe (1997). Further reading[edit]
Giovanni Quessep Giovanni Quessep Esguerra (San Onofre, 31 de diciembre de 1939) es un poeta colombiano. Quessep es descendiente de abuelos libaneses que emigraron al país a finales del siglo XIX, huyendo de la persecución del imperio otomano. Biografía[editar] El apellido original era Quessed, pero durante los trámites burocráticos terminó por escribirse con P final. Aunque regresaron al Líbano, veinticinco años después volvieron definitivamente a Colombia. En 1949, su familia tiene que abandonar San Onofre durante el periodo de Violencia bipartidista en Colombia. Después de sus estudios secundarios, viaja a Bogotá y estudia Filosofía y Letras en la Universidad Javeriana y más tarde realiza un postgrado de Literatura Hispanoamericana en el Instituto Caro y Cuervo. En 1961 publica su primer libro, Después del paraíso, libro convencional, ceñido a la métrica y a la rima del soneto, que lo distanció de sus contemporáneos nadaístas. Acerca del Autor[editar] Según James J. Obras[editar] Enlaces Externos[editar]
Maslow's hierarchy of needs Maslow's hierarchy of needs, represented as a pyramid with the more basic needs at the bottom[1] Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in Psychological Review.[2] Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. Maslow used the terms "physiological", "safety", "belongingness" and "love", "esteem", "self-actualization", and "self-transcendence" to describe the pattern that human motivations generally move through. Maslow's theory was fully expressed in his 1954 book Motivation and Personality.[5] The hierarchy remains a very popular framework in sociology research, management training[6] and secondary and higher psychology instruction. Hierarchy Physiological needs Safety needs Safety and Security needs include:
William Morris William Morris self-portrait, 1856 William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was an English artist, writer, textile designer and socialist associated with the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood and English Arts and Crafts Movement.[1][2] He founded a design firm in partnership with the artist Edward Burne-Jones, and the poet and artist Dante Gabriel Rossetti which profoundly influenced the decoration of churches and houses into the early 20th century. As an author, illustrator and medievalist, he helped to establish the modern fantasy genre, and was a direct influence on postwar authors such as J. R. R. Life[edit] Early life and education[edit] William Morris was born in Walthamstow on 24 March 1834, the third child and the eldest son of William Morris, a partner in the firm of Sanderson & Co., bill brokers in the City of London. Morris's painting La belle Iseult, also inaccurately called Queen Guinevere, is his only surviving easel painting, now in the Tate Gallery. Red House[edit]