


Blogging about tech, mostly.: The Raspberry Pi and Wireless RF (XRF) Temperature Loggers Remote Temperature Logging - Why? In our house one room has three exposed wall, as well as two double width windows fitted (one on each side of the room). In the winter, this is a cold room. We're in the process of getting the central heating and double glazing replaced (they're both over 15-20 years old respectively) and are very ineffecient - I was however wondering what improvement we'd see once this work had been done. A Pi, wireless communication, python, Linux, soldering...now this sounded like fun! First I searched for what I could use for this - what could I use that captured and could transmit temperature information - and most importantly, what could do this in a wireless way? I found the answer using a combination of 1 Slice of Pi, a 2 Temperature XRF Sensor's and 3 XRF Wireless RF Radios, all of which I got from CISECO. The documentation of the above is pretty decent, but there were still a number of threads you have to tie together to get all of this to work, so here we go: 1.
Votre blogue à la maison sur Raspberry Pi Nous verrons dans ce tutoriel comment installer un Raspberry Pi pour en faire un serveur web hebergé chez vous, derriere votre box internet. Sommaire Conventions établies adresse IP du rpi = 192.168.1.10 (nom : rpi) adresse IP de votre ordinateur = 192.168.1.11 (nom : pc) adresse IP de votre box Internet = 192.168.1.1 (nom : box) votre compte sur le pc = votre_login_pc votre compte sur le rpi = votre_login_rpi nom du site = nomsite.sytes.net (un fournisseur de DNS dynamique gratuit) Je n'utilise pas sudo, donc les commandes se font par un passage en root par su ;Sur le rpi, la connexion est possible par wifi avec une clé USB, mais j'utilise l'Ethernet ;Le tutoriel est entièrement basé sur Linux et il n'y a pas d'interface graphique, sauf accident. Achat du rpi J'ai acheté les produits ci-dessous chez www.kubii.fr. hdparm -t --direct /dev/sdc sd 20 MB/s hdparm -t --direct /dev/sdd usb1 29 MB/s hdparm -t --direct /dev/sde usb2 22 MB/s hdparm -t --direct /dev/sdf usb3 22 MB/s Raspi-config gameslp
Les commandes Linux les plus utiles pour son Raspberry Pi | L'univers du micro-PC Raspberry Pi accessible à tous Quel que soit le système d’exploitation installé sur son Raspberry Pi, il est possible de l’utiliser de différentes manières. La façon la plus intuitive consiste à utiliser sa souris et à naviguer via l’interface graphique proposée par le système d’exploitation pour réaliser les actions souhaitées : changer de répertoire, créer un fichier, lancer un programme… Mais toutes ces actions sont également réalisables en ligne de commandes c’est à dire en saisissant des commandes dans un terminal. La base de la base Première étape et non des moindres : ouvrir le terminal permettant d’y saisir des commandes. Si vous avez le système d’exploitation installé Raspbian, alors il suffit de cliquer sur l’icône LXTerminal sur le bureau : Il est également possible de le retrouver dans le menu des programmes, dans la catégorie « Accessoires ». Une fois ouvert, vous devriez vous retrouver face à une fenêtre noire comme celle-ci : Les commandes les plus utiles Commandes de commande Système Fichiers & repertoires
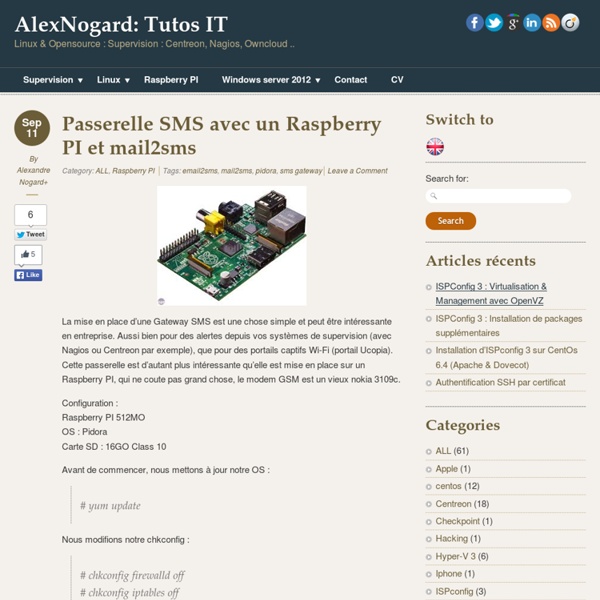
Random Geeky Ramblings: Raspberry Pi as a SMS Gateway using Gammu Today was one of those days where I thought I'd find something useful for my Raspberry Pi to do, rather than sit in a box unloved. I was thinking how we send a lot of monitoring notifications as emails and how bad email is as a single method notification, especially if what you are monitoring is your connection to the internet... Internet connection goes down, how do you send the notification out? I had a 3G USB dongle also sitting around doing nothing, so as a test I stuck a Pay+Go simcard in, made sure it had some credit and connected it to my Raspberry Pi. This is how I got it to send an SMS (Will likely expand this post as I add features). What library to use? First off I had to work out the best existing library to interact with the 3G dongle. I came across Gammu, which started as a fork of Gnokii. Thankfully Gammu provides packages so installing it on Raspbian was nice and simple: $ sudo apt-get update$ sudo apt-get install -y gammu-smsd gammu python-gammu usb-modeswitch vim $ lsusb $ id
Replace Google Reader with a Raspberry Pi With Google Reader shutting down this July, you might be looking for another way to stay on top of your feed subscriptions. Why not set up a Raspberry Pi to do the not-so-heavy lifting instead of importing your feeds into yet another web-based service? After all, you never know when anyone (or everyone) is going to pull the pin on their aggregators — especially since RSS is supposed to be dead already anyway. Just follow Conor O’Neill’s lead and install Tiny Tiny RSS on your Raspberry Pi. That makes it a pretty ideal Google Reader replacement if you’ve got a decent internet connection and are comfortable setting up port forwarding on your router. Don’t have a Raspberry Pi? One thing to be aware of is that your comparatively limited processing and bandwidth mean that Tiny Tiny has to work a little harder to retrieve all that feed content.
Installer un serveur WEB sur raspberry (http,php,mysql,ftp) [TUTO] - Réseaux, Internet, Téléphonie et Services en Ligne Le but de ce petit tutorial est de monter un serveur WEB (html, php, mysql, phpMyAdmin et serveur ftp) sur un raspberry où a été préalablement installée la distribution raspbian. Au final, il s'agit donc d'héberger son site sur un raspberry! Ce tutorial fait suite au précédent s’agissant de l’installation de la distribution raspbian sur une clef USB (voir ici). Le serveur devra offrir les fonctionnalités de base d’un serveur WEB et être accessible depuis le internet. En outre, il disposera de « stratégies » basiques de sauvegarde afin de pouvoir restaurer rapidement le serveur. CHAPITRE III : SAUVEGARDER LE SERVEUR : Work in progress ANNEXES : Work in progress L’objectif est bien ici de disposer d’un serveur WEB avec toutes les fonctionnalités de base, mais encore de rendre accessible celui-ci sur le WEB et dont de faire un minimum attention à la sécurité. Pour l’essentiel de l’installation, je me suis inspiré de ce tutorial (en anglais) : mkdir public #!
NotiPi Notifications via SMS Text or Twitter from the Pi Fred Sonnenwald and Hamish Cunningham, June 2013 The general idea of NotiPi, or notifications, is to let the Raspberry Pi interact with you in ways not tied to sitting in front of the monitor. Here we'll look at two options for texting (using the net or using a mobile phone handset) and finish up with the Twitter option. The general idea here is that there are loads of companies out there that offer what is called SMS gateway service. The webpage method is a sort of end-user thing that's friendly to you and I, but is a bit more complex to get the Pi talking to. BulkSMS Unfortunately we can't just use any company that provides this service. To understand the API (or really any programming concept or protocol) I find that you can approach it in two ways. To save you the tedium of working through either the API or the example code and here we'll provide you with a rough outline of how it works. The key-pairs A unique message ID (stop_dup_id).
Raspberry Pi Review Back in personal technology prehistory—you know, before computers were idiot-proof enough to grace any living room—it was tough to use a PC without possessing an intimate understanding of how and why it worked. The advent of prefabricated machines and graphical operating systems has helped the industry explode like those of us who witnessed its birth could never have dreamed of, but that remarkable success has come at the cost of the pioneering spirit that started it all. But all hope of regaining that foundational force it is not lost. The Raspberry Pi ($35, as tested), a tiny and brilliantly inexpensive proto-computer, encourages exactly the kind of exploration and tinkering that are nowadays often relegated to even the fringes of the DIY and enthusiast communities, and demands your active participation and intellectual engagement. Features Before getting into what the Raspberry Pi can do, we need to examine what you get with it. And what hardware it is! Software is another matter.
Raspberry serveur Web Après avoir créé votre carte SD, et après avoir démarré pour la première fois votre Raspberry Pi, il y a de fortes chances que vous souhaitiez l’utiliser comme un serveur web. La Raspberry Pi comme serveur web, pourquoi ? Mais pourquoi utiliser la Raspberry comme un serveur Web, plutôt que de faire appel à des prestataires de services spécialisés dans l’hébergement web ? Tout d’abord, d’un point de vue économique, il faut savoir que les services d’hébergement web ne sont pas gratuits et qu’il faut sortir le porte-monnaie tous les mois/ans. Contrairement à la Raspberry qui demande juste une connexion. De plus, en choisissant la Raspberry, vous avez la possibilité de modifier vos services à souhait (exemples : la taille du disque, l’hébergement de Database, etc.), ce qui n’est en général pas le cas chez les hébergeurs spécialisés, qui vendent souvent des hébergements mutualisés avec une faible capacité de configuration. Installation du serveur Apache avec Raspbian Apache, c’est quoi ? cat .
Sensor - Temperature XRF development sensor - THERMISTOR Important note on XRF v2.0 As of 27th November 2013 we are now shipping XRF v2.0 modules, these are based on the SRF v1.2 module. Althouth they look diffrent from the v1.5 they are compatible with the expection on some LLAP personalites, for more details see this blog post XRF v2.0. llapThermistor is not affected Product description This sensor kit is for making a wireless temperature sensor. Monitor temperature remotely (with the XRF option everything you need for a self contain temperature sensor in one kit)Easy communication (just add an XRF to the board and an SRF-Stick to your PC for instant communication)Log data to the cloud (use one of the many cloud based loggers of information) The sensor is encased in a smart, strong black enclosure. Features: Compact and easily deployableFits in the matchbox size ABS box providedEach pin of the XRF is broken out onto the outer edge for easy access and developmentMade in the UK Kit contents: Cloud providers: Technical data Downloads Documentation
Systèmes d'exploitation Linux et Unix optimisés pour Raspberry Pi Voici une liste des systèmes d’exploitation optimisés précisément pour la Raspberry Pi. Systèmes d’exploitation officiels Raspbian, La distribution officielle dérivée de Debian Arch linux, optimisé pour Raspberry pi RISC OS, créé à Cambridge, par Acorn. La première mouture date de 1987 1987 Certains de ses développeurs avaient travaillé sur la création du processeur ARM. Pour les débutants Noobs, créé par la fondation Raspberry Pi, pour aider les debutants dnas leur première approche du mini-ordinateur. Systèmes d’exploitation ultra-lights Pi-Point, version ultra-épurée de Raspbian (seulement SSH de pré-installé) Moebius, système d’exploitation minimaliste dérivé de Debian/ARM BerryTerminal, basé sur le système d’exploitation ltsp.org PiCore, 25Mo, idéal pour un système embarqué SliTaz, 22Mo, démarre votre micro-ordinateur en moins de 10 secondes! Systèmes d’exploitation pour le piratage et les tests d’intrusion Kali, système d’exploitation le plus connu pour les tests de pénétration
Wireless Projects - PrivateEyePi Project Wireless sensors and a RaspberryPi open up a world of possibilities. The Internet Of Things (IOT) is phenomenon sweeping the world at this moment where everyday things (cars, homes, household appliances, plants) are being connected to the IOT where we can monitor, control and alert in ways not possible before. RF communications can be a complex subject, but I have eliminated all the complexity by using pre-programmed devices that have the RF communication libraries already loaded. The components are plug and play ready to use. You do not need to know anything about RF communications or serial communications in order to do these projects. Although these projects do provide software to connect your wireless sensors to the PrivateEyePi alarm system, you can use them for any wireless application you have in mind. Follow the following steps:
Système de vidéo-surveillance abordable avec des Raspberry Pi Aujourd’hui nous allons voir comment créer un système de télé-surveillance grâce à un Raspberry Pi et divers types de caméras. Ce système a pour vocation d’être utilisé dans le cardre d’une télé-surveillance domestique. Il doit permettre de garder un oeil en temps réel sur sa maison, et sauvegarder un historique des images en cas de besoin. La capture d’écran ci-dessous vous donne un aperçu du résultat final du système qui est actuellement installé chez moi. Nous verrons comment utiliser trois différents types de caméras pour vous permettre de construire votre système avec le matériel dont vous disposez déjà : Si vous souhaitez vous équiper, je vous conseille fortement d’opter pour le module Raspberry Pi Caméra, très petit, qui offre un rapport qualité/prix imbatable. Note : Je ne reviens pas ici sur l’installation et l’utilisation de ces caméras. Quand on parle de « vidéo surveillance », on s’imagine un flux « vidéo ». Problème réseau L’utilité de la vidéo par rapport aux photos #! #!