Narada Bhakti Sutra Narada Bhakti Sutra Chapter 2 Verse 26
Bhaktivedanta VedaBase: Nārada Bhakti Sūtra 26 phala-rūpatvāt phala — of the fruit; rūpatvāt — because of being the form. After all, bhakti is the fruit of all endeavor.
Difference Between Consumer and User
Consumer vs User We think we know the meanings of the words consumer and user. Of course, we do, as consumers are people who consume (literally) or make use of a product in the household.
Le cahier de Satyâ : l'alphabet sanskrit et la Devanâgarî
Les 48 phonèmes Ceci est le classement des phonèmes de l'alphabet sanskrit suivant le grammairien Pânini. Un 'phonème' est un son articulé que l'on peut représenter par un 'graphème'. Formation d'une syllabe Contrairement au français où les lettres s'ajoutent simplement les unes aux autres, la syllabe sanskrite est le fruit d'une ligature, comme notre Æ.
Academy Open Textbooks
We’re about so much more than just these textbooks. Students: We have almost 100 free, full-length certificate courses ready for you to take right now. Many of our courses can connect to zero-tuition college credit through our dozens of partner colleges and universities. Educators: Want more resources for your classroom? Saylor Academy’s courses are built from curated OER and are openly-licensed for reuse — you can adopt and adapt our materials to meet your needs.
Les principales langues du monde par familles
Les linguistes dénombrent environ 7 000 langues, auxquelles on peut ajouter des dizaines de milliers de dialectes. Le classement ci-dessous (environ 800 langues) ne donne évidemment qu'un aperçu de cette immense variété. Pour retrouver une langue si vous ne connaissez pas sa famille, utilisez la fonction Edition, Rechercher de votre navigateur. Les langues éteintes n'ont généralement pas été citées. Attention, les chiffres sont donnés à titre indicatif et sont à prendre avec précaution. Si vous avez des informations plus fiables ou plus précises, ou que vous avez constaté des erreurs, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
The Price is Right: 11 Excellent Sites for Free Digital Textbooks
Books | Feature The Price is Right: 11 Excellent Sites for Free Digital Textbooks If you're committed to shifting your curriculum to e-textbooks, consider trying free first. Here are the best sites for digital books that won't cost your students a dime. By Dian Schaffhauser08/14/13
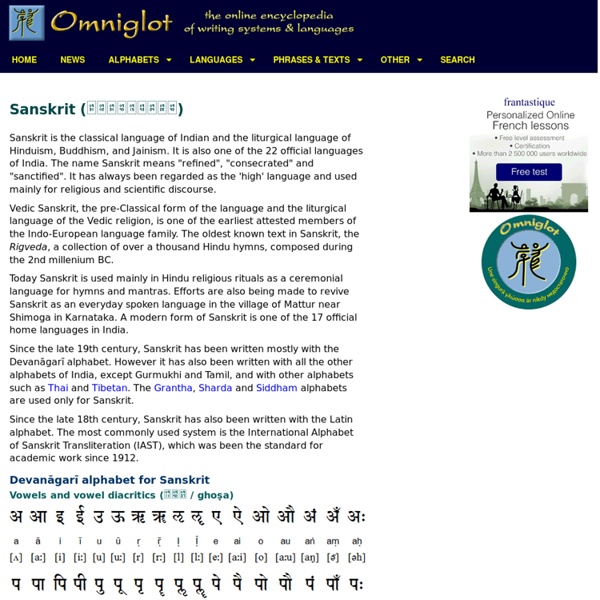
Sanskrit
Certaines informations figurant dans cet article ou cette section devraient être mieux reliées aux sources mentionnées dans les sections « Bibliographie », « Sources » ou « Liens externes »(juillet 2014). Améliorez sa vérifiabilité en les associant par des références à l'aide d'appels de notes. Le sanskrit ou sanscrit[1] (संस्कृतम् (saṃskṛtam)) est une langue indo-européenne de la famille indo-aryenne, autrefois parlée dans le sous-continent indien.
The Internet Grammar of English
Welcome to the Internet Grammar of English! The Internet Grammar of English is an online course in English grammar written primarily for university undergraduates. However, we hope that it will be useful to everyone who is interested in the English language.
Langues en Inde
Les langues en Inde sont très diverses et appartiennent à plusieurs familles linguistiques. La langue officielle du gouvernement central est l'hindi. La Constitution prévoyait que l'anglais cesse d'être langue officielle après 15 années mais, face à la protestation des États non hindiphones, le Parlement a adopté une loi qui maintient son statut de langue seconde. En outre, 22 langues sont listées dans la Huitième Annexe de la Constitution. Histoire[modifier | modifier le code]
Bolivarium - Libertador
Esta fuente histórica ha sido puesta en servicio gracias al esfuerzo mancomunado de la Academia Nacional de la Historia (ANH) y del Instituto de Investigaciones Históricas Bolivarium de la Universidad Simón Bolívar, ambas instituciones venezolanas. La digitalización y posterior automatización se efectuó teniendo como base la colección de microfilmes donados por la Fundación Lecuna a la USB a principios de los años 80 ́ del siglo XX. Tal fuente fue producida en 1961 y procesada digitalmente en el año 2011, lo cual generó dificultades técnicas de difícil solución, a pesar de lo cual se logró poner al servicio del público más del 90% del acervo documental contenido en los originales.
Proto-Indo-Européens
Les Proto-Indo-Européens (PIE) sont, selon la thèse la plus communément admise, un peuple ancien, locuteur du proto-indo-européen, un langage préhistorique reconstitué de l'Eurasie. La connaissance de ce peuple vient principalement de la reconstruction linguistique. Il aurait diffusé sa langue, sa culture, ses codes et ses croyances à la quasi-totalité des peuples de l'Europe actuelle (Baltes, Celtes, Germains, Grecs, Latins, Slaves) et certains peuples d'Asie (tels que les Iraniens - Perses, Kurdes, Ossètes, Pachtounes et autres peuples Iraniens -, Indiens, Arméniens). Définition[modifier | modifier le code]
Devanagari
Origins[edit] Devanagari is part of the Brahmic family of scripts of Nepal, India, Tibet, and South-East Asia.[4] It is a descendant of the Gupta script, along with Siddham and Sharada.[4] Eastern variants of Gupta called nāgarī are first attested from the 7th century CE; from c. 1200 CE these gradually replaced Siddham, which survived as a vehicle for Tantric Buddhism in East Asia, and Sharada, which remained in parallel use in Kashmir. An early version of Devanagari is visible in the Kutila inscription of Bareilly dated to Vikram Samvat 1049 (i.e. 992 CE), which demonstrates the emergence of the horizontal bar to group letters belonging to a word.[1] nāgarī is the Sanskrit feminine of nāgara "relating or belonging to a town or city". It is feminine from its original phrasing with lipi ("script") as nāgarī lipi "script relating to a city", that is, probably from its having originated in some city.[5]