The Case for Data Warehousing | The Data Warehousing Information Center
The following is a list of the basic reasons why organizations implement data warehousing. This list was put together because too much of the data warehousing literature confuses "next order" benefits with these basic reasons. For example, spend a little time reading data warehouse trade material and you will read about using a data warehouse to "convert data into business intelligence", "make management decision making based on facts not intuition", "get closer to the customers", and the seemingly ubiquitously used phrase "gain competitive advantage". In probably 99% of the data warehousing implementations, data warehousing is only one step out of many in the long road toward the ultimate goal of accomplishing these highfalutin objectives. The basic reasons organizations implement data warehouses are: To perform server/disk bound tasks associated with querying and reporting on servers/disks not used by transaction processing systems The concern here is security.
Six Architectural Styles of Data Hubs by Malcolm Chisholm
Data hubs are an important component in information architecture. However, they are rather diverse, and this diversity often means that the term “hub” means quite different things to different people. It also means that a definition of “data hub” is inevitably going to be rather generic. The following definition is used here: A data hub is a database which is populated with data from one or more sources and from which data is taken to one or more destinations. A database that is situated between one source and one destination is more appropriately termed a “staging area”. Why Data Hubs? The more that data is understood to be an enterprise resource that needs to be shared and exchanged, the more likely it is that data hubs will appear in enterprise information architectures. They often needlessly replicate movement of the same data. Data hubs, therefore, may present a better alternative, although we need to be cautious. The Publish-Subscribe Data Hub Figure 2 shows this hub architecture.
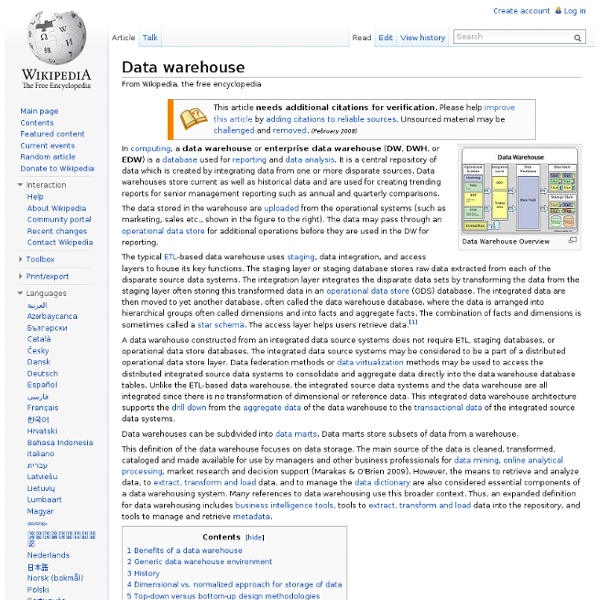
Data Warehouse Architecture
There are many questions around Data Warehousing, ranging from WHEN to do a formal data warehouse vs when to use a data mart/subject oriented star schema approach vs when to use federated NOW data. Other questions are why would you use a Data Warehouse today? Is it still a relevant approach in Information Management? In this entry I will provide my opinion on the subject, and we’ll see what we can discover. As always, I’d love your comments and feedback on the subject. Why should I use a Data Warehouse? There are hundreds of reasons why a data warehouse is useful to your organization, I would suggest the following list be a good starting point: (If you have these needs you may need a true back-end enterprise scalable historical data store : or Enterprise Data Warehouse)…. When should I NOT build a Data Warehouse? Do NOT confuse Data Warehousing With Non-Agility… When should I use a Federated Query Approach? Ok – So what are we talking about here?
Business Intelligence Buyer's Guide for Enterprises
Posted October 11, 2010 By Drew RobbFeedback The enterprise BI market may be dominated by the likes of SAP, Oracle and IBM, but smaller names like Information Builders also have much to offer. Which business intelligence (BI) product is right for you? Info-Tech Research analyst Gareth Doherty cautions users that the BI field has so many tools and sub-categories that evaluation can be confusing. This buyer's guide to enterprise business intelligence, therefore, takes a rather narrow view of the market for the sake of simplicity. "Choosing a BI suite involves a long-term commitment to a product and vendor that could result in an expensive divorce if the relationship sours," said Doherty. Boris Evelson, an analyst at Forrester, recommends sticking to the tried and true evaluation steps: Without further ado, here are some of the major candidates. IBM Cognos IBM Cognos 8 Business Intelligence provides a broad view of system activity and the ability to streamline environment changes.
Managing Data in the Data Hub
By: Alex Berson and Larry Dubov Service provider takeaway: Managing data in the data hub raises concerns of acquiring, rationalizing, cleaning, transforming, and loading data. This section of the chapter excerpt from the book Mastering Data Management and Customer Integration for a Global Enterprise will focus on the procedures and best practices for consultants managing data in the data hub. Download the .pdf of the chapter here. Armed with the knowledge of the role of the enterprise data strategy, we can discuss CDI Data Hub concerns that have to deal with acquiring, rationalizing, cleansing, transforming, and loading data into the Data Hub as well as the concerns of delivering the right data to the right consumer at the right time. In this chapter, we also discuss interesting challenges and approaches of synchronizing data in the Data Hub with applications and systems used to source the data in the first place. Data Zone Architecture Approach Loading Data in the Data Hub Introduction
Choosing the Right Microsoft Reporting Technology Part 1: Report Services
As Business Intelligence has evolved over the years the number of tools we have to choose from for presenting data has advanced drastically. With so many tools to choose from it can be rather confusing (especially when your company is just getting their feet wet in BI) to determine which tool is the right one for an organizations reporting needs. Just within the Microsoft suite of tools (not including third-party tools) you have Reporting Services, Excel, PowerPivot, PerformancePoint and Power View. Many companies try to marry themselves to one or two reporting tools and fit their needs into the restrictions of the tool(s) they have chosen. The truth is not a single one of these tools can solve all reporting needs. While each one of these tools by themselves may be able to present your data, you will find that using a combination approach will conclude in a much more well rounded and impressive reporting solution. What it is The reports developed with the tool are highly customizable.



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2025-08-03 18:28
by raviii Aug 4
data warehouse: A large data store containing the organization’s historical data, which is used primarily for data analysis and data mining. It is the data system of record.
Found in: Hurwitz, J., Nugent, A., Halper, F. & Kaufman, M. (2013) Big Data For Dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey, United States of America: For Dummies. ISBN: 9781118504222. by raviii Jan 1