


CambridgeDeclarationOnConsciousness.pdf (application/pdf Object) 15 Interesting Facts about Dreams Dreaming is one of the most mysterious and interesting experiences in our lives. During the Roman Era some dreams were even submitted to the Roman Senate for analysis and dream interpretation. They were thought to be messages from the gods. Dream interpreters even accompanied military leaders into battles and campaigns! In addition to this, it is also known that many artists have received their creative ideas from their dreams. But what do we actually know about dreams? Here are 15 interesting facts about dreams – enjoy and what’s most important, don’t forget to share your dream stories in the comment section! 1. Within 5 minutes of waking half of your dream is forgotten. 2. People who became blind after birth can see images in their dreams. 3. Every human being dreams (except in cases of extreme psychological disorder). 4. Our mind is not inventing faces – in our dreams we see real faces of real people that we have seen during our life but may not know or remember. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
3D map of human brain is the most detailed ever - health - 20 June 2013 The folds, creases and intricate internal structures that make up the human brain are being revealed in unprecedented detail. A new three-dimensional map called BigBrain is the most detailed ever constructed, and should lead to a more accurate picture of how the brain's different regions function and interact. Until now, the precise placement of the neurons that make up our brain circuitry has been difficult to map, largely because the human brain's surface is covered with folds and creases. Slicing a brain exposes only two dimensions, so it is often unclear where and how the cells within these folds are organised in three-dimensional space. To make the new map, Katrin Amunts of the Jülich Research Centre in Germany and her colleagues embedded a 65-year old woman's brain in wax, sliced it into more than 7400 sections each 20 micrometres thick – one-fifth of the width of a human hair – and made digital images of the slices, also at a resolution of 20 micrometres. Tour de force
Instant Expert 31: The human brain Cookies on the New Scientist website close Our website uses cookies, which are small text files that are widely used in order to make websites work more effectively. Find out about our cookies and how to change them Log in Your login is case sensitive I have forgotten my password close My New Scientist Look for Science Jobs Instant Expert 31: The human brain (Image: Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging)It took thousands of years, but our understanding of how the brain works has brought us to the brink of enlightenment. Milestones of neuroscience We now have a detailed understanding of the brain's building block – the neuron. More than one way to map a mind Injuries were once the key to learning how the brain worked, but advanced imaging techniques are now giving us detailed maps of where our skills ariseRead more From tiny neurons to expansive minds How does the brain generate a conscious mind? Looking over the neuroscience horizon Download a paper brain to build yourself REVIEW: 19:00 16 April 2014
Stages of Sleep Usually sleepers pass through five stages: 1, 2, 3, 4 and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. These stages progress cyclically from 1 through REM then begin again with stage 1. A complete sleep cycle takes an average of 90 to 110 minutes. The first sleep cycles each night have relatively short REM sleeps and long periods of deep sleep but later in the night, REM periods lengthen and deep sleep time decreases. Stage 1 is light sleep where you drift in and out of sleep and can be awakened easily. In stage 2, eye movement stops and brain waves become slower with only an occasional burst of rapid brain waves. Slow wave sleep comes mostly in the first half of the night, REM in the second half. In the REM period, breathing becomes more rapid, irregular and shallow, eyes jerk rapidly and limb muscles are temporarily paralyzed. Infants spend almost 50% of their time in REM sleep. The brain waveform during REM has low amplitudes and high frequencies, just like the waking state. Microsleep
BREAKTHROUGH: DMT Found in the Pineal Gland of Live Rats In a major breakthrough in consciousness and psychedelic studies, Cottonwood Research Foundation has published a paper (soon to appear in the Journal Biomedical Chromatography) documenting the presence of DMT in the brains of living rats. For decades researchers have hypothesized that DMT may be one of the neurochemicals responsible for consciousness, dreams and visionary experiences. It’s certainly responsible for these and ever weirder experiences for those who have smoked it or taken Ayahuasca. DMT has been documented as naturally occurring in human blood, but this was not conclusive evidence that it is produced in the brain. DMT is structurally related to Serotonin, Melatonin and Pinoline, so the small traces in human blood could be an enzymatic breakdown product of these precursor molecules. Now we have clear proof of DMT being manufactured in the living Pineal Glands of rats, and that the genes responsible for this exist in the Pineal Gland and Retina! From the press release:
Rubber Hand Trick Reveals Brain-Body Link | Wired Science The rubber hand illusion is more than a vaguely creepy parlor trick. It’s a window into relationship between our mental and physical self-conception. During the illusion, a participant’s hand is hidden, and a rubber hand positioned so that it appears as her own. Suddenly the rubber hand literally feels like it belongs to her. Scientists have now shown that the hidden hand’s temperature drops during the illusion: its effects aren’t simply mental, but physical as well, and could even hint at as-yet-unknown processes of disease. "These findings show that the conscious sense of our physical self, and the physiological regulation of our physical self, are linked," write a team of researchers led by Oxford University’s G. At first, this may seem a retelling of mind-body linkage: embarrassment causes blushing, fear a burst of strength. When participants in the study confused a rubber hand for their own, their hidden hands became half a degree colder. Video: New ScientistImage: PNAS See Also:
Understanding Sleep: Deep Sleep, REM Sleep, Cycles, Stages, and The power of sleep Many of us try to sleep as little as possible. There are so many things that seem more interesting or important than getting a few more hours of sleep, but just as exercise and nutrition are essential for optimal health and happiness, so is sleep. The quality of your sleep directly affects the quality of your waking life, including your mental sharpness, productivity, emotional balance, creativity, physical vitality, and even your weight. No other activity delivers so many benefits with so little effort! Understanding sleep Sleep isn’t exactly a time when your body and brain shut off. The good news is that you don't have to choose between health and productivity. Myths and Facts about Sleep Myth 1: Getting just one hour less sleep per night won’t affect your daytime functioning. Myth 2: Your body adjusts quickly to different sleep schedules. Myth 3: Extra sleep at night can cure you of problems with excessive daytime fatigue. How many hours of sleep do you need? REM sleep
Banishing consciousness: the mystery of anaesthesia - health - 29 November 2011 Read full article Continue reading page |1|2|3 I WALK into the operating theatre feeling vulnerable in a draughty gown and surgical stockings. I smile weakly and ask for a gin and tonic. I have had two operations under general anaesthetic this year. What they didn't tell me was how the drugs would send me into the realms of oblivion. The development of general anaesthesia has transformed surgery from a horrific ordeal into a gentle slumber. That is starting to change, however, with the development of new techniques for imaging the brain or recording its electrical activity during anaesthesia. Consciousness has long been one of the great mysteries of life, the universe and everything. Altered consciousness doesn't only happen under a general anaesthetic of course - it occurs whenever we drop off to sleep, or if we are unlucky enough to be whacked on the head. It was a Japanese surgeon who performed the first known surgery under anaesthetic, in 1804, using a mixture of potent herbs.
3D map of human brain is the most detailed ever - health - 20 June 2013 The folds, creases and intricate internal structures that make up the human brain are being revealed in unprecedented detail. A new three-dimensional map called BigBrain is the most detailed ever constructed, and should lead to a more accurate picture of how the brain's different regions function and interact. Until now, the precise placement of the neurons that make up our brain circuitry has been difficult to map, largely because the human brain's surface is covered with folds and creases. Slicing a brain exposes only two dimensions, so it is often unclear where and how the cells within these folds are organised in three-dimensional space. To make the new map, Katrin Amunts of the Jülich Research Centre in Germany and her colleagues embedded a 65-year old woman's brain in wax, sliced it into more than 7400 sections each 20 micrometres thick – one-fifth of the width of a human hair – and made digital images of the slices, also at a resolution of 20 micrometres. Tour de force
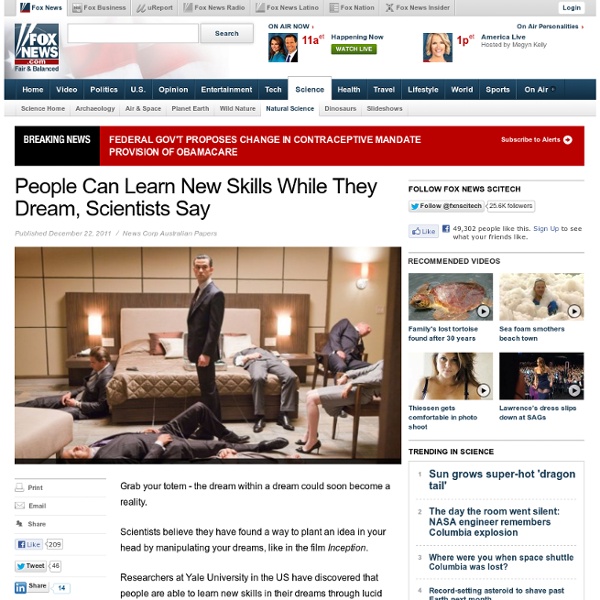
Lucid Dreaming Tips - How to Lucid Dream - Tips for Lucid Dreaming / Lucid Dreams The Six Basic Steps There are many techniques and methods that you can use for inducing lucid dreams, but there is an underlying process behind most, if not all of them. I have broken this underlying process down into six basic steps to serve as a foundation for your lucid dream training. Once you absorb these steps and start following them, it is only a matter of time before you have your first lucid dream. In case you are wondering how long it will take for you to have your first one, just follow through with the steps and have faith that you will have one. 1) Doing the Mental Prep-Work 2) Increasing dream recall 3) Keeping a dream journal 4) Becoming familiar with your Dreams 5) Adding Awareness to your Waking Consciousness 6) Linking your Awareness to your Dreams Step One) Doing the Mental Prep-Work This step involves setting up the right mental foundation and building a mental framework that will maximize your success. Here are four key questions that you need to ask yourself. 1.) 2.) 3.)