


La guerre de l’Internet est commencée at SÉRENDIPITÉ Lors du Chaos Computer Congress, à Berlin, en décembre dernier, Cory Doctorow annonçait que l’Internet ouvert est devenu l’enjeu d’une guerre sans merci entre les tenants du contrôle et les défenseurs des libertés individuelles (Lockdown, The coming war on general purpose computing). Nous subissons déjà, par le biais de nos ordinateurs et applications, un contrôle insidieux : comment on accède aux contenus (des interfaces si faciles à utiliser);à quoi on nous donne accès (des contenus sélectionnés et contrôlés pour notre bien). The fantasies of those days were like a boring science fiction adaptation of the Old Testament Book of Numbers, a tedious enumeration of every permutation of things people do with information—and what might be charged for each.Unfortunately for them, none of this would be possible unless they could control how people use their computers and the files we transfer to them. Vidéo de la conférence de Cory Doctorow, The coming war on general computation.
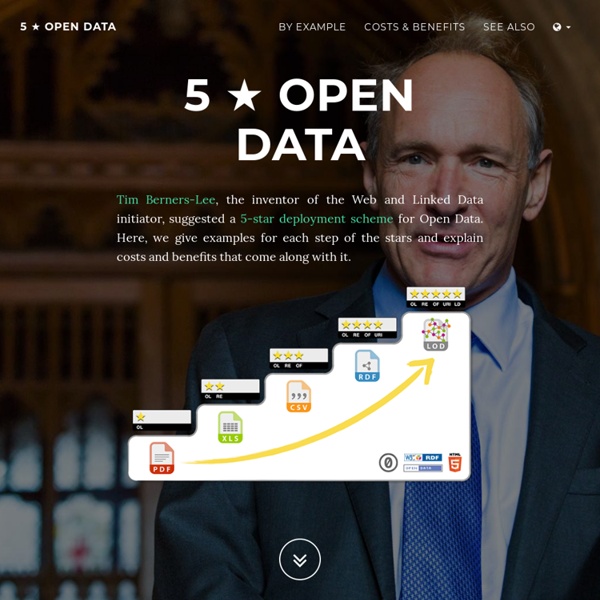
Données ouvertes Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Donnée. Selon les pays, une part plus ou moins importante de la donnée publique est mise à disposition de tous dans le champ des données ouvertes. Ce mouvement est en expansion Les données ouvertes à la Loupe Autocollants utilisés par les militants des données ouvertes Une donnée ouverte est une donnée numérique d'origine publique ou privée. L'ouverture des données (en anglais open data) représente à la fois un mouvement, une philosophie d'accès à l'information et une pratique de publication de données librement accessibles et exploitables. Elle s'inscrit dans une tendance qui considère l'information publique comme un bien commun (tel que défini par Elinor Ostrom) dont la diffusion est d'intérêt public et général. En Europe et dans certains pays, des directives et lois imposent aux collectivités de publier certaines données publiques sous forme numérique. Remarque : Le présent article est généraliste.
PHILOWEB | Web and Philosophy scientific events Kony2012, bonne consience ou prise de conscience ? Le 5 mars dernier, l'ONG "Invisible Children" publiait une vidéo, un documentaire de 30 minutes, pour sensibiliser les gens au personnage de Joseph Kony ( chef des rebelles de l'Armée de résistance du Seigneur en Ouganda). Une campagne humanitaire au succès fulgurant qui va droit aux donateurs sans passer par les médias...Mais derrière l'enthousiasme, quelques critiques fusent. Alors Kony2012, bonne conscience ou prise de conscience? (Voici un lien vers une version mal sous-titrée en français) Plus de 100 millions de vues en 6 jours, un score incroyable qui fait de cette vidéo la vidéo la plus virale de l'histoire du web. Que nous dit cette vidéo en préambule ? "Rien n'est plus puissant qu'une idée qui a fait son chemin."" Beaucoup de phrases accrocheuses qui ont très certainement beaucoup joué dans l'adoption du message par la jeunesse américaine traditionnellement peu sensible aux causes internationales. Cette séquence, je vous laisserais la découvrir ainsi que la suite du documentaire.
Open data (dossier complet) : formats, licences, réutilisation des données et projets L’édition papier de la Gazette des Communes datée du 21 janvier 2013 (n°3/2157) propose un dossier complet sur l’Open Data : le service public augmenté avec un point sur les formats, les licences et la gratuité en débat, favoriser la réutilisation des données et inscrire les actions pour des données au service du territoire. Qu’est-ce que l’Open Data (ou données ouvertes) – cf. Wikipédia : « Une donnée ouverte (en anglais open data) est une information publique brute, qui a vocation à être librement accessible et réutilisable. La philosophie pratique de l’open data préconise une libre disponibilité pour tous et chacun, sans restriction de copyright, brevets ou d’autres mécanismes de contrôle. » Open Data : où en est-on ? Ce dossier sur les données ouvertes / open data réalisé par Frédéric Ville et coordonné par Romain Mazon s’interroge sur 3 points principaux : En mouvement : le débat se poursuit Favoriser la réutilisation : les citoyens sur le pont Pour en savoir plus Licence :
Eduquer au numérique, les enseignants ne sont pas seuls « Plus de 4000 lieux publics d’accès à l’internet sont ouverts en France, dans lesquels un ou plusieurs animateurs multimédias accompagnent, initient chacun à maîtriser et bien utiliser ces outils et services offerts par internet et plus largement par les technologies de l’information et de la communication.» (Netpublic.fr) Des ressources locales Ces lieux d’accès publics à internet plus communément appelés Espaces Publics Numériques (EPN) sont souvent des lieux financés par les collectivités locales. Ainsi en février les EPN sont invités à proposer des animations en lien avec le programme « Internet plus sur » (Safer Internet Day) destiné à promouvoir une utilisation plus sûre et plus responsable de l’Internet fixe et mobile chez les jeunes. Le numérique pour tous Au-delà de la formation des enfants à un usage maîtrisé des nouvelles technologies, il est primordial que ces notions puissent s’exporter en dehors de l’école.
Une eurodéputée demande à Bruxelles de vérifier la légalité de Facebook En attendant que l'Union européenne révise effectivement la directive 95/46/CE sur la protection des données personnelles, Bruxelles va devoir se pencher sur les règles du réseau social Facebook et s'assurer qu'elles sont bien conformes avec la législation actuelle. L'eurodéputée socialiste Françoise Castex a en effet adressé une question écrite prioritaire en ce sens à la Commission. "Facebook conserve sur le long terme les données de ses utilisateurs sans que ces derniers ne puissent donner leur consentement explicite à cette utilisation de leurs données, contrairement à ce que prévoit la directive européenne sur la protection de la vie privée" note la parlementaire. Une mauvaise habitude prise par le site communautaire et à laquelle l'Union européenne doit mettre un terme. "Pour chaque citoyen européen, garder la maîtrise de ses données personnelles est un droit fondamental.
Vers une fiscalité des données [Info Owni] La mission sur la fiscalité du numérique, dont les conclusions sont attendues mi-décembre, envisage de créer une fiscalité fondée sur les données personnelles. L'idée est simple : plus une boîte ouvre ses données aux utilisateurs, moins elle est taxée. Toutes les entreprises pourraient donc être visées. Une petite bombe. “Les données personnelles sont le nouveau pétrole de l’internet”. Et pourquoi pas aussi le levier d’une nouvelle fiscalité en France ? Coup de tonnerre pour tous ceux qui se frottaient déjà les mains à l’idée de prélever les seuls “GAFA” (Google, Amazon, Facebook et Apple), championnes de l’optimisation fiscale : le projet des deux rapporteurs impliquerait en effet toutes les firmes qui disposent d’informations sur leurs utilisateurs. Une idée originale dans le débat plus connu sous le sobriquet réducteur mais significatif de “Taxe Google” et sur lequel nombre se sont déjà cassés les dents. Fiscalité des données Le tout, sous contrôle de l’utilisateur. e-TVA
The Value of Social Loyalty With most brands just trying to work out how to best use social media, it’s interesting to look at the flip side where social loyalty is now the big focus of the airline industry (look at all the great KLM work), where social loyalty plays will no doubt transform traditional style frequent flyer programs faster than anything we’ll see over the next few years… This infographic looks at the future of social loyalty for the airline industry. SimpliFlying conducted a study on how frequent travellers (who travel at least five times a year) use social media and there are some interesting take outs:
Fiche Libres savoirs, les biens communs de la connaissance Auteur(s) du livre: Ouvrage collectif coordonné par VecamÉditeur: C&F Éditions978-2-915825-06-0Publié en 2011Première rédaction de cet article le 5 novembre 2011 Qu'est-ce qu'il y a de commun entre la paysanne mexicaine qui réclame de pouvoir faire pousser des semences de maïs de son choix, le parisien qui télécharge de manière nonhadopienne un film qu'il ne peut pas acheter légalement, la chercheuse états-unienne qui veut publier ses découvertes sans enrichir un parasite qui vendra très cher le journal scientifique, le programmeur brésilien qui développe du logiciel libre, et l'industriel indien qui veut fabriquer des médicaments moins chers ? Tous veulent pouvoir utiliser librement le savoir issu des communs. Les communs, ce sont tous les biens, matériels ou intellectuels, qui n'ont pas été capturés par des intérêts privés et qui sont gérés ensemble. Cet ouvrage collectif fait le tour de la question pour les communs immatériels, ceux dont l'usage par l'un ne prive de rien les autres.
Web sémantique Web sémantique La majorité du Web est destiné à être lu. Il n'est pas fait pour être manipulé de façon intelligente par des programmes informatiques, en général incapables de caractériser les informations qu’ils parcourent.Le Web sémantique vise à faciliter l'exploitation des données structurées, pour donner du sens au contenu des pages Web, en permettant leur interprétation par des machines. Il ne s’agit pas d’un web à part, mais plutôt d’une extension ou d’une amélioration du Web courant où chaque donnée acquiert un sens défini, afin de créer un réseau d'informations structurées, disponibles en ligne et facilement réutilisables. L’ensemble repose sur des normes, des standards ouverts comme RDF et SPARQL, et des recommandations évitant ainsi redondances, conversions lourdes et permettant la traçabilité des données sources.Les enjeux en bibliothèques sont multiples. Généralités AMAR, Muriel et MENON, Bruno. SUR, Serge, BLOCH, Laurent, BOULLIER, Dominique, et al. BNF. PEYRARD, Sébastien.