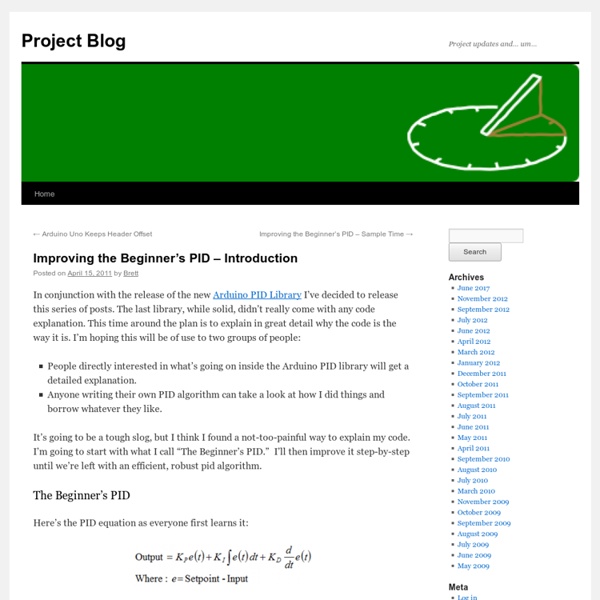
Linear Actuator - PID Control
A linear actuator is a motor that has been geared to extend and contract an arm rather than rotate a shaft. Many applications that use linear actuators require precise position control, but since DC motors can ordinarily only be told how fast to go (on a scale from -100% and 100% duty cycle) you need to program a control system. In order to make a control system, you'll need a linear actuator that has a built-in feedback device such a as a potentiometer. Introduction This application guide is designed to explain the basics of PID control and how to implement a basic control loop using Phidgets. Phidgets The following setup was used to build this application guide: You could use the 1064_1 - PhidgetMotorControl HC instead, but it doesn't have an analog input for the feedback device, so you'd also need to use a device with an analog input and change the program accordingly in this case. PID Control Basics Proportional Control Integral Control Derivative Control Sample Program ActuatorPID Algorithm
Régulation PID, comment la régler 1/2 | rhaaa
Étant donné que je n’ai pas encore tout le matériel nécessaire pour avancer mes autres projets, j’en profite pour approfondir un peu mes connaissances théoriques et vous en fait donc profiter. Mon projet ici est simple : Réguler une température à l’aide d’un microcontrolleur, mais surtout bien comprendre les tenants et aboutissements des différents réglages et algorithmes. L’objectif ici n’est pas tant d’expliquer ce qu’est un PID, ni comment il fonctionne dans le detail, mais plutôt de donner une méthode permettant d’approximer les coefficients du régulateur. Je profiterais de cette expérience pour faire 2 articles : – celui-ci concernant le PID a proprement parler – Un second article concernant ma méthode pour obtenir des courbes « lives » a partir d’un arduino et d’un PC. Qu’es-ce qu’un PID Pour simplifier, on parlera dans la suite de régulation de température, vu que ce sera notre application ici. Formule PID, source ControlGuru Description du materiel Méthode de réglage Définitions Avec:
BEST_PID_POSITION_EXAMPLE
Published by: ober on June 22, 2012. By Kong Wai Weng RH2T Mag, Vol.4, Mar 2010 PID control system is one of the most mature and commonly used control strategies in the industrial for decades thanks to its simple but effective algorithm. In this article, we will discuss the basic concept of PID controller and how to implement it in the embedded system. Introduction Closed loop control system is an essential topic for embedded systems, bringing together actuators and sensors with the control algorithm in software. Besides speed control, PID control system can also be used to control other parameters such as position, temperature, water level, stability, etc. The Problem – DC Motor Position Control. Before we begin to design a PID controller, we need to understand the problem. We want to move the output shaft of the motor from current position to target position There are a few terms commonly used to describe the PID control loops, such as: The Hardware – PR24 The Implementation of PID Controller
Implémenter un PID sans faire de calculs ! » Sciences et Techniques
Sur beaucoup de site sur le web, lorsque l'on trouve un article parlant de la régulation PID, on se heurte souvent à des fonctions de transfert et à des équations dans le domaine de Laplace. Alors implémenter un PID est-il impossible sans avoir une base solide en mathématiques ? Heureusement non, loin de là. Outre l'approche mathématiques, le PID peut très bien s'expliquer de façon intuitive "avec les mains". Le but de cet article est justement d'essayer d'expliquer comment marche une régulation PID sans entrer dans les calculs ni sans utiliser les fonctions de transfert du système et autres équations quelque peu cabalistiques pour les non-initiés. Imaginez que vous conduisez votre voiture sur l'autoroute et que vous souhaitez stabiliser votre vitesse à 130 km/h pil-poil ! Règle 1 : Avec cette méthode, pas de problème. Règle 2 : C'est alors que vous vous dites : " Zut ! Règle 3 : Arrivé à 130km/h, vous vous dites : " ça y est, j'y suis ! Le régulateur proportionnel (P : première règle)
PID EQUATIONS IN A SINGLE PICTURE
PID Theory Explained
1. Control System The basic idea behind a PID controller is to read a sensor, then compute the desired actuator output by calculating proportional, integral, and derivative responses and summing those three components to compute the output. Before we start to define the parameters of a PID controller, we shall see what a closed loop system is and some of the terminologies associated with it. Closed Loop System In a typical control system, the process variable is the system parameter that needs to be controlled, such as temperature (ºC), pressure (psi), or flow rate (liters/minute). In many cases, the actuator output is not the only signal that has an effect on the system. Figure 1: Block diagram of a typical closed loop system. Defintion of Terminlogies The control design process begins by defining the performance requirements. Figure 2: Response of a typical PID closed loop system. Some systems exhibit an undesirable behavior called deadtime. Back to Top 2. 3. Table 1. 4. [+] Enlarge Image
AN_IDIOT'S_GUIDE_TO_PID_ALGORITHM
PID_CAR_EXAMPLE_FOR_POSITION_FEEDBACK
PID_SPING_EXAMPLE_FOR_FORCE_FEEDBACK
A_GOOD_EXPLANATION_ABOUT_PID