PHP Programming
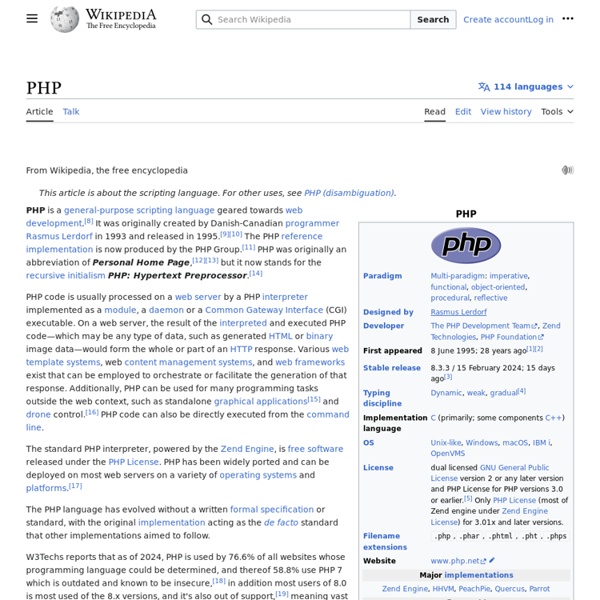
PHP is a scripting language designed to fill the gap between SSI (Server Side Includes) and Perl, intended for the web environment. Its principal application is the implementation of web pages having dynamic content. PHP has gained quite a following in recent times, and it is one of the frontrunners in the Open Source software movement. Its popularity derives from its C-like syntax, and its simplicity. PHP is currently divided into two major versions: PHP 4 and PHP 5, although PHP 4 is deprecated and is no longer developed or supplied with critical bug fixes. If you've ever been to a website that prompts you to login, you've probably encountered a server-side scripting language. Basically, PHP allows a static webpage to become dynamic. Before you embark on the wonderful journey of Server Side Processing, it is recommended that you have a basic understanding of the HyperText Markup Language. Setup and Installation Note: Before contributing, check out the discussion page. The Basics
Web application framework
History[edit] Around the same time, full integrated server/language development environments first emerged, such as WebBase and new languages specifically for use in the web started to emerge, such as ColdFusion, PHP and Active Server Pages. Types of framework architectures[edit] Most web application frameworks are based on the model–view–controller (MVC) pattern. Model–view–controller (MVC)[edit] Push-based vs. pull-based[edit] Three-tier organization[edit] In three-tier organization, applications are structured around three physical tiers: client, application, and database.[7][8][9][10] The database is normally an RDBMS. Framework applications[edit] General-purpose website frameworks[edit] For example, Zend Framework. Discussion forums, wikis and weblogs[edit] For example, WikiBase/WikiWikiWeb. Organizational portals[edit] For example, JBoss Portal or eXo Platform. Content management systems (CMS)[edit] Features[edit] Web template system[edit] Caching[edit] Security[edit] Scaffolding[edit] Ajax[edit]
2012-07-16 - Absolute Beginners Guide to Drupal
Bash
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Bash may refer to:
VsPhp
This page was copied mindlessly from (Google Cache) Common Ground Both PHP and Python: are interpreted, high level languages with dynamic typing are OpenSource (except where various Zend products, recommended by some, are employed) are supported by large developer communities are easy to learn (compared to C++, Perl) are easy to extend in C, C++ and Java are extremely portable. They run on almost all platforms in existence without recompilation. support for variable number of function arguments. have the ability to freeze live objects in a string representation (for storing arbitrary objects on disk, moving them over the network, etc); they can then be converted back to identical objects with data intact. Compared as Languages What strengths do PHP have that Python doesn't? What weaknesses does PHP have that Python doesn't? (more verbose) syntax from C/C++ and Perl, with lots curly braces and dollar signs and "->"-s confused tableau of function names.
Web content management system
A web content management system (WCMS)[1] is a software system that provides website authoring, collaboration, and administration tools designed to allow users with little knowledge of web programming languages or markup languages to create and manage website content with relative ease. A robust WCMS provides the foundation for collaboration, offering users the ability to manage documents and output for multiple author editing and participation. Most systems use a content repository or a database to store page content, metadata, and other information assets that might be needed by the system. Administration is also typically done through browser-based interfaces, but some systems require the use of a fat client. A WCMS allows non-technical users to make changes to a website with little training. Capabilities[edit] Automated templates Access control Some WCMS systems support user groups. Scalable expansion Easily editable content Scalable feature sets Web standards upgrades Workflow management
CMS comparison - WordPress vs Joomla vs Drupal / WebsiteSetup.org
If you’re thinking about building a website or blog, you should consider using one of the best CMS available in the market. A CMS (content management system) helps you create, manage, and modify the contents of your website without the need for any HTML or CSS coding skills. The easy-to-use nature of the modern CMS platforms means that anyone can build themselves a great-looking website all on their own. You don’t need to be a web developer, a designer, or have any previous experience with website building either. In this post, we look through three of the most popular and best CMS platforms coming into 2020, compare their pros and cons, and help you pick one. The three best CMS that we’re looking into are: WordPressJoomlaDrupal Here’s everything you need to know about them: 1. Talking about the costs involved in using any of these CMS gets real tricky real fast. These side costs involve chiefly two things: a domain name and web hosting. A domain name is your website’s address on the web. 2.
authentication - ubuntu - how can I avoid typing a password on every admin action