

211.167.103.141:82/1Q2W3E4R5T6Y7U8I9O0P1Z2X3C4V5B/nd.edu/~manufact/MPEM pdf_files/Ch02.pdf.
Fatigue limit. Representative curves of applied stress vs number of cycles for steel (in blue and showing an endurance limit) and aluminium (in red and showing no such limit).
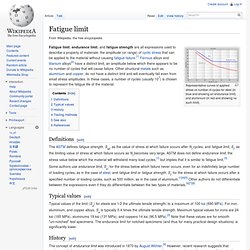
Definitions[edit] The ASTM defines fatigue strength, SNf, as the value of stress at which failure occurs after Nf cycles, and fatigue limit, Sf, as the limiting value of stress at which failure occurs as Nf becomes very large. ASTM does not define endurance limit, the stress value below which the material will withstand many load cycles,[1] but implies that it is similar to fatigue limit.[3] Typical values[edit] History[edit] The concept of endurance limit was introduced in 1870 by August Wöhler.[9] However, recent research suggests that endurance limits do not actually exist, that if enough stress cycles are performed, even the smallest stress will eventually produce fatigue failure.[5][10] Testing methods[edit] Tension-compression testing : Samples are repeatedly switched between a tensile and a compressive load.
BendingTorsional. Index file for a HTML Fatigue database. Search - eBooks & Audio Books Online Library.
HVAC Design Tools, Heating And Air Conditioning, TRACE™ 700 - Analysis Software - Analysis Tools. Release notes Release 6.3 Release 6.3 Release 6.2 [Version 6.3.0] 9/6/2013 This update contains the following items: Added LEED Guide, a step-by-step guide on modeling for LEED V3.Added baseline building creator, a one-step process for building a minimally compliant building, according to Appendix G 90.1-2007.Added ASHRAE 90.1-2007 Appendix G baseline systems.
Back to top [Version 6.2.10] 2/28/2013 This update contains the following items: Back to top [Version 6.2.9] 10/3/2012 This update contains the following items: Added kWh/Ton-hr metric to the economic summary report. Back to top [Version 6.2.8] 3/30/2012 This update contains the following items: Back to top [Version 6.2.7] 7/8/2011 This update contains the following items: Back to top [Version 6.2.6.5] 10/05/2010 Back to top [Version 6.2.6] 9/1/2010 The Fuel Source and Reject Condenser Heat to Reference Type fields have been updated to Heating Plant and Heat Rejection Equipment, respectively for:
Nastran. FEM kurz und bündig. Die Finite Elemente Methode (FEM), bzw.

Finite Elemente Analyse (FEA), ist ein numerisches Verfahren zur Lösung komplexer Berechnungen und findet überwiegend im Ingenieurwesen Anwendung. Das häufigste Einsatzgebiet ist der rechnerische Nachweis von Neukonstruktionen. Mittels einer FEM Berechnung kann an virtuellen Prototypen auf einem Computer überprüft werden, ob die Anforderungen hinsichtlich der physikalischen Eigenschaften erfüllt sind. Somit können mögliche Schwachstellen bereits frühzeitig in der Entwicklungs- bzw. Konstruktionsphase erkannt und eliminiert werden. Mittels FEM Analysen kann eine Vielzahl von physikalischen Aufgabenstellungen berechnet werden. Lineare/nichtlineare StatikEigenwertprobleme (Eigenfrequenzen, Modalanalysen)Temperaturfeldberechnungendynamisches Antwortverhalten im Zeit- und FrequenzbereichErdbebensimulationenRotordynamikStabilitätsuntersuchungenStrömungssimulationLebensdaueranalysenTopologieoptimierung Die Ursprünge der FEM reichen bis in das 19.
Opting for Optimization, Part 1 by Desktop Engineering. Introduction to Finite Element Analysis. Introduction to Finite Element Analysis A Brief History Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was first developed in 1943 by R.
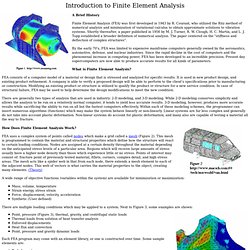
Courant, who utilized the Ritz method of numerical analysis and minimization of variational calculus to obtain approximate solutions to vibration systems. Shortly thereafter, a paper published in 1956 by M. J. By the early 70's, FEA was limited to expensive mainframe computers generally owned by the aeronautics, automotive, defense, and nuclear industries. What is Finite Element Analysis? FEA consists of a computer model of a material or design that is stressed and analyzed for specific results. There are generally two types of analysis that are used in industry: 2-D modeling, and 3-D modeling. How Does Finite Element Analysis Work? FEA uses a complex system of points called nodes which make a grid called a mesh (Figure 2). A wide range of objective functions (variables within the system) are available for minimization or maximization: Types of Engineering Analysis.
FRACTURE. Introduction to Finite Element Analysis.