

The Fantastical World of Parasites- The Beginners Guide to Identifyin… Uwaga na pasożyty! Dla hodowcy drobiu ogromnym problemem mogą się okazać choroby pasożytnicze.
Liczba gatunków pasożytniczych mogących żyć na drobiu jest ogromna. Straty spowodowane pasożytami mogą być tym samym bardzo duże. Pasożyty są przyczyną występowania wielu chorób, pogarszają w dużej mierze wyniki produkcyjne i w konsekwencji mogą powodować upadki ptaków. Opracowano szereg różnych programów zwalczania pasożytów i wiele preparatów do przeciwdziałania i zapobiegania inwazjom. W nowoczesnych fermach drobiarskich należałoby oczekiwać jedynie inwazji nielicznych gatunków pasożytów. Charakterystyka wybranych pasożytów zewnętrznych Ptaszyniec kurzy (Dermanyssus gallinae)Ptaszyniec kurzy jest bardzo szkodliwym i dokuczliwym pasożytem zewnętrznym drobiu.
Cały cykl rozwojowy ptaszyńca w sprzyjających warunkach trwa ok. 7 dni. Świerzbowiec ptasi (Cnemidocoptes mutans)Knemidokoptozę, czyli świerzb wywołują różne gatunki świerzbowców, lecz najczęściej jest to Cnemidocoptes mutans. Bartosz Korytkowski Bydgoszcz. PowerPoint Presentation - FKH UNAIR by ewghwehws. Bird Vet Melbourne. Intestinal rupture caused by a heavy round worm (ascarid) infestation Worms in Birds: Roundworms, tapeworms, gizzard worms, gape worms Common worm parasites in pet birds include roundworms (e.g.
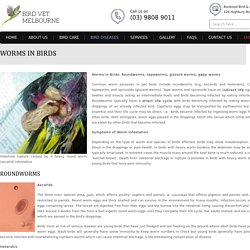
Ascarids and Heterakis), Capillaria, strongyles, tapeworms and spiruroids (gizzard worms). Tape worms and spiruroids have an indirect life cycle with a variety of beetles and insects acting as intermediate hosts and birds becoming infected by eating infected beetles or insects. Roundworms typically have a direct life cycle with birds becoming infected by eating worm eggs passed in the droppings of an already infected bird. Symptoms of Worm Infestation Depending on the type of worm and species of birds affected, birds may show malabsorption, diarrhoea, vomiting, blood in the droppings or poor health. Ascarids The three main species areA. galli, which affects poultry, pigeons and parrots, A. columbae that affects pigeons and parrots and A. platyceri, which is restricted to parrots. Heterakis Tapeworms. Tuberculosis in Birds: Insights into the Mycobacterium avium Infections.
LARYNGOTRACHEITIS - Diseases of Poultry. 232.Laryngotracheitis (LT) is a viral infection in hens, pheasants and peacocks characterized by catarrhal haemorrhagic to fibrinous inflammation of the respiratory tract.
It is manifested in laryngotracheal and conjunctival form. In the laryngotracheal form, suffocation, rales and cough are observed. The head and the neck are strongly extended forward and upward during inspiration. 233.mucous coats of the larynx and the trachea are catarrhally haemorrhagically to fibrinously inflamed. Most outbreaks are encountered between the age of 4 and 14 weeks although the disease affects fowl of any age. 234.Haemorrhagic laryngotracheitis. Poultrydiseases.pdf.
Candidiasis. Overview of Candidiasis in Poultry: Candidiasis: Merck Veterinary Manual. Candidiasis is a mycotic disease of the digestive tract of various avian species, including chickens, turkeys, and quail caused by Candida albicans.
It commonly develops after use of therapeutic levels of various antibiotics or when using unsanitary drinking facilities. Lesions are most frequently found in the crop and consist of thickened mucosa and whitish, raised pseudomembranes. The same lesions may be seen in the mouth and esophagus. Occasionally, shallow ulcers and sloughing of necrotic epithelium may be present. HISTOMONOSIS - Diseases of Poultry. 362..
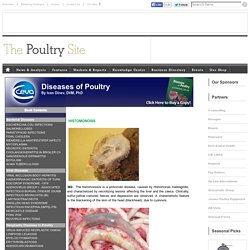
The histomonosis is a protozoan disease, caused by Histomonas meleagridis, and characterized by necrotizing lesions affecting the liver and the caeca. Clinically, sulfur-yellow coloured faeces and depression are observed. A characteristic feature is the blackening of the skin of the head (blackhead), due to cyanosis. 363.Pathoanatomically, bi¬lateral enlargement of caeca with thickening of walls is observed. The aetiological agent is Histomonas meleagridis, a polymorphic flagellate that is present as flagellate in caeca and as amoeba in tissues. 364.Often, the occurring typhlitis is the cause for adhesive peritonitis. 365.Susceptible species are turkeys, chickens, pheasants, rock partridges, guinea fowl, and geese. 366.. 367.In older cases, crusts of dense caseous masses are formed into the carca that thicken this intestinal wall and reduce the lumen (top right: transverse cross section through caeca.)
NADIS - National Animal Disease Information Service. By John Dalton BVMS MRCVS Many of the diseases that cause problems on the rearing field continue into the release pen period.
Additional comment is made on these when necessary Ascarid worms Described in detail in part 4 - the rearing field. Aspergillosis. Domestic Poultry Diseases. In this section there is a list of the more common diseases of domestic poultry together with notes on notifiable diseases (diseases that must be notified to the authorities) ASPERGILLOSIS Caused by the inhalation of fungal spores.
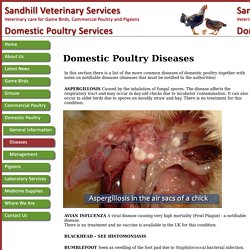
The disease affects the respiratory tract and may occur in day-old chicks due to incubator contamination. It can also occur in older birds due to spores on mouldy straw and hay.