

Atomic Emission Spectra - the Origin of Spectral Lines. By the early 1900s, scientists had made the following observations: When a sample of gaseous atoms of an element at low pressure is subjected to an input of energy, such as from an electric discharge, the atoms are themselves found to emit electromagnetic radiation.On passing through a very thin slit and then through a prism the light (electromagnetic radiation) emitted by the excited atoms is separated into its component frequencies.

The familiar dispersion of white light is illustrated below: Electromagnetic Spectrum - Introduction. The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation.
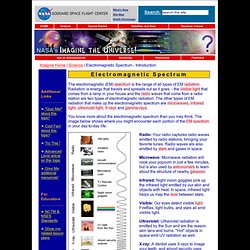
Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in your house and the radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. The other types of EM radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays and gamma-rays. High School Chemistry/Light and the Atomic Spectra. We now know how light can act as a wave or a particle, depending on the situation.
You might wonder, though, why a chemistry textbook would waste a whole lesson on light. Light, like matter, is part of the universe, but chemists aren't responsible for studying the entire universe.