

Nucleus Accumbens Deep Brain Stimulation Produces Region-Specific Alterations in Local Field Potential Oscillations and Evoked Responses In Vivo. Abstract Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens (NAC) region is an effective therapeutic avenue for several psychiatric disorders that are not responsive to traditional treatment strategies.

Nonetheless, the mechanisms by which DBS achieves therapeutic effects remain unclear. A Microsaccadic Rhythm Modulates Gamma-Band Synchronization and Behavior. Conrado A. Bosman 1 , Thilo Womelsdorf 1 , Robert Desimone 2 , 3 , and Pascal Fries 1 + Author Affiliations Correspondence should be addressed to Dr. Top-down and bottom-up design. Top-down and bottom-up are both strategies of information processing and knowledge ordering, used in a variety of fields including software, humanistic and scientific theories (see systemics), and management and organization.
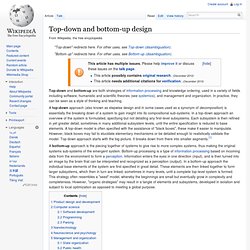
In practice, they can be seen as a style of thinking and teaching. A top-down approach (also known as stepwise design and in some cases used as a synonym of decomposition) is essentially the breaking down of a system to gain insight into its compositional sub-systems. In a top-down approach an overview of the system is formulated, specifying but not detailing any first-level subsystems. Each subsystem is then refined in yet greater detail, sometimes in many additional subsystem levels, until the entire specification is reduced to base elements. A top-down model is often specified with the assistance of "black boxes", these make it easier to manipulate. Product design and development[edit] Computer science[edit] Software development[edit] Programming[edit] Parsing[edit] Event Related Potentials (ERP) Laboratory - Brain and Language Lab. Electroencephalography/Event Related Potentials (EEG/ERP) Laboratory The method of event-related brain potentials Event-related brain potentials (ERPs) are a non-invasive method of measuring brain activity during cognitive processing.

The transient electric potential shifts (so-called ERP components) are time-locked to the stimulus onset (e.g., the presentation of a word, a sound, or an image). Each component reflects brain activation associated with one or more mental operations. In contrast to behavioral measures such as error rates and response times, ERPs are characterized by simultaneous multi-dimensional online measures of polarity (negative or positive potentials), amplitude, latency, and scalp distribution. The methodological advantages of ERPs have resulted in an ever increasing number of ERP studies in cognitive neuroscience, cognitive psychology, psycholinguistics, neurolinguistics, neuropsychology and neurology.
The Georgetown EEG/ERP Laboratory. TOPDOWN. So far, we have concentrated in this unit on what is called bottom-up processing (also known as data-driven processing ).

In bottom-up or data-driven processing, what happens is a little bit like the Pandaemonium model we looked at in class. That is, the outside data drive the system. Sensory inputs get registered onto a sensory memory, and then are processed at higher and higher levels until a match is finally found with something in long-term memory. So, again using Pandaemonium as an example, light hits the rods and cones in the retina (the image demons ).
At the next level up, these data are automatically analyzed in terms of features (the feature demons). But there is another pathway that is very important in perception and pattern recognition. To see how this might operate, let’s look at a modified version of the Pandaemonium model. Now, this isn’t the only way for top-down processing to operate, but it certainly should give you a feel for what should happen in these cases. Binaural Beats - Sound Example. As discussed in the context of Figure 5-5 of "Auditory Neuroscience" (reproduced here below) ITD cues for sound location are derived from the interaural phase.
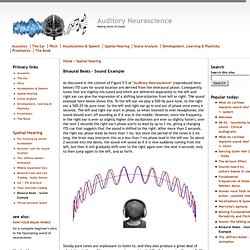
Conequently, tones that are slightly mis-tuned and which are delivered separately to the left and right ear can give the impression of a shifting lateralization from left or right. THe sound example here below shows this. To the left ear we play a 500 Hz pure tone, to the right ear a 500.25 Hz pure tone. So the left and right ear go in and out of phase once every 4 seconds. The left and right ear start in phase, so when listened to over headphones, the sound should start off sounding as if it was in the middle.
Steady pure tones are unpleasant to listen to, and they also produce a great deal of adaptation in the auditory nervous system, making it difficult to perceive them well. This demo is designed to be listened to over stereo headphones. Neuro-Programmer 3 - Innovative Brainwave Entrainment Software. How does NP3 work?
It’s surprising science, but thanks to modern equipment it’s easy to prove that this works because we can watch it happening on an EEG. And over 80 years of scientific investigation have revealed many useful applications for this method, which are being widely used today.5 Neuro-Programmer 3 takes advantage of the latest research in this field to deliver the most effective neural stimulation experience. Benefits Inspired and informed by the best practices and research in the fields of psychology, neurology, and audio-visual stimulation studies, Neuro-Programmer 3 is a software application with unlimited potential and broad capabilities.
Although it is incredibly simple to use, it’s also one of the most effective tools for positive mental change that you’ll ever find. 1. Back to the top.