


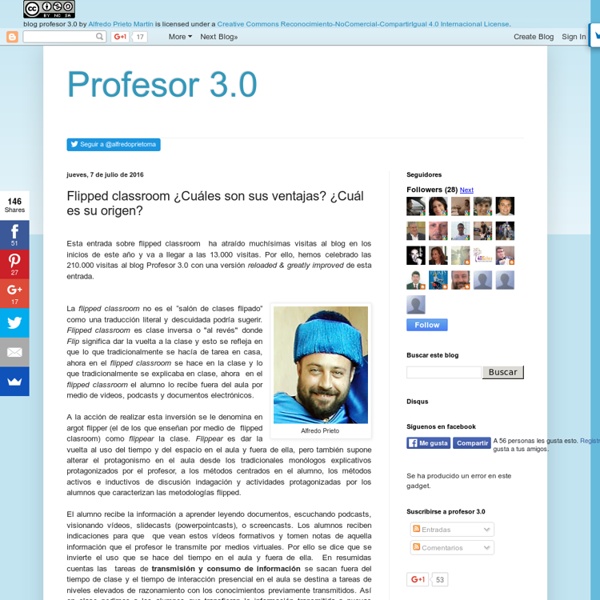
Cómo aplicar la pedagogía inversa o flipped classroom en diez pasos La pedagogía inversa o flipped classroom es un nuevo método que propone dar la vuelta a la clase tradicional e invertir el orden en el proceso de aprendizaje. Frente al modelo de enseñanza habitual, donde el profesor explica la lección en clase y los alumnos escuchan y realizan los deberes en su casa, la flipped classroom concede a los alumnos la responsabilidad de revisar los contenidos teóricos en casa, para que luego puedan resolver sus dudas y trabajar los conceptos en clase de forma individual o colaborativa. Esta metodología tiene muchas ventajas. Te mostramos cómo aplicarla en el aula mediante un sencillo video tutorial. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Descarga en PDF la infografía “Flipped Classroom dentro y fuera del aula” ¿Qué te parece esta metodología? ¡Comparte en redes sociales este artículo!
Uso de dispositivos móviles en la evaluación formativa a coste cero en el flipped learning forte. Socrative para profesores dummies Hace unos años se desarrrolló en universidades de Estados Unidos lo que allí llamaban el "clickerism". El uso de "clickers" (mandos de respuesta a distancia personales) para realizar evaluación formativa en clase y fomentar las discusiones en clase. Aquí en España, tan retrasados en educación como siempre, este movimiento educativo innovador casi no llego a conocerse. Los clickers eran muy costosos y sólo selectos departamentos podían permitírselos. Ahora gracias a las posibilidades del BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) la situación ha cambiado radicalmente porque se han desarrollado Apps como Mentimeter, Socrative, Kahoot o Quizizz que permiten usar los smartphones de los alumnos como sistemas de respuesta personales con coste cero para la institución (salvo tener Acceso wifi a Internet en las aulas). Es más, la evaluación formativa no solo tiene efectos muy positivos en la retención a largo plazo sino que también estimula el estudio de manera muy eficaz.
IPad = Flipped Classroom Made Easy | IPAD 4 SCHOOLS Yes, the Flipped Classroom (Video lessons watched before class time) is a fashionable topic but whilst there’s still chalk-and-talk together with standardised testing I feel I must continue to push it. And no, it’s not just chalk-and-talk in disguise. It creates a whole new learning environment for the student. I haven’t taught a whole class for 6 months! All my teaching is now one-to-one and not surprisingly, my grades are soaring. In the classroom I only teach individual students the specific points they highlight as unclear after watching the video lesson and I monitor progress on the projects they’ve designed to prove understanding of the content. Flipping my classroom has changed my career. Why should all teachers flip their classroom? Online videos should replace all whole-class teaching because: So here’s my workflow for those who are interested 1. 2. 3. STEP 1: Online Account setup STEP 2: Recording a lesson Now open the Explain Everything app. STEP 3: Uploading the lesson Like this:
Consejos prácticos sobre cómo implementar el flipped classroom El proceso de implementación de un nuevo modelo de aprendizaje requiere superar obstáculos y desarrollar habilidades. La preparación para el proceso de implementación debe permitir que el profesor pueda anticipar los obstáculos y ejercitar las habilidades que más necesitará para instaurar una sistema de aprendizaje inverso. Para comprender la serie de habilidades que el profesor necesitará experimentar y desarrollar para implantar un modelo de enseñanza inversa es conveniente que los profesores candidatos a implementar el flipped exploren los siguientes recursos: El flipped tiene un gran impacto sobre el proceso de enseñanza –aprendizaje y sobre la mejora de los resultados de aprendizaje. • Recursos a explorar: ¿Qué os podemos garantizar si aplicáis las metodologías propuestas para invertir vuestras asignaturas? Debéis hacer caso a nuestros consejos y motivar a vuestros alumnos para que se tomen en serio el estudio previo de los temas. La carga de trabajo para el profesor
How to flip the classroom | Flipped Institute Flipping is easy – and with a little thought and planning, teachers can use the flipped model to create engaging learning experiences for their students. This section covers the nuts and bolts of flipping – from creating videos, to introducing the flipped concept, to practical ideas for using class time differently. What are teachers saying? As an English teacher, I have several teaching concepts going at once, so flipping works well for me. I may have kids watch a lesson at home to learn about literary devices in a book we are reading in class. Then the next day, they can point them out to me as we read. The flipped classroom is about making sure that the "voice" most often heard in the classroom is that of the student, not the teacher.
Examples of Videos / Videos Looking for examples of flipped videos, or wish to share yours? If you are willing to share an example or two of your videos with others, please fill out this Google form. If you are looking for examples of teacher or student-created videos, check out this list of samples to get an idea of how you may wish to curate or create your own. A Sample of Videos on Flipped Learning Just a Few Videos about Flipped Learning Subject Specific Videos Math Science English Language Arts Cultivating Independent Thinkers Through Flipped Learning (3:23, Gudenrath)Grade 5 Language Arts – Singular and Plural Possessive (5:35, Highfill)Reading is Thinking: Nothing to Do (Video and writing assignment) (4:04 & 1:59, Highfill)Plot Structure at the IMA (7:08, Cockrum)Creating Interesting Characters in a Story (6:44, Cockrum)Reading Genres—Types of Biographies (3:39, Cockrum, student made) Social StudiesEarly Greek Civilization (7:55, Driscoll) Judaism: Core Beliefs and Practices (5:44, Driscoll) Faculty Meetings
Scaling Flipped Learning Part 1: Technology Strategy – Flipped Learning Simplified A 2014 study indicates that 46% of U.S. principals expect that new teachers to the profession should already know how to flip a class upon graduation from a teacher training program. There is also a growing body of research which demonstrates that flipped learning is showing significant growth in student achievement, satisfaction, and teacher satisfaction. As schools begin to implement the model, what kinds and type of support should school leaders provide? This past year I worked with a group of teachers from a variety of schools which was implementing flipped learning into their classes. I was with them three to four times during the year and got to know their successes and challenges. Several of them had great results and are saying they can never go back. I have pondered their situation and have come to the conclusion that we need a more systemic approach to flipped learning. Technology Technology infrastructure matters. Integration Video Creation Video Hosting Workflows
Scaling Flipped Learning Part 2: Shifting Pedagogy – Flipped Learning Simplified Individual teachers across the world who are flipping their classes, are often working in isolation and small pockets. However, as the movement has grown, there is an increasing need to think systemically about how to scale flipped learning. I believe three systems need to change for flipped learning to flourish on a large scale in a school or district: technological systems, pedagogical systems, and evaluation methodologies. Good practice encourages student-teacher contact.Good practice encourages cooperation among students.Good practice encourages active learning.Good practice gives prompt feedback.Good practice emphasizes time on task.Good practice communicates high expectations.Good practice respects diverse talents and ways of knowing. Ms. So how can schools and systems scale flipped learning from the perspective of pedagogy? Mindset Change – For a large scale adoption of flipped learning to occur, teachers must believe that active learning is superior to passive learning.
Scaling Flipped Learning Part 3: Teacher Evaluation – Flipped Learning Simplified As more and more schools adopt flipped learning on a larger scale, there is a need to think systemically about evaluation systems. This is the third in a series on how to scale flipped learning. In the first post I discussed technological systems, in the second I discussed pedagogical systems, and in this post, I will explore how evaluation systems need to change when flipped learning is scaled. During my twenty-four years as a classroom teacher, I was evaluated many times by administrators. The vast majority of these evaluations consisted of the principal sitting in my class and watching me “teach.” He or she took notes, plugged the information into a rubric, and then later we sat down and discussed how things went. But then I flipped my class, and direct content delivery happened outside of class. During my second year of flipping my class, I was up for a review. As a school expands flipped learning, it is imperative that the evaluation systems get redrawn. Chime in.
Scaling Flipped Learning Part 4: Learning Spaces – Flipped Learning Simplified “We don’t just want to flip classes; we want to flip schools.” Ignacio Romero, MT Groupo, Spain This sentiment expressed by Ignacio resounds with me. One of the greatest strengths of flipped learning has been its grassroots nature. It started with teachers trying to do what was best for their students and has grown into a worldwide movement. However, often individual teachers struggle to implement the model because their schools have not thought systemically about implementation. Prior to flipping my class, students faced the front of the room. on the screen and a whiteboard. As I realized that the focus of the room was no longer on teaching, but rather learning, I rethought many things. Rearrange Your Furniture First, I simply rearranged the furniture. Interactive Whiteboards After about a year of flipping my class, I received a grant for a SmartBoard. Analog Whiteboards Purchase Collaborative Furniture Provide Quiet Spaces in a Noisy Room this is usually very cost prohibitive. You Chime In
Scaling flipped learning Part 5: Student Buy-In – Flipped Learning Simplified As flipped learning continues to grow, there is a greater need for flipped learning to scale beyond individual teachers flipping, to larger roll-outs with systemic planning and leadership. This post is the 5th out of 7 in a series. The previous posts were:• Part 1: Scaling Flipped Learning: Technological Needs at Scale• Part 2: Scaling Flipped Learning: Pedagogical Needs at Scale• Part 3: Scaling Flipped Learning: Changing Evaluation Systems• Part 4: Scaling Flipped Learning: Learning Spaces • Part 5: Scaling Flipped Learning: Student Buy-In • Part 6: Scaling Flipped Learning: Parent Buy-In (Not yet published) • Part 7: Scaling Flipped Learning: Teacher Buy-In (Not yet published) Many teachers make the assumption that all students will embrace flipped learning quickly. How do you help students to embrace flipped learning? Share with Students the Benefits of Flipped Learning This past year I worked with a school in Australia that wanted to scale flipped learning.
Scaling Flipped Learning Part 6: Parent Buy-In – Flipped Learning Simplified As flipped learning continues to grow, there is a greater need for flipped learning to scale beyond individual teachers flipping, to larger roll-outs with systemic planning and leadership. This post is the 6th out of 7 in a series. The previous posts were: Sometimes students don’t always communicate with their parent’s accurate information about what is happening in school. If a child is struggling in class, they often look for something/someone to blame. Creative Communication Strategies Flip Your Back to School Night Have teachers flip back to school night (curriculum night) by creating short videos for parents to watch before the event. Host a Traditional Meeting I worked with a school whi ch embraced flipped learning, and they set up a series of meetings with parents. Flip Community-School Meetings School leaders often meet with parents and community leaders. Letters/Email/Newsletters Home What Message Should You Send in these Communications? Greater Interaction Active Learning