


How Plenary works Time for discussion before taking a decision A parliamentary report put to the vote in plenary is generally the subject of a debate in which the Commission, the representatives of the political groups and individual MEPs express their views. Speaking time per person, often very short, depends on the number of Members who have asked for the floor. Unlike the voting, which is sometimes held at a very rapid pace, the debates can last for several hours, depending on the number of Members who wish to speak. They usually speak in their own language, and what they say is interpreted simultaneously by the interpreters into the other official EU languages. Speaking time in the Chamber is allocated according to the following criteria: a first fraction of speaking time is divided equally amongst all the political groups, then a further fraction is divided among the groups in proportion to the total number of their members. 12 noon: the voting marathon Votes are generally held around midday.
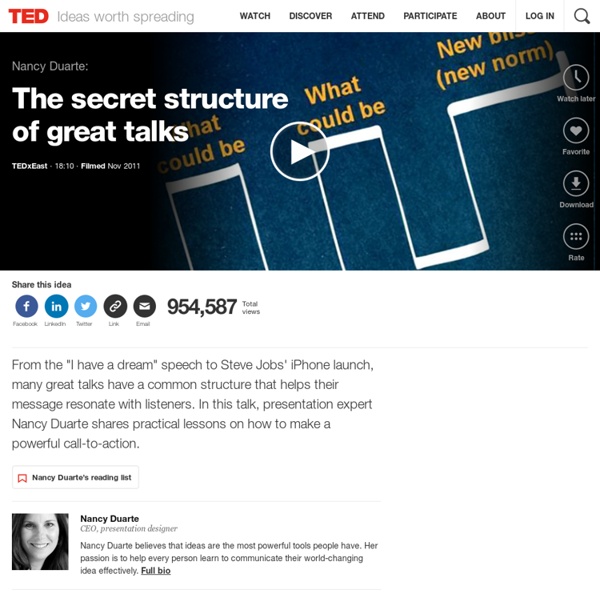
Structure Your Presentation Like a Story - Nancy Duarte by Nancy Duarte | 8:00 AM October 31, 2012 After studying hundreds of speeches, I’ve found that the most effective presenters use the same techniques as great storytellers: By reminding people of the status quo and then revealing the path to a better way, they set up a conflict that needs to be resolved. That tension helps them persuade the audience to adopt a new mindset or behave differently — to move from what is to what could be. And by following Aristotle’s three-part story structure (beginning, middle, end), they create a message that’s easy to digest, remember, and retell. Here’s how it looks when you chart it out: And here’s how to do it in your own presentations. Craft the Beginning Start by describing life as the audience knows it. After you set that baseline of what is, introduce your vision of what could be. What is: We fell short of our Q3 financial goals partly because we’re understaffed and everyone’s spread too thin. Let’s go back to that Q3 update.
Vienna Philharmonic Symphonic orchestra The Vienna Philharmonic (VPO; German: Wiener Philharmoniker), founded in 1842, is an orchestra considered to be one of the finest in the world.[1][2][3] The Vienna Philharmonic is based at the Musikverein in Vienna, Austria. Its members are selected from the orchestra of the Vienna State Opera. Selection involves a lengthy process, with each musician demonstrating his capability for a minimum of three years' performance for the opera and ballet. After this probationary period, the musician may request an application for a position in the orchestra from the Vienna Philharmonic's board. History[edit] Precursors and formation[edit] Nicolai and the orchestra gave only 11 concerts in the ensuing five years, and when Nicolai left Vienna in 1847, the orchestra nearly folded (New Grove notes the disruption caused by the Revolution of 1848 as a hindrance). The era of subscription conductors: 1860–1933[edit] Vienna Philharmonic at the rehearsal, Felix Weingartner is conducting.
How we work You may already have seen or heard interpreters at work whispering for heads of state or interpreting in sound-proof booths at large international conferences. The ability to interpret is a skill many claim but few truly possess. Consider the process of interpretation: the interpreter listens to the speaker, understands the message and converts it into another language, speaks to the delegates and all the while monitors his output to ensure elegant delivery. What are the processes involved? Interpreting is a constant to-ing and fro-ing between different ways of thinking and cultural universes. Conference interpreters usually work in a team put together for a specific conference according to the event's working languages. Today, interpreters spend most of their time performing simultaneous interpretation. The majority of professional conference interpreters now have more than two working languages - on average, AIIC interpreters have 3, 4. Modes of Interpretation Simultaneous Consecutive
Organization & Preparation Tips | Garr Reynolds Official Site Before you even open up PowerPoint, sit down and really think about the day of your presentation. What is the real purpose of your talk? Why is it that you were asked to speak? What does the audience expect? Before you begin to formulate the content of your presentation, you need to ask yourself many basic questions with an eye to becoming the best possible presenter for that particular audience. Who is the audience? What are their backgrounds? What is the purpose of the event? Is it to inspire? Why were you asked to speak? What are their expectations of you? Where is it? Find out everything you can about the location and logistics of the venue. When is it? Do you have enough time to prepare? No matter how great your delivery, or how professional and beautiful your supporting visuals, if your presentation is not based on solid content, you can not succeed. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that in order for your audience to understand anything, you must tell them everything.
businessinsider Tim Dorr via Flickr How do you get people interested in you when you only have 30 seconds? Whether you're in a job interview, networking at a cocktail party, or happen to run into Warren Buffett in the elevator, quickly persuading others to think you're the most interesting person they'll meet is no easy task. "Most people can't present what they've done effectively," Paul McDonald, a senior executive director at staffing firm Robert Half, told Business Insider. Below, McDonald shares eight steps to crafting the perfect elevator pitch. This is an update of an article originally written by Vivian Giang. 2. After studying your résumé and LinkedIn profile, write down four bullet points that explain why you're great, said McDonald. Discuss your work history, background, skills, accomplishments, and goals. 3. People love stories, McDonald said, so tell them a story.
The amazing brains of the real-time interpreters One morning this summer I paid a visit to the sole United Nations agency in London. The headquarters of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) sits on the southern bank of the Thames, a short distance upstream from the Houses of Parliament. As I approached, I saw that a ship’s prow, sculpted in metal, was grafted like a nose to the ground floor of this otherwise bland building. Inside I met a dozen or so mostly female IMO translators. They were cheerful and chatty and better dressed than you might imagine for people who are often heard but rarely seen. I walked upstairs to a glass-fronted booth, where I prepared to witness something both absolutely remarkable and utterly routine. Let’s unpick what she did that morning and itemise its components. As the delegate spoke, Pinkney had to make sense of a message composed in one language while simultaneously constructing and articulating the same message in another tongue. Intriguing region Humorous pitfalls Some speakers talk too fast.
About Us Alexei Kurakin, Novato lectures, paradigm, self-organization, networks, mind, consciousness, chaos, intelligence, nonlinear, evolution, cooperation The topic of today's lecture is a critique of the Newtonian Paradigm, or a critique of our all-pervasive and sub-conscious habit to interpret and represent the World surrounding us in mechanistic terms. The purpose of this lecture is to facilitate a paradigm shift in our current world perception. The shift from a reductionist, mechanistic and deterministic perception of the world to a dynamic, holistic view of the world, the view of the world as an ever evolving system of interacting, interconnected and interdependent complex systems that co-exist and co-evolve on different spatio-temporal scales. Slide 1. Credits to Dr. Alexei Kurakin September 2003, Novato, CA
Daniel Gile Daniel Gile (* 1948) ist ein französischer Übersetzer und Konferenzdolmetscher. Er lehrt als Universitätsprofessor an der École Supérieure d'Interprètes et de Traducteurs (ESIT) der Universität Paris III – Sorbonne Nouvelle. Leben[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Daniel Gile studierte Mathematik, bevor er sich einem Übersetzer- und Dolmetscherstudium zuwandte. 1984 promovierte er im Fach Japanisch mit einer Dissertation zur Ausbildung von Übersetzerberufen (La formation aux métiers de la traduction japonais-français: problèmes et méthodes) am Pariser Institut national des langues et civilisations orientales (INALCO). 1987 begann er dort eine außerordentliche Professur. Forschung[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Daniel Giles Forschungsschwerpunkt liegt auf der Ausbildung von Dolmetschern, Übersetzern und wissenschaftlichem Nachwuchs. Sonstige Aktivitäten und Mitgliedschaften[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Publikationen (Auswahl)[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Vienna Hotels: Holiday Inn Vienna City Hotel in Vienna, Austria Enjoy a relaxing stay at Holiday Inn Vienna City, a family-run hotel in arty Freihausviertel just 5 minute walk from Naschmarkt food market. You'll receive a warm welcome from the friendly staff at Holiday Inn Vienna City, only 30 minutes from Vienna International Airport. Settle in to your guest room, decorated in Wiener Moderne style, and relax in our peaceful courtyard garden. You can discover Vienna's top sights by foot and from the nearby Kettenbrückengasse U-Bahn View More You'll receive a warm welcome from the friendly staff at Holiday Inn Vienna City, only 30 minutes from Vienna International Airport. Allow our professional team to organize your conference or seminar for up to 50 delegates in our 4 naturally lit meeting rooms, all with wireless Internet. You can savoir a buffet breakfast or dine on Viennese and international cuisine in our restaurant and quiet courtyard garden, and linger for drinks in the chic Lobby bar. View Less
Danica Seleskovitch Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Danica Seleskovitch est née à Paris le et morte à Cahors le (à 79 ans). Interprète de conférence, elle fonda, entre autres, la Théorie interprétative de la traduction. Biographie[modifier | modifier le code] Danica Seleskovitch[1] est née d’une mère française, issue d’une famille de la bourgeoisie du Nord et d’un père serbe, philosophe, appartenant à une lignée d’intellectuels yougoslaves. Depuis l’enfance, elle maîtrise plusieurs langues : d’abord le français, sa langue maternelle (chez les Seleskovitch, on a toujours parlé français) ; elle parle l’allemand comme une autochtone, et elle connaît le serbo-croate, la langue de son père. Dès son arrivée à Paris, en 1946, elle s'inscrit à la Sorbonne, où elle entreprend simultanément deux licences, d’allemand et d’anglais. Son père meurt au printemps 1950. Dès le début de sa carrière d'interprète de conférence, elle réfléchit à son métier et à la façon dont le sens passe en interprétation.