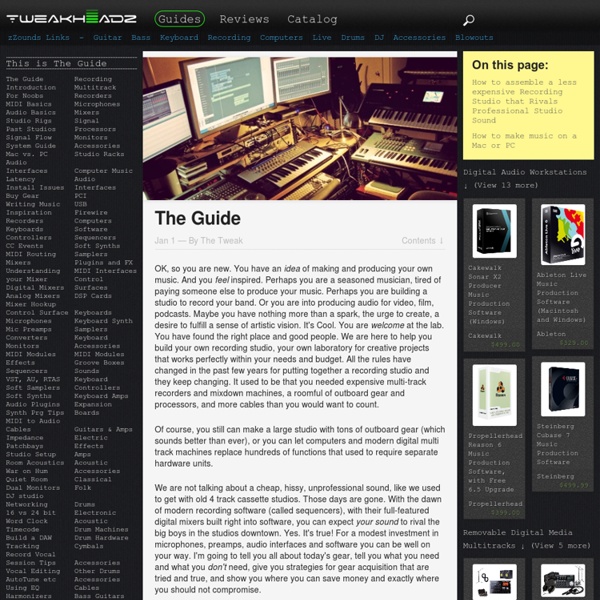
Guide To Home And Project Music Studios
Google+ and Marketing
Don’t Underestimate the Power of Google+ Uninformed marketing professionals and business owners have long considered Google+ to be the ugly stepchild of social media giants such as Facebook and Twitter, largely dismissing the growing platform as a waste of time. Even though Google+ is a relatively new player in the social media game, it has a constantly evolving platform combined with unique features and important SEO capabilities that must not be overlooked. In fact, if your business has 100 followers with active engagement, your Google search engine results position can improve by 14 spots. Here are eight reasons that marketers should incorporate Google+ into their clients’ social media efforts: Instant Indexing and SEO. Google+ has experienced unprecedented growth since its launch. Do you have any Google+ tips?
ToneDen Blog
Index page
mylittleremix.com • Index page
Battle of the Bits
NeuroHop Forum
Related:
Related:



