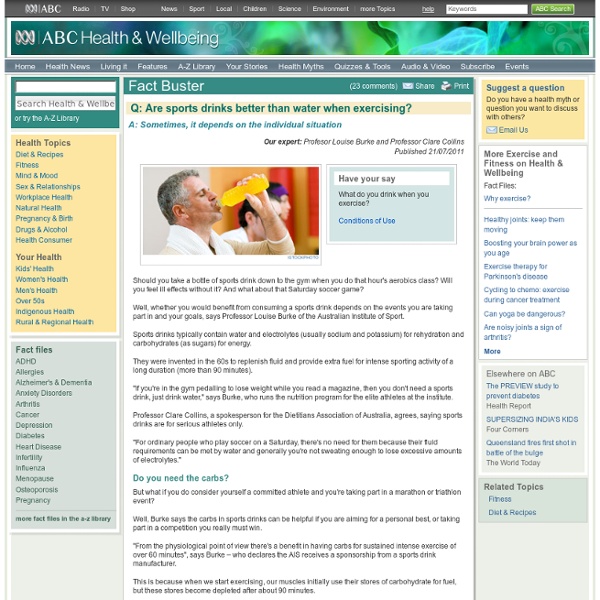
Are sports drinks better than water when exercising? - Health & Wellbeing
Taping Techniques
Strapping with adhesive tape is important for the prevention of joint injuries, especially the ankle and hand. Taping is also essential during early management of injury and rehabilitation. Recurrence of injury when the athlete recommences training is less likely with supportive taping.1 A variety of sports use taping to prevent injury. Ankle taping can protect the ankle from injury when an athlete lands awkwardly. Preventative taping has also been found to: Reduce severity of injury to the ligament Lower recurrence of injury by as much as 75%3, Give the most support while limiting backward bending4 Reference Gray SD.
Sports Coach :: Climate control: acclimatising to the heat
Author: Lisa Yates, Sports Dietitian, The Coaches Edge Issue:Volume 27 Number 1 Exercising in hot, humid conditions when the body is not accustomed to it can place the body under great stress. The demand for circulation to working muscles, which are producing heat, overtakes the need for blood flow to the skin to transport heat away from the body. As a result, body temperature rises. Couple this with dehydration and the risks of heat illness, and poor performance increases. Athletes travelling overseas or to different climates should consider heat acclimatisation an important preparation strategy. What is heat acclimatisation? The benefits of heat acclimatisation have been known for many years (Robinson 1967). What are the benefits of being heat acclimatised? Acclimatisation produces: How can coaches ‘climate control’ their athletes? There is a variety of heat exposure protocols that can achieve heat acclimatisation. Frequency of exercise Exercise duration Exercise intensity References
Heat Regulation of the Body During a Muscular Exercise
In order to avoid hyperthermia, heat exhaustion or heat stroke, the body is equipped with mechanisms to prevent large changes in temperature. Exercise is a high-energy state, requiring the breakdown of nutrients to fuel muscle contraction. The increased metabolism observed in muscles is correlated with elevated tissue temperatures. Adaptations in blood flow and sweat production serve to regulate heat removal during muscular exercise. The work of exercise requires energy. When multiple muscle groups begin contracting and increasing their activity, large amounts of heat are produced. Your body has the capacity to filter off excess heat energy if temperatures increase above a certain point. The second step in the process of removing heat from the body involves cooling the skin with sweat.
Body Temperature While Exercising
During exercise your body's system for regulating temperature is kicked up into high gear. Heat production by the body can cause your internal temperature to rise up to as high as 104 degrees Fahrenheit, which can lead to potentially fatal complications. Fortunately, your body has internal processes that allow for control over this rise. However, you can take steps toward providing your body with the means to more efficiently cool yourself. When you exercise, the rate at which your body makes energy rapidly increases. The hypothalamus of the brain works as the thermostat for temperature control inside the body. The body regulates its temperature by means of convection, conduction and evaporation. You can be proactive at helping your body regulate its temperature.
Thumb Taping - Thumb Strapping - Strap Thumb
Health > Taping Techniques > Thumb Taping The following thumb taping techniques are designed to support the thumb and reduce stress on the thumb during activity. They can be used for both the treatment and prevention of thumb injuries. You should discuss the suitability of these thumb taping techniques with your physiotherapist prior to using them. What sort of tape should be used to tape my thumb? There are many different tapes and bandages available for use by physiotherapists and patients. Benefits of Thumb Taping When used correctly, thumb taping techniques can: Aid healing of thumb injuries. Indications for Thumb Taping It is generally beneficial to tape a thumb in the following instances: Following certain thumb injuries – Thumb taping may be beneficial following certain thumb injuries (such as a thumb sprain). When should I avoid Thumb Taping? Thumb taping should be avoided in the following instances: Thumb Taping Techniques Anchor Figure 1 – Anchor Side Loop Figure 2 – Side Loop Front Loop
Ankle Taping - Ankle Strapping
Health > Taping Techniques > Ankle Taping The following ankle taping techniques are designed to support the ankle and reduce stress on the ankle during activity. They can be used for both the treatment and prevention of ankle injuries.You should discuss the suitability of these taping techniques with your physiotherapist prior to using them. Generally, they should only be applied provided they are comfortable and do not cause an increase in pain, discolouration, pins and needles, numbness or excessive redness of the foot and ankle. What sort of tape should be used to tape my ankle? There are many different tapes and bandages available for use by physiotherapists and patients. Benefits of Ankle Taping When used correctly, ankle taping techniques can: Indications for Ankle Taping It is generally beneficial to tape an ankle in the following instances: When should I avoid Ankle Taping? Ankle taping should be avoided in the following instances: Ankle Taping Techniques Anchor Figure 1 – Anchor Stirrups
Related:
Related:



