


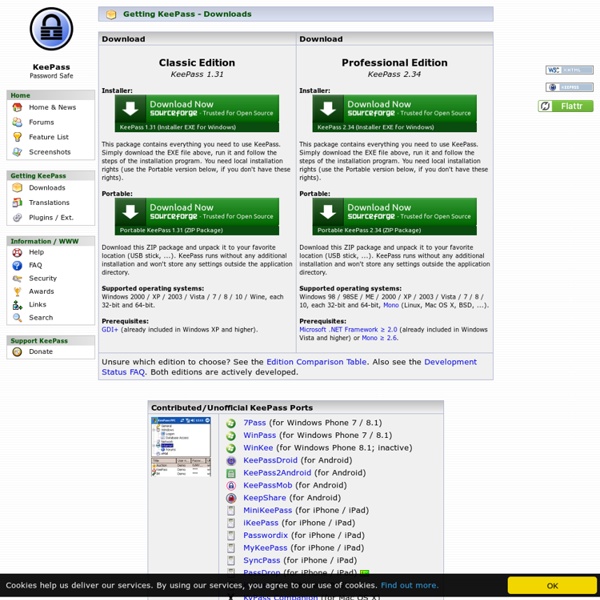
“The LastLogonTimeStamp Attribute” – “What it was designed for and how it works” - Ask the Directory Services Team Warren here. In Windows Server 2003 we introduced the lastLogontimeStamp attribute. Administrators can use the lastLogontimeStamp attribute to determine if a user or computer account has recently logged onto the domain. Using this information administrators can then review the accounts identified and determine if they are still needed and take appropriate action. Intended Use It is important to note that the intended purpose of the lastLogontimeStamp attribute to help identify inactive computer and user accounts. If you are looking for more “real-time” logon tracking you will need to query the Security Event log on your DC’s for the desired logon events i.e. 528 –Windows XP\2003 and earlier or 4624 Windows Vista\2008 . IMO your best bet for near real-time data is to use an event log collection service to gather all domain controller security event logs to a centralized database. How it worked in Windows 2000 How it works in Windows Server 2003 and later Requirements 1. 1.
Free Computer Security - Personal Software Inspector (PSI) Stay secure by updating insecure programs onyour computer with the Secunia PSI The Secunia Personal Software Inspector (PSI) is a free computer security solution that identifies vulnerabilities in non-Microsoft (third-party) programs which can leave your PC open to attacks. Simply put, it scans software on your system and identifies programs in need of security updates to safeguard your PC against cybercriminals. Using a scanner like Secunia PSI 3.0 is complementary to antivirus software, and as a free computer security program, is essential for every home computer. Learn more about PSI in these short videos PSI 3.0 WalkthroughSo simple that anyone can be secure! Tim and DaveShort animated story about security and why Tim is happier than Dave.Watch now (YouTube) Technical Product SheetHere is the full rundown of technical specifications for PSI 3.0Download now (PDF) Reviews Secunia PSI named as Security app of the week by Softpedia. Bill Mullins' Weblog- Tech Thoughts Screenshots History All ok!
Learning Lotus Notes clients : Configuring the Lotus Notes Client with Gmail Launch the Lotus Notes Client after installing it: Click Next a. a. a. a. a. a Enter your Gmail e-mail address b. Select Use the Default a. Select Accounts: a. Basics tab: a. Advanced Tab: a. Save & Close. a. Basics Tab: a. Advanced Tab: a. a. Basics Tab: a. Servers Tab: a. Ports tab: No changes (ensure TCPIP is checked) Mail Tab: a. Save & Close. a. Restart the client. How to Build a Computer - Your Guide to building a PC Tutoriel flash d'un routeur Linksys WRT54GL avec le firmware DD-WRT Flasher un routeur Linksys WRT54G(L) avec le firmware DD-WRT A travers cet exercice, vous allez apprendre à flasher votre point d'accès linksys WRT54G ou WRT54GL avec le firmware alternatif DD-WRT 1/ Vérification de la version du routeur Pour commencer, relevez le numéro de série de votre WRT54G(L). 2/ Téléchargement des firmwares Nous partons sur la base d'un wrt54gl strictement d'origine , et tout juste sorti de sa boite pour cet exemple. -dd-wrt.v23_mini_generic.bin à télécharger ici -dd-wrt.v23_wrt54g.bin à télécharger ici Le premier firmware, le mini, sert au premier flash, lorsqu'on flash le routeur depuis son firmware linksys d'origine. 3/ Le flash Reliez le wrt à votre ordinateur avec un cable réseau rj45. Par défaut, le nom d'utilisateur est vide, et le mot de passe est admin. Rendez vous dans l'onglet administration, et choisissez firmware upgrade: Cliquez sur parcourir, et choisissez l'emplacement du firmware dd-wrt.v23_mini_generic.bin: Rendez vous dans l'onglet administration.
How To Assemble A Desktop PC Building a computer can be a very rewarding experience. Since you’re reading this, you’re probably thinking about building your next computer instead of buying one pre-built. This is a very viable option these days and can bring many benefits; you can learn a lot about computer hardware by building one, you get a totally personalized computer, you can choose better components and you may be able to save some money and have fun. Additionally, if you are the sort of person who wants to understand how things work, if you take broken stuff apart just to see how it all fits together, if you have a drawer somewhere full of “parts” you think may come in handy someday, then you just may be in the right place. Contents Noted contributors · External links · Development Note to editors Please look at the talk page before editing this book. New sections and content first go into Development. See also Buyer's Guide For Building a Computer
Tutoriel Rogue AP, hotspots en danger: ettercap, dnsspoof et man in the middle sous backtrack Comprendre ce qu'est une Rogue AP et éviter les dangers liés aux hotspots wifi (man in the middle, ettercap, dnsspoof) A travers ce tutoriel, vous allez découvrir à quel point il est aisé de créer un faux point d'accès ressemblant à s'y méprendre à un hotspot wifi. Vous réaliserez ainsi qu'il est extremement dangereux de se connecter à des réseaux wifi mal protégés, qu'il s'agisse de hotspots ou de réseaux utilisant le WEP. 1/ Vidéo de démonstration Cette vidéo aborde le problème sur un ton humoristique, afin de détendre l'atmosphère. Mais les problèmes liés aux rogue ap (point d'accès pourri ou voyou) ne sont pas à prendre à la légère, car le meme type de scénario est possible si, connecté à un hotspot, vous vous rendez sur le site de votre banque, ou si vous allez consulter vos mails. Convaincus? 2/ L'architecture réseau La victime était à la base connectée à un hotspot légitime. 3/ L'attaque, ettercap et dnsspoof -Ettercap Fonctionnement: ettercap -T -M arp:remote /ip-victime/ /ip-routeur/
Configuration d'une interface - routeur Cisco Configuration les interfaces des routeurs Cisco (vitesse, duplex, adresse IP), afficher la conf, activation et désactivation. Affichage des informations concernant les interfaces La commande suivante affiche la configuration courante d'une interface. R1#sho running-config interface fastEthernet 0/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 98 bytes ! Et voici la commande pour afficher les valeurs des compteurs d'une interface: Plusieurs infos intéressantes: le port est up ou down, l'interface est de type fast ethernet, fonctionne en full duplex avec un débit de 100Mbit/s. Modification de la description, la vitesse et le duplex d'une interface Ajout d'une description R2(config)#int fastEthernet 0/1 R2(config-if)#description vers routeur R2 Paramétrage de la vitesse et du mode duplex d'un port. Paramètre disponible pour une interface fast ethernet 100Mbit/s R2(config-if)#speed ? R2(config-if)#duplex ? Pour fixer la vitesse à 10Mbit/s puis le mode duplex half: