


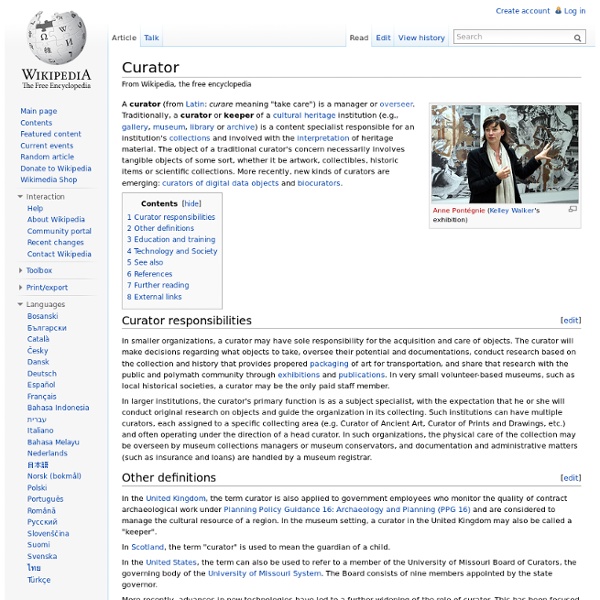
Archival science Science of storage, registration and preservation of historical data Archival science, or archival studies, is the study and theory of building and curating archives, which are collections of documents, recordings, photographs and various other materials in physical or digital formats. An archival record preserves data that is not intended to change. In order to be of value to society, archives must be trustworthy. An archive curator is called an archivist; the curation of an archive is called archive administration. Archival science emerged from diplomatics, the critical analysis of documents.[3][4] In 1540, Jacob von Rammingen (1510–1582) wrote the manuscript of the earliest known archival manual. Rammingen elaborated a registry for the Augsburg city council. Metadata comprises contextual data pertaining to a record or aggregate of records. Provenance in archival science [edit] The principle of provenance Practices before the emergence of provenance Emergence of provenance
Information science Academic field concerned with collection and analysis of information Information science is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information.[1] Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems. Historically, information science (informatics) is associated with computer science, data science, psychology, technology, library science, healthcare, and intelligence agencies.[2] However, information science also incorporates aspects of diverse fields such as archival science, cognitive science, commerce, law, linguistics, museology, management, mathematics, philosophy, public policy, and social sciences. [edit]
Archive Accumulation of historical records An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials – in any medium – or the physical facility in which they are located.[1][2] Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization.[citation needed] Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism",[3] and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on the grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. History[edit]
Sound recording and reproduction Prehistory[edit] Phonautograph[edit] Main article: Phonautograph Phonograph[edit] Phonograph cylinder[edit] On April 30, 1877, French poet, humorous writer and inventor Charles Cros submitted a sealed envelope containing a letter to the Academy of Sciences in Paris fully explaining his proposed method, called the paleophone. Disc phonograph[edit] Recording of Bell's voice on a wax disc in 1885, identified in 2013 [more details] Emil Berliner with disc record gramophone The next major technical development was the invention of the gramophone disc, generally credited to Emile Berliner and commercially introduced in the United States in 1889, though others had demonstrated similar disk apparatus earlier, most notably Alexander Graham Bell in 1881.[7] Discs were easier to manufacture, transport and store, and they had the additional benefit of being louder (marginally) than cylinders, which by necessity, were single-sided. Electrical recording[edit] Other recording formats[edit]
Cognitive science Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the mind and its processes.[1] It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works. It includes research on intelligence and behavior, especially focusing on how information is represented, processed, and transformed (in faculties such as perception, language, memory, reasoning, and emotion) within nervous systems (human or other animal) and machines (e.g. computers). Cognitive science consists of multiple research disciplines, including psychology, artificial intelligence, philosophy, neuroscience, linguistics, and anthropology.[2] It spans many levels of analysis, from low-level learning and decision mechanisms to high-level logic and planning; from neural circuitry to modular brain organization. The fundamental concept of cognitive science is "that thinking can best be understood in terms of representational structures in the mind and computational procedures that operate on those structures. Principles[edit]
Data storage From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Recording of information in a storage medium Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Data storage in a digital, machine-readable medium is sometimes called digital data. Recording media[edit] A recording medium is a physical material that holds information. Some recording media may be temporary either by design or by nature. Global capacity, digitization, and trends[edit] A 2003 UC Berkeley report estimated that about five exabytes of new information were produced in 2002 and that 92% of this data was stored on hard disk drives. In a more limited study, the International Data Corporation estimated that the total amount of digital data in 2007 was 281 exabytes, and that the total amount of digital data produced exceeded the global storage capacity for the first time.[6] See also[edit] References[edit]
Archival appraisal Process of examining a body of records to determine its value for an archival library In archival science and archive administration, appraisal is a process usually conducted by members of the record-holding institution (often professional archivists) in which a body of records is examined to determine its value for that institution. It also involves determining how long this value will last. The activity is one of the central tasks of an archivist, to determine the archival value of specific records. When it occurs prior to acquisition, the appraisal process involves assessing records for inclusion in the archives. In an archival context, appraisal is the process of determining whether records and other materials have permanent (archival) value. History of appraisal theory [edit] Muller, Feith & Fruin: the Dutch Manual, 1898 Sir Hilary Jenkinson, 1922 Sir Hilary Jenkinson was a British archivist and Deputy Keeper of the Public Record Office upon his retirement. In 2010, scholar Richard J.
Preservation (library and archival science) In library and archival science, preservation is a set of activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record, book, or object while making as few changes as possible. Preservation activities vary widely and may include monitoring the condition of items, maintaining the temperature and humidity in collection storage areas, writing a plan in case of emergencies, digitizing items, writing relevant metadata, and increasing accessibility. Preservation, in this definition, is practiced in a library or an archive by a librarian, archivist, or other professional when they perceive a record is in need of care. Collections care is the general maintenance and preventive care of a collection as a whole. Preservation and recording of magnetic tapes at Fonoteca Nacional (National Sound Archive of Mexico). Environmental controls are necessary to facilitate the preservation of organic materials and are especially important to monitor in rare and special collections.
Cataloging A handwritten subject card from the National Library of Medicine's old card catalog recalls the precomputer days when information had to be created, classified, and sorted by hand. HMD Prints & Photos, PP059772.7. In library and information science, cataloguing (UK) or cataloging (US) is the process of creating metadata representing information resources, such as books, sound recordings, moving images, etc. Cataloging provides information such as creator names, titles, and subject terms that describe resources, typically through the creation of bibliographic records. Bibliographic control provides the philosophical basis of cataloging, defining the rules for sufficiently describing information resources to enable users to find and select the most appropriate resource. Six functions of bibliographic control[edit] Ronald Hagler identified six functions of bibliographic control.[2] "Identifying the existence of all types of information resources as they are made available History[edit]
Social science Social science is an academic discipline concerned with society and the relationships among individuals within a society. It includes anthropology, economics, political science, psychology and sociology. In a wider sense, it may often include some fields in the humanities[1] such as archaeology, history, law, and linguistics. Positivist social scientists use methods resembling those of the natural sciences as tools for understanding society, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. History[edit] The history of the social sciences begins in the Age of Enlightenment after 1650, which saw a revolution within natural philosophy, changing the basic framework by which individuals understood what was "scientific". The beginnings of the social sciences in the 18th century are reflected in the grand encyclopedia of Diderot, with articles from Rousseau and other pioneers. Branches[edit] Anthropology[edit] Communication studies[edit] Economics[edit]
Psychology Psychology is an academic and applied discipline that involves the scientific study of mental functions and behaviors.[1][2] Psychology has the immediate goal of understanding individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases,[3][4] and by many accounts it ultimately aims to benefit society.[5][6] In this field, a professional practitioner or researcher is called a psychologist and can be classified as a social, behavioral, or cognitive scientist. Psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behavior, while also exploring the physiological and biological processes that underlie cognitive functions and behaviors. While psychological knowledge is often applied to the assessment and treatment of mental health problems, it is also directed towards understanding and solving problems in many different spheres of human activity. Etymology History Structuralism Functionalism Psychoanalysis Behaviorism Humanistic