


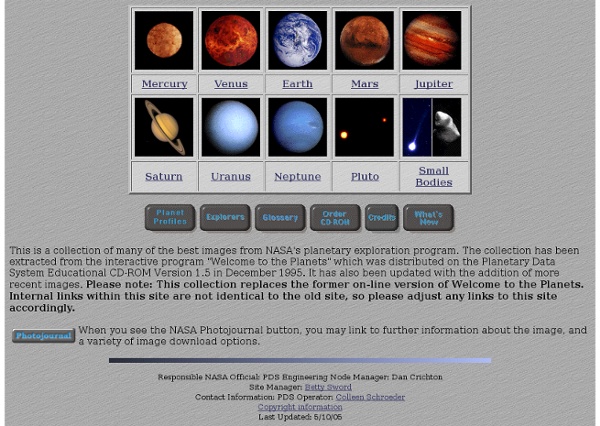
: Planets Planets: The planet count in our solar system has gone as high as 15 before new discoveries prompted a fine tuning of the definition of a planet. The most recent change was in 2006 when scientists reclassified Pluto as a new kind of object - a dwarf planet. Dwarf Planets: This new class of worlds helps us categorize objects that orbit the Sun but aren't quite the same as the rocky planets and gas giants in our solar system. There could be hundreds more of these small worlds far out there waiting to be discovered. Moons: This count includes only the moons orbiting the eight planets in our solar system. Asteroids: New asteroids are discovered on an almost daily basis. Comets: Orbiting spacecraft such as SOHO have raised this tally in recent years by catching the comets as they plunge toward the Sun - and sometimes vaporize.
Planets - Zoom Astronomy Advertisement. EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.Click here to learn more. (Already a member? Click here.) The Planets (plus the Dwarf Planet Pluto) Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, many dwarf planets (or plutoids), an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The eight planets that orbit the sun are (in order from the sun): Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Easy ways to remember the order of the planets (plus Pluto) are the mnemonics: "My Very Excellent Mother Just Sent Us Nine Pizzas" and "My Very Easy Method Just Simplifies Us Naming Planets" The first letter of each of these words represents a planet - in the correct order. The largest planet is Jupiter. The inner planets are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Generally, the farther from the Sun, the cooler the planet. Density of the Planets The Mass of the Planets
Windows to the Universe Planet The planets were thought by Ptolemy to orbit Earth in deferent and epicycle motions. Although the idea that the planets orbited the Sun had been suggested many times, it was not until the 17th century that this view was supported by evidence from the first telescopic astronomical observations, performed by Galileo Galilei. By careful analysis of the observation data, Johannes Kepler found the planets' orbits were not circular but elliptical. As observational tools improved, astronomers saw that, like Earth, the planets rotated around tilted axes, and some shared such features as ice caps and seasons. Since the dawn of the Space Age, close observation by space probes has found that Earth and the other planets share characteristics such as volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. History Printed rendition of a geocentric cosmological model from Cosmographia, Antwerp, 1539 Babylon Greco-Roman astronomy India Medieval Muslim astronomy European Renaissance 19th century 20th century
Solar System Discovery and exploration Andreas Cellarius's illustration of the Copernican system, from the Harmonia Macrocosmica (1660) For many thousands of years, humanity, with a few notable exceptions, did not recognize the existence of the Solar System. Structure and composition The orbits of the bodies in the Solar System to scale (clockwise from top left) The principal component of the Solar System is the Sun, a G2 main-sequence star that contains 99.86% of the system's known mass and dominates it gravitationally.[13] The Sun's four largest orbiting bodies, the gas giants, account for 99% of the remaining mass, with Jupiter and Saturn together comprising more than 90%. Most large objects in orbit around the Sun lie near the plane of Earth's orbit, known as the ecliptic. The overall structure of the charted regions of the Solar System consists of the Sun, four relatively small inner planets surrounded by a belt of rocky asteroids, and four gas giants surrounded by the Kuiper belt of icy objects.
יפו- סיור ביום ובלילה יפו היא אחת מערי הנמל העתיקות בארץ ישראל ובאגן הים התיכון. היא קשורה קשר אמיץ למאורעות ההיסטוריים שארעו בארץ-ישראל בפרט והאגן המזרחי של הים התיכון בכלל, מאז תחילת ההתיישבות בה. היא נבנתה על צוק רם, הבולט מקו החוף אל תוך הים ולרגליו נמצא הנמל. על תולדותיה אנו למדים הן מהמקורות ההיסטוריים והן מהחפירות שנערכו ביפו וסביבותיה. השרידים הקדומים ביותר שנתגלו ביפו (באזור החמאם ובתוכו) הם שרידי חלקלקה שהקיפה את הגבעה במאה ה-י"ח לפנה"ס (תקופת הברונזה התיכונה ב'). בשטח החפירות המרכזי (שטח A ) הנמצא כיום בתוך "גן שער רעמסס" נתגלו שרידים של יישוב משלהי המאה ה-י"ז והמחצית הראשונה של המאה ה-ט"ז לפנה"ס. מתקופת הברונזה המאוחרת (מחצית שנייה של המאה ה-ט"ז והמאה ה-ט"ו לפנה"ס) נתגלו שרידי בניינים בנויים מלבנים על יסודות אבן. א. ב. ג. ד. מתקופת הברזל נתגלו בעיקר שרידים דלים הכוללים קרמיקה פלישתית ושרידי מקום מקודש "מקדש האריה" – אולם שמידותיו 5.8X4.4 מ' ובו שני בסיסים לעמודי עץ שתמכו את התקרה. בתנ"ך מופיעה יפו לראשונה בתיאור גבולות שבט דן: "ומי הירקון והירקון עם הגבול מול יפו" (יהושוע י"ט, מ"ו).
The Nine Planets Solar System Tour The Solar System - Astronomy For Kids - KidsAstronomy.com Our solar neighborhood is an exciting place. The Solar System is full of planets, moons, asteroids, comets, minor planets, and many other exciting objects. Learn about Io, the explosive moon that orbits the planet Jupiter, or explore the gigantic canyons and deserts on Mars. What Is The Solar System? The Solar System is made up of all the planets that orbit our Sun. Everything in the Solar System orbits or revolves around the Sun. How Did The Solar System form? This is an important question, and one that is difficult for scientists to understand. Scientists believe that the Solar System evolved from a giant cloud of dust and gas. At the center of this spinning cloud, a small star began to form. Further away from the center of this mass where the star was forming, there were smaller clumps of dust and gas that were also collapsing. A Great Storm Once ignited, the Sun's powerful solar winds began to blow. The Solar System Has Over 100 Worlds It is true that there are only eight planets.