The value of reinforcing positive behaviour for our teens
As children approach adolescence, they sometimes begin testing limits, bending the rules and otherwise going against the grain. While this is normal behaviour for teens, it can be incredibly trying for you, as a parent. Teenagers may also be dealing with the stresses that come with trying to fit in with their peers and assert their growing independence.
Discipline strategies for teenagers
Teenage discipline: the basics Discipline isn’t about punishment. It’s about teaching children appropriate ways to behave. For teenagers, discipline is about agreeing on and setting appropriate limits and helping them behave within those limits.
Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples]
Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior. Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement
Teenagers: 20 tips for good behaviour
1. Take time to actively listen Actively listening means paying close attention to what your child is saying and feeling, rather than thinking of what you want to say next. This shows your child that you care and that you’re interested. 2. Set clear rules about behaviour Family rules make expectations about behaviour clear. If you can, involve all family members in the discussions about rules.
Operant Conditioning (B.F. Skinner)
How Reinforcement and Punishment Modify Behavior Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning normally attributed to B.F. Skinner, where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Through operant conditioning behavior which is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior which is punished will occur less frequently.
How to Reward Your Teen for Good Behavior
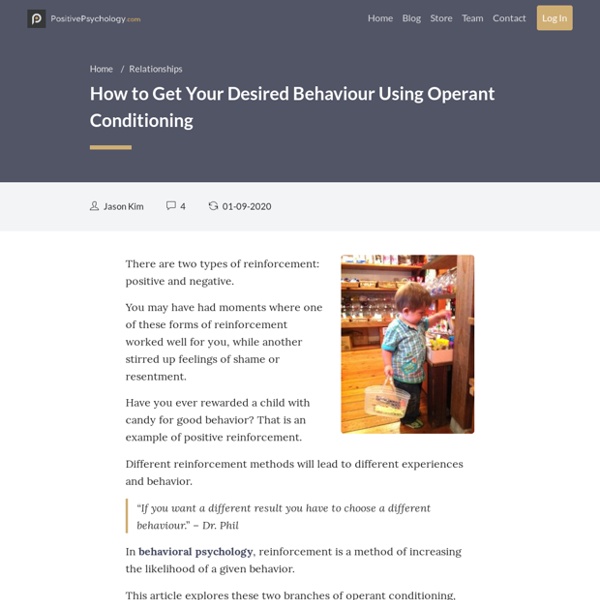
Teenagers are young adults who are trying to learn the ways of the world. When they do something great at school or at home or simply make a healthy decision, parents can give them a reward. The reward does not have to be money, but it is a nice way to say "thank you" or "I'm proud of you."
What Is Operant Conditioning and How Does It Work?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that employs rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence (whether negative or positive) for that behavior.1 For example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light is on, they receive a food pellet as a reward. When they press the lever when a red light is on, they receive a mild electric shock.
What Is Operant Conditioning and How Does It Work?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that employs rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence (whether negative or positive) for that behavior.1 For example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light is on, they receive a food pellet as a reward.
Call these helplines if you need emotional or psychological support
As we do our part to practise safe-distancing to protect the health of ourselves and those around us, paying attention to our mental and emotional well-being is equally important as well. Connect with family or friends Staying connected with family and friends through phone or video calls can do a lot for your mental health.
14 Best Examples Of Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that employs punishments and rewards for behavior. In this method, a link is established between a behavior and a consequence (whether positive or negative) for that behavior. For example, when a monkey presses a button when a LED is on, he receives a banana as a reward.
Effective Consequences for Teenagers
If you’re having trouble giving effective consequences to your teen, know that you are not alone. Many parents tell me that nothing seems to work, and that coming up with the right thing for their child can seem like an impossible task. If you’re the parent of an adolescent, you may have grounded your child, taken away their video games, or suspended their driving privileges for months on end. But as James Lehman says, you can’t punish kids into acceptable behavior—it just doesn’t work that way. “You can’t punish kids into acceptable behavior.”
Parenting and B.F. Skinner: It All Boils Down to Operant Conditioning - Kars4Kids Parenting
Do you remember the Youtube video that went viral about the three dogs that learned how to drive a Mini-Cooper? In case you don’t, I’ve included the clip to remind and entertain you. In the video, three dogs rescued by the SPCA in New Zealand are trained by professional animal trainers to drive a mini-Cooper. Through months of painstaking training, the dogs are taught simple behaviors that when fit together will create a series of behaviors needed to drive a car. By the end of the training period, the dogs were able to climb into the driver’s seat, start the ignition, put the car into gear, accelerate, and navigate the car around a track. It’s a masterpiece in operant conditioning and illustrates how a well-designed behavioral modification plan can reinforce desirable behaviors and eliminate less desirable ones.
The Study of Punishment in Psychology
Punishment is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to any change that occurs after a behavior that reduces the likelihood that that behavior will occur again in the future. While positive and negative reinforcements are used to increase behaviors, punishment is focused on reducing or eliminating unwanted behaviors. Punishment is often mistakenly confused with negative reinforcement. The difference: Reinforcement increases the chances that a behavior will occur and punishment decreases the chances that a behavior will occur. Types of Punishment Behaviorist B.
How to Deal With a Disrespectful Teenager: 10 Tips for Frustrated Parents
Are you dealing with a disrespectful teenager? Maybe he mutters under his breath when you ask him to do his homework. Or maybe she slams her room door when you tell her that she can’t go out with her friends. If so, you’re probably at your wits’ end. You love your teenagers and you want the best for them.