Atomic-scale magnetic memory - United States - StumbleUpon
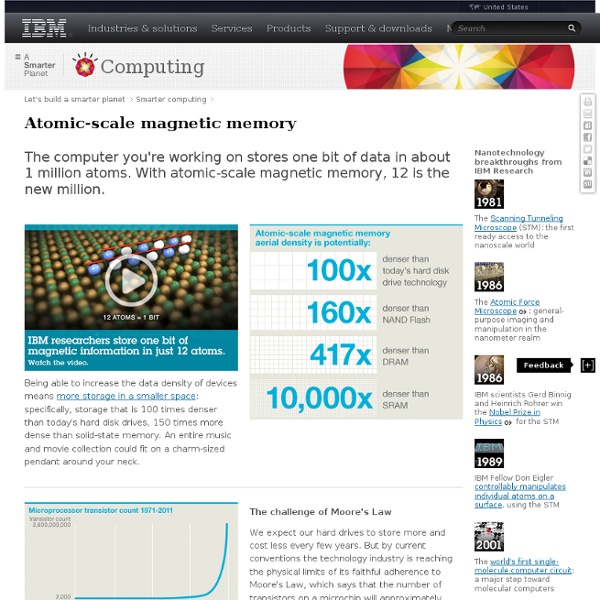
The world's smallest bit Scientists from IBM Research have been investigating and controlling matter on an atomic scale for decades. So, naturally, their latest quest would involve greatly decreasing the storage capacity needed for one bit of data, which on today's computers stands at about 1 million atoms. They set out to develop the ultimate memory chips of the future. By studying the behavior of atoms, researchers can identify crucial factors for building smaller, faster and more energy-efficient devices for business and consumers. A history of innovation As one of the last remaining industrial labs, IBM continues to emphasize fundamental science and investment in R&D. And now, will likely change computing and data storage—and maybe even what you wear around your neck—forever.
- StumbleUpon
If you’ve been following Microsoft’s Kinect , then you know that all sorts of development has taken place around it. The motion sensor has had a significant impact on the Xbox 360 , but the development that is taking place on the computer side is much more clever. Of course, independent developers aren’t bound by commercial viability, or even tastefulness, so we’ve seen a lot of fun stuff happening with the Kinect that Microsoft surely never imagined. Russian Roulette , as anyone who has seen The Deer Hunter will know, is a lethal game which has a very high chance of an unfortunate outcome. The setup looks pretty simple: the Kinect recognizes your face and then your hand in the shape of a firearm. And if you lose… well you’ve probably already seen the video or the screenshot below. Kinect Russian Roulette was an art project, by Theo Watson, for the Art Hack Day . As a game KRR might get old fast, but it could still be useful. via Theo Watson
Design Ideas and Tech Concepts - Toxel.com
The Best PCs You Can Build for $600 and $1200
Glass door with a surprise - StumbleUpon
Posted on November 23, 2010 in Bizarre Rate this Post (1 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5) Loading ... So... Check this out on our Partner Network
Laws of Simplicity - Home
Save All Around by Powering Your Computer Down
Experts discuss the costs of powering your computer down vs. leaving it in standby mode. Having to boot up your computer each time you want to use it can be inconvenient, but keeping it in sleep mode may not be the best alternative. The sleep mode on your computer is designed to keep the machine on while drawing a small amount of power. This only costs about $50 more per year on your electric bill, which seems low, but the true cost of leaving it in this mode may actually be higher. According to our experts, you shouldn't leave your computer on standby if you're going to be away for more than an hour. Turning your computer on and off won't cause damage. So, when it comes to your computer, be mindful of letting it sleep for too long and power down instead.
Scientists Discover The Oldest, Largest Body Of Water In Existence--In Space | Fast Company - StumbleUpon
Scientists have found the biggest and oldest reservoir of water ever--so large and so old, it’s almost impossible to describe. The water is out in space, a place we used to think of as desolate and desert dry, but it's turning out to be pretty lush. Researchers found a lake of water so large that it could provide each person on Earth an entire planet’s worth of water--20,000 times over. Yes, so much water out there in space that it could supply each one of us all the water on Earth--Niagara Falls, the Pacific Ocean, the polar ice caps, the puddle in the bottom of the canoe you forgot to flip over--20,000 times over. The water is in a cloud around a huge black hole that is in the process of sucking in matter and spraying out energy (such an active black hole is called a quasar), and the waves of energy the black hole releases make water by literally knocking hydrogen and oxygen atoms together. The new cloud of water is enough to supply 28 galaxies with water.
Wearable Computers Could Help Build A Better You
In 1961, Claude Shannon and Edward Thorp built the world's first wearable computer. The cigarette-pack-size device tracked the speed of a roulette wheel and sent tones via radio to a gambler's earpiece to help predict where the ball would land. The goal of wearable computers hasn't changed much since. One of the newest methods for spurring self-improvement is to turn every task into a game. Gamification has problems; an app doesn't know when you're lying.Yet the systems have problems. Wearing a computer instead of carrying one could eliminate all those downsides. More-advanced tracking may eventually allow HUDs to predict and prevent bad behavior instead of merely recording it.
Related:
Related: