Understanding the Bystander Effect
If you witnessed an emergency happening right before your eyes, you would certainly take some sort of action to help the person in trouble, right? While we might all like to believe that this is true, psychologists suggest that whether or not you intervene might depend upon the number of other witnesses present. What Is the Bystander Effect? The term bystander effect refers to the phenomenon in which the greater the number of people present, the less likely people are to help a person in distress. When an emergency situation occurs, observers are more likely to take action if there are few or no other witnesses. Being part of a large crowd makes it so no single person has to take responsibility for an action (or inaction).
How To Counteract The Bystander Effect - University of Pittsburgh Student EMS
Counteracting The Bystander Effect It is a beautiful spring day in Oakland. There are just a few weeks left until summer break and everyone is ready to go home. You are in Cathy studying and you see that the person a few tables over seems to be passed out. You notice they haven't moved in hours. Hundreds of people have walked by and seem to take notice but no one has done anything.
More than 50 years on, the murder of Kitty Genovese is still throwing up fresh psychological revelations
By Christian Jarrett The horrific killing of Catherine “Kitty” Genovese in New York in 1964 inspired research into what’s known in social psychology as the Bystander Phenomenon – our increased disinclination to intervene when in the company of others. That’s because early reports told how 38 witnesses to Genovese’s murder did nothing to help. But in fact it’s now clear that several people did intervene.
Richmond High School Gang Rape
Oct. 30, 2009 — -- Members of the Richmond, Calif., community were stunned by the alleged rape and assault of a high school student after a school dance last Saturday. But a nationwide news audience was even more astonished by allegations that about 20 people in the immediate area observed about 10 men and boys gang rape and beat the 15-year-old girl for two-and-a-half hours on the Richmond High School campus and did not contact authorities. Psychology experts say the incident, if it occurred as described, may have been the result of escalating wildness facilitated by an isolated, heavily male environment. "If one of the boys or men grabbed her and pulled her toward him ... and somebody else did something else so it became more and more sexual in nature ... we now have a [group of boys] who are pretty wild," said John Darley, a professor of psychology and public affairs at Princeton University. "Each act licensed what had gone before, and it also made more likely what came next."
How to Overcome the Bystander Effect
Psychologists have long been interested in exactly why and when we help other people. There has also been a tremendous amount of interest in the reasons why we sometimes don't help others. The bystander effect is a social phenomenon that occurs when people fail to help those in need due to the presence of other people.
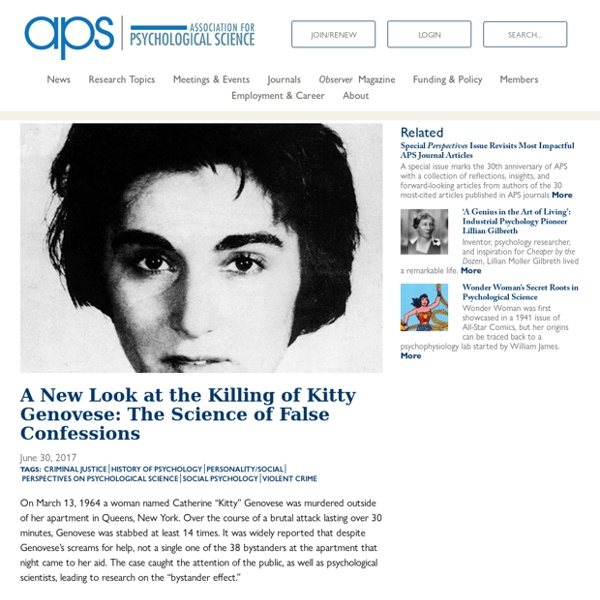
The murder of "Kitty" Genovese that led to the Bystander Effect & the 911 system
Catherine “Kitty” Genovese was a 28-year-old woman who was brutally murdered outside of her Queens apartment in New York City on March 13, 1964. Genovese’s attack lasted around 30 minutes as she was stabbed 14 times by a man named Winston Moseley. It was originally reported that there were 38 bystanders who turned their back on Genovese’s early morning cries for help, shutting their doors to silence her screams. Although that judgment was later proven to be inaccurate, the murder was considered the driving force behind our emergency 911 system today and the discovery of the term that so many psychologists are still researching: “The Bystander Effect.” It was around 3 o’clock in the morning when Genovese arrived home from managing a local bar where she worked. Kitty Genovese
The Bystander Effect: Reactions and Causes - PSYCHROD
Bystander Effect: Reactions and Causes The bystander effect is an element of social psychology that implies that when the number of bystanders is increased in an emergency situation, the less likely any of the bystanders will aid, or assist in the situation (Aronson, Wilson, & Akert, 2013). The bystander effect is one of the most significant well established social psychology findings, which manifested in the late 1960’s (Levine & Crowther, 2013).
Panama City Spring Break Gang Rape
In March of 2015, while onlookers drank and partied, a young woman was brutally raped by three male college students. Later in April of 2015, while watching the news, the young victim recognized her tattoos in the video that portrayed the violent rape. It was then she realized, it was her that was being violated. Was it a flood of emotion or numbness that she felt as she watched her body being publicly abused?