

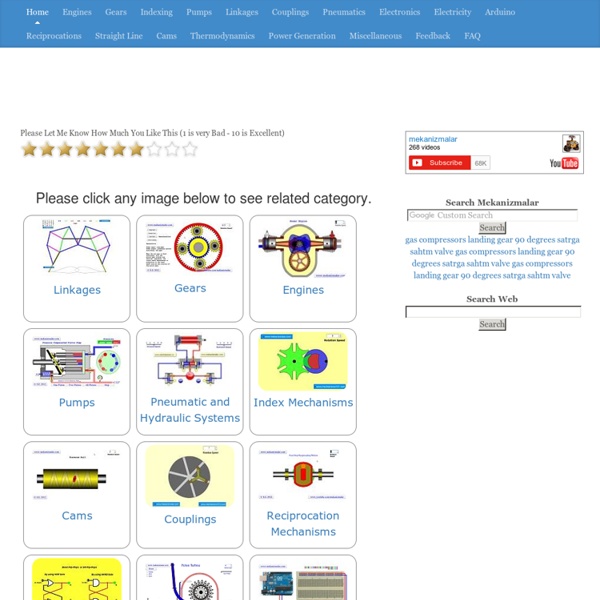
Mechanisms Introduction A mechanism considered to be an assembly of mechanical items designed to achieve a specific purpose within a machine. There are clearly an infinite number of mechanisms available but the notes and links are concentrating on the specific ones as listed below. For specific information on linkages please refer.. Linkages Motion Control Using Computers The notes below relate generally to mechanical methods for providing relative motion and forces. Although the motions of many of high technology machines and computer systems are being controlled by computers. Classification Of Mechanisms There are many methods of classifying mechanisms. Snap Action Mechanisms Snap action mechanisms are also called toggle and bi-stable mechanism are widely used for components for simple toggle switches to clamps. Linear Actuators Stationary Screws with rotating nuts This group include machine tool traversing mechanisms, jacks, valve drives etc etc. Fine adjustment mechanisms Clamping Mechanisms Ratchets
Servo Motor Guide What is a Servo Motor? A Servo Motor is a motor which is part of a servomechanism. It is typically paired with some type of encoder to provide positioning and speed feedback. Servo Motor Basics A Servo Motor is defined as an automatic device that uses an error-correction routine to correct its motion. A servomechanism may or may not use a servo motor. A servo motor can be a DC, AC, or brushless DC motor, combined with a position sensor; in most cases, a digital encoder. How to Operate Servo in JogHow to Operate Servo in Speed Control Physical Properties of a Servo Motor A Servo Motor consists of three major parts: a motor, control board, and potentiometer (variable resistor) connected to the output shaft. Where are Servo Motors used? Servos are extremely useful in robotics and automation. What Industries are Servo Motors used in? Servo motors are seen in applications such as factory automation, robotics, CNC machinery, and packaging. How Does a Servo Motor Work? How to Select a Servo Motor
30lb Fighting Robot-Nyx The pile of flat stock was waterjet cut by Westar Mfg. out of 6061 aluminum and 4130 steel. Drawings for this collection of parts along with materials, thicknesses and quantities can be found here. The top armor and two supplimental weapons were not included in that collection to allow modifications to be made for weight purposes. These drawings were done with the intent that most would be made on a waterjet, and as such did not require dimensioning. With the great deal of interlocking components, the order of assembly is important. The other main piece of the day was countersinking the holes on the inner rails to ensure there would be no contact between the moving roller chain and the bolt heads.
Motor controller Applications[edit] Every electric motor has to have some sort of controller. The motor controller will have differing features and complexity depending on the task that the motor will be performing. More complex motor controllers may be used to accurately control the speed and torque of the connected motor (or motors) and may be part of closed loop control systems for precise positioning of a driven machine. For example, a numerically controlled lathe will accurately position the cutting tool according to a preprogrammed profile and compensate for varying load conditions and perturbing forces to maintain tool position. Types of motor controllers[edit] Motor controllers can be manually, remotely or automatically operated. An electric motor controller can be classified by the type of motor it is to drive such as permanent magnet, servo, series, separately excited, and alternating current. Motor starters[edit] A reversing starter can connect the motor for rotation in either direction.
Marine propulsion A view of a ship's engine room Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a ship or boat across water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of a motor or engine turning a propeller, or less frequently, in jet drives, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the design of marine propulsion systems. Steam engines were the first mechanical engines used in marine propulsion, but have mostly been replaced by two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines, outboard motors, and gas turbine engines on faster ships. Nuclear reactors producing steam are used to propel warships and icebreakers, and there have been attempts to utilize them to power commercial vessels. Power sources[edit] Pre-mechanisation[edit] Until the application of the coal-fired steam engine to ships in the early 19th century, oars or the wind were used to assist watercraft propulsion.