


RUSA Professional Competencies for Reference and User Services Librarians 2017 Portfolio - Hive Kansas City The Hive KC Portfolio shows the range of projects we’ve funded with innovation funds from the Gigabit Fund and the Hive Drive Fund, along with a pipeline of active proposals we are actively engaging for support with local funders of the Hive KC Digital Drive Fund. These grantees are some of Hive KC’s most active and committed contributors. Their projects reflect exemplar collaborations within our community, showcasing connected learning and next generation Ed Tech experiences and digital literacy programs and pilots. Hive KC supports a competitive grant making process aimed at providing a platform for Hive practitioners to explore the innovative solutions and imaginative next-generation approaches to learning that lie at the heart of Hive’s goals to create impact and learning outcomes in Kansas City and beyond. Gigabit Fund projects Hive Drive projects KC Women in Technology’s Tech sHeroes
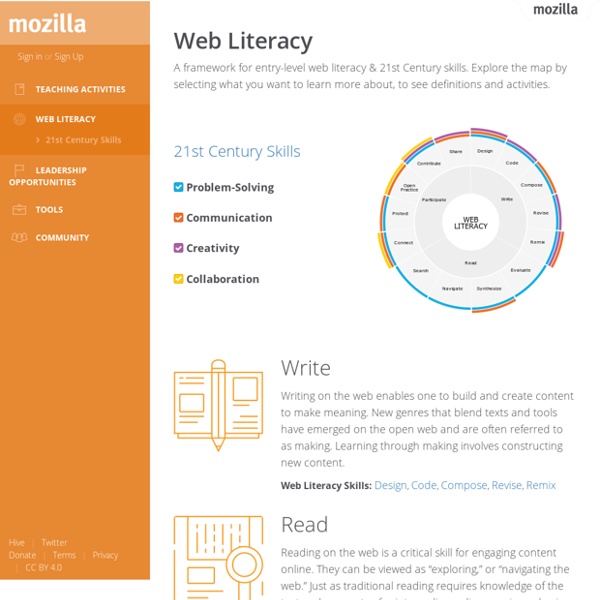
Web Literacy 2.0 Authors: An-Me Chung, Iris Bond Gill, Ian O'Byrne This paper captures the evolution of the Mozilla Web Literacy Map to reach and meet the growing number of diverse audiences using the web. The paper represents the thinking, research findings, and next iteration of the Web Literacy Map that embraces 21st Century Skills (21C Skills) as key to leadership development. As technology becomes more ubiquitous, and more people come online, Mozilla continues to refine its strategies to support and champion the web as an open and public resource. To help people become good citizens of the web, Mozilla focuses on the following goals: 1) develop more educators, advocates, and community leaders who can leverage and advance the web as an open and public resource, and 2) impact policies and practices to ensure the web remains a healthy open and public resource for all. Specifically, these skills are described as: “Read” is how we explore the web. Research Findings Specifically, the map needs to be: Read
Standards for Libraries in Higher Education | Association of College & Research Libraries (ACRL) - Approved by the ACRL Board of Directors, October 2011 Revision approved by the ACRL Board of Directors, February 2018 Print copies of the 2018 revision will soon be available from the Association of College and Research Libraries for $15.00 for a package of 10, including standard postage. Association of College and Research Libraries Attn: Standards Fulfillment 50 East Huron Street Chicago, IL 60611 To order, call 312-280-2523, or email acrl@ala.org. ACRL has a history of supporting librarians in understanding and using the association’s standards and guidelines. PDF version of the Standards for Libraries in Higher Education Table of Contents Introduction Principles and Performance Indicators Appendices 1. Introduction The Standards articulate expectations for library contributions to institutional effectiveness. Institutions are encouraged to use these Standards as they best apply to their local mission and vision. Sources Consulted Standards Structure 1. align with the principles; Notes 1. 2. 1.
Home FRAMEWORK — FutureWe Why do students start school with a creative lateral thinking rating of 98% but finish with 12%, especially when its been identified as one of THE key future skills? A focus on this literacy means students and workers will be able to have the big picture ‘metanoia’ perspective they will need. > Incorporates open play, curiosity, harnessing failure, resilience, growth mindset and valuing divergent thinking. Having the best solution or project are great but to truly effect the future and have a lasting impact students and workers need to know how to be a vital member of their community, AND how to have that community support them back. This literacy also covers empathy, collaboration and networking skills, being comfortable with giving and receiving feedback, taking on leadership and even keeping a place for civility among much more. The best solutions are useless if no one knows about them.
EntreComp: The Entrepreneurship Competence Framework - Abstract: The development of the entrepreneurial capacity of European citizens and organisations is one of the key policy objectives for the EU and Member States. Ten years ago, the European Commission identified sense of initiative and entrepreneurship as one of the 8 key competences necessary for a knowledge-based society. The EntreComp framework presented in this report proposes a shared definition of entrepreneurship as a competence, with the aim to raise consensus among all stakeholders and to establish a bridge between the worlds of education and work. Developed through a mixed-methods approach, the EntreComp framework is set to become a reference de facto for any initiative aiming to foster entrepreneurial capacity of European citizens. It consists of 3 interrelated and interconnected competence areas: ‘Ideas and opportunities’, ‘Resources’ and ‘Into action’.
Information Literacy Access and Evaluate Information Access information efficiently (time) and effectively (sources)Evaluate information critically and competentlyUse and Manage InformationUse information accurately and creatively for the issue or problem at handManage the flow of information from a wide variety of sourcesApply a fundamental understanding of the ethical/legal issues surrounding the access and use of information Additional resources: 1. ALA | Information Literacy AASL provides leadership for the development of dynamic, student-centered school library media programs. 2. 21st Century Literacies Curriculum The 21st Century Literacies Curriculum presents the process and essential skills for embedding information literacy strategies across all areas of the curriculum.
Learning to swim in the Digital Ocean: new DigComp report develops proficiency levels in detail Education and employment authorities, organisations, companies and citizens from EU Member States count today with specific tools to improve and streamline Digital and Entrepreneurial skills. DigComp describes what digital competence is and groups the competences in five areas. Its latest version, DigComp 2.1, describes those competences across eight proficiency levels, from foundation/beginner to highly specialised, and offers examples of use applied to employment and education in the form of infographics and visual guides. It was presented today at an event in Brussels where organisations from across Europe explained their own initiatives based on these competence frameworks. At today's event, we learnt from initiatives such as transforming prison education to improve the employability opportunities of inmates brought by SFEDI Group. Background More information from all our studies can be found on the JRC Science Hub research topic on Learning and Skills.