


Glande pinéale Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Épiphyse. Vue tridimensionnelle de l'épiphyse (en rouge) Connue depuis au moins l'époque de Galien (au IIe siècle ap. Fonctions[modifier | modifier le code] La synthèse de la mélatonine se fait en quatre étapes enzymatiques dans l'épiphyse à partir de l'acide aminé essentiel tryptophane, en passant par une étape de synthèse de la sérotonine. Dans l'espèce humaine, la glande pinéale croît en volume jusqu'à l'âge d'un à deux ans puis se stabilise [5],[6] mais sa masse augmente à partir de la puberté. Il semblerait que l'épiphyse joue donc aussi un rôle dans la régulation du développement sexuel par le fait que la mélatonine aurait un effet antigonadotrope qui inhibe l'apparition des caractères sexuels secondaires. Enfin, l'épiphyse participe aussi à la régulation des rythmes infradiens liés aux saisons (hibernation, œstrus). Neuroanatomie et neurophysiologie[modifier | modifier le code]
Conifer cone The male cone (microstrobilus or pollen cone) is structurally similar across all conifers, differing only in small ways (mostly in scale arrangement) from species to species. Extending out from a central axis are microsporophylls (modified leaves). Under each microsporophyll is one or several microsporangia (pollen sacs). The female cone (megastrobilus, seed cone, or ovulate cone) contains ovules which, when fertilized by pollen, become seeds. The female cone structure varies more markedly between the different conifer families, and is often crucial for the identification of many species of conifers. Female cones of the conifer families[edit] Pinaceae cones[edit] Intact and disintegrated fir cones The members of the pine family (pines, spruces, firs, cedars, larches, etc.) have cones that are imbricate (that is, with scales overlapping each other like fish scales). Araucariaceae cones[edit] Podocarpaceae cones[edit] Berry-like Podocarpus cone Cupressaceae cones[edit] Sciadopityaceae cones[edit]
Melanin theory Melanin theory is a pseudoscientific theory of Black racial superiority,[1] based on the physical properties of melanin, a natural polymer and organic semiconductor.[2] In humans, melanin is the primary determinant of skin color. People whose ancestors lived for long periods in the regions of the globe near the equator generally have larger quantities of eumelanin in their skins. Melanin theorists assert that the possession of greater quantities of melanin gives black people inherent superiority. Conversely, its lack demonstrates the alleged inhumanity and inferiority of white people. Scientists consider melanin theory to be pseudoscience. Science and the melanin theory[edit] There is, however, a correlation between cutaneous melanin and the substantia nigra vis-a-vis Parkinson's disease, a neurological disease condition in which there is a loss of melanin-pigmented cells of the substantia nigra. Claims of melanin theory[edit] White people as albino mutants[edit] Frances Welsing[edit]
The Pineal Gland - The "Seat of the Soul"? Wonderful article, that needs to be shared! Entirely by Gary Vey (viewzone.com), After writing se... Wonderful article, that needs to be shared! Entirely by Gary Vey (viewzone.com), After writing several articles on reincarnation and enlightenment, many readers asked me why I never mentioned the significance of the pineal gland -- a small structure about the size of a pea, located in the middle of the brain. Descartes was obsessed with understanding who we are. He observed that the senses can be fooled, that most of what we think we know is really illusion and finally struggled with the possibility that our own identity as individuals was also not real. His famous statement endures: Cogno ergo sum -- I think, therefore I am. Although the soul is joined with the entire body, there is one part of the body [the pineal] in which it exercises its function more than elsewhere... Today, with an understanding of computers, we might take issue with Descartes. Brain Sand
Aliments qui alimentent la glande pinéale Notre glande pinéale autrement connu comme notre glande maîtresse ou de la glande qui régit sur notre troisième œil est le centre de la conscience psychique dans l’esprit humain. Il est de la taille d’un pois et se situe dans une grotte située derrière la glande pituitaire. Elle produit naturellement une hormone mélatonine qui régule appelé les rythmes du corps quotidien qui traitent directement avec le jour et les cycles de la nuit. Développer et élargir la fonction et l’énergie de votre glande pinéale est extrêmement important car il affecte tous les systèmes de votre corps physique et il a le potentiel pour déterminer l’expansion ou la contraction de votre conscience psychique, la conscience et l’expérience. La lumière du soleil est extrêmement important pour la glande pinéale et oui le soleil est une forme de nourriture que la nourriture est une substance qui nourrit le corps. glande pineale
Serotonin Serotonin /ˌsɛrəˈtoʊnɨn/ or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), platelets, and the central nervous system (CNS) of animals, including humans. It is popularly thought to be a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness.[6] Serotonin secreted from the enterochromaffin cells eventually finds its way out of tissues into the blood. There, it is actively taken up by blood platelets, which store it. When the platelets bind to a clot, they release serotonin, where it serves as a vasoconstrictor and helps to regulate hemostasis and blood clotting. In addition to animals, serotonin is found in fungi and plants.[10] Serotonin's presence in insect venoms and plant spines serves to cause pain, which is a side-effect of serotonin injection. Functions[edit] Receptors[edit] Gauge of food availability (appetite)[edit] Effects of food content[edit] [edit]
Melanin, Afrocentricity, and Pseudoscience | Bernard Ortiz de Montellano Ortizde Montellanol showed affinities with tropical African patterns and differed notably from theMaghreb pattern. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Nile valley was pri-marily settled by immigrants from both the Sahara and from more southern areasand that Egyptian culture was formed by the fusion of Saharan and Nilotic peoples(Hassan, 1988). The mixture of phenotypes suggested by the archaeological andskeletal evidence is amply supported by representations in art and sculpture (Ver-coutter, 1978; O’Connor, 1971; “rigger, 1978; Kelly, 1991). et al. offer fur-ther review of Egyptian biological status (this volume). a multiracialsociety that did not discriminate internally on the basis of color, but looked downon all foreigners regardless of color (Yurco, 1989,1990; Snowden, 1970,1989,1992;Young, 1992; Levine, 1992; Coleman, 1992). racially mixed society with all of Greek civilization was stolen from Egypt(James, 1988; Ben-Yochannan, 1971). the superiority of Egyptians, the primary source
You need headphones... Pourquoi et comment détartrer votre glande pinéale La glande pinéale pourrait être la partie la plus importante de votre système nerveux tout entier. Il s’agit essentiellement d’une antenne spirituelle, votre équivalent physique d’un troisième œil. Il est essentiel pour atteindre des niveaux plus élevés de conscience tout en restant dans un corps physique. → Activer la pinéale pour accéder aux mondes parallèles, un mécanisme naturel qui fera passer l’humanité à l’ère spirituelle La glande pinéale se trouve au centre géométrique du cerveau. La calcification fait en sorte que les cristaux dans la glande s’attachent aux dépôts de minéraux. Les effets de la calcification sont la dépression, l’anxiété, la boulimie/anorexie, la schizophrénie et d’autres formes de maladies mentales. La calcification de la glande pinéale est causée principalement par le fluorure qui circule dans notre sang. Calcification …? Malheureusement, pour la plupart des gens, la glande pinéale est fortement entartrée. Eau, alimentation et mode de vie Zéolite Chlorella Coriandre
Melatonin Melatonin The hormone can be used as a sleep aid and in the treatment of sleep disorders. It can be taken orally as capsules, tablets, or liquid. It is also available in a form to be used sublingually, and there are transdermal patches. There have been few clinical trials, particularly long-term ones, in the use of melatonin in humans. Discovery[edit] Biosynthesis[edit] Melatonin biosynthesis involves four enzymatic steps from the essential dietary amino acid tryptophan, which follows a serotonin pathway. In bacteria, protists, fungi, and plants melatonin is synthesized indirectly with tryptophan as an intermediate product of the shikimic acid pathway. Regulation[edit] In vertebrates, melatonin secretion is regulated by norepinephrine. It is principally blue light, around 460 to 480 nm, that suppresses melatonin,[24] proportional to the light intensity and length of exposure. Animals[edit] Plants[edit] Functions[edit] Circadian rhythm[edit] Antioxidant[edit] Immune system[edit] Medical uses[edit]
DÉTARTRER LA GLANDE PINÉALE REMETTRE EN FONCTION SA GLANDE PINÉALE 4ème partie La glande pinéale est le centre recevant les rayons du soleil qui, une fois reçus sont réfléchis dans différentes directions du corps. En outre, elle est le récepteur de la couronne d’énergie, et elle détient une quantité incroyable d’informations à propos de notre passé, celui de notre âme, tout comme pour notre avenir, pour notre évolution, et toute l’histoire de l’univers. Tout est stocké à l’intérieur de notre Soi supérieur dans la conscience universelle. Il serait impossible de recevoir toutes ces informations en une seule fois. Ainsi la glande pinéale est une antenne radio de coordination, recevant les rayons les plus forts à venir par le biais de toutes les sources de lumière. L’influence première en est une d’un plan magnétique, ce n’est pas une lumière électrique, mais l’énergie gravitationnelle. Le macrocosme contient notre planète, l’univers, les galaxies et les différents systèmes stellaires. Points précis de la pinéale
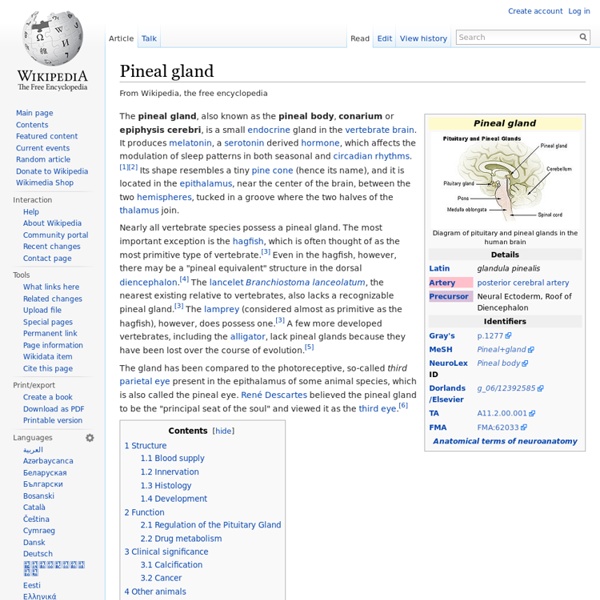
Endocrine system In addition to the specialised endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart and gonads, have secondary endocrine functions. For example the kidney secretes endocrine hormones such as erythropoietin and renin. A number of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. As opposed to endocrine factors that travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system, other signaling molecules, such as paracrine factors involved in paracrine signalling diffuse over a relatively short distance. The word endocrine derives from the Greek words ἐνδο- endo- "inside, within," and κρίνειν krinein "to separate, distinguish". Endocrine organs and known secreted hormones[edit] Endocrine glands in the human head and neck and their hormones Hypothalamus[edit] Pineal body (epiphysis)[edit] Pituitary gland (hypophysis)[edit] Thyroid[edit] Skin[edit]
Pourquoi et comment détartrer votre glande pinéale La glande pinéale pourrait être la partie la plus importante de votre système nerveux tout entier. Il s’agit essentiellement d’une antenne spirituelle, votre équivalent physique d’un troisième œil. Il est essentiel pour atteindre des niveaux plus élevés de conscience tout en restant dans un corps physique. La glande pinéale se trouve au centre géométrique du cerveau. Elle est creuse et rempli d’un fluide contenant des cristaux. La calcification fait en sorte que les cristaux dans la glande s’attachent aux dépôts de minéraux. Les effets de la calcification sont la dépression, l’anxiété, la boulimie/anorexie, la schizophrénie et d’autres formes de maladies mentales. La mélatonine, souvent dénommée hormone du sommeil, est surtout connue comme étant l’hormone centrale de régulation des rythmes chronobiologiques, et d’un certain point de vue, de pratiquement l’ensemble des sécrétions hormonales.(…) Elle est sécrétée par la glande pinéale en réponse à l’absence de lumière. Calcification … ?