


Man Chooses to Cut Off His Hand – And Get a Bionic One (video For the second time in a calendar year, a patient has chosen to cut off his own hand so that he could be fitted with a bionic one. It is a testament to the progress of bionics that patients are beginning to favor the technological alternative over ineffective biological treatments. Milo In 2001, while on vacation in his native Serbia, the patient called “Milo” was severely injured in a motorcycle accident. He skidded into a lamppost, crushing his leg and right shoulder. The bionic hand, manufactured by the German prosthetics company Otto Bock, is equipped with six sensors that overly the skin and detect neuronal signals in the forearm. Milo just woke from surgery earlier this week and hasn’t had time yet to verify the operation’s success. Patrick Last year a 24-year old Austrian man named Patrick became one of the first patients ever to undergo ‘elective amputation’ surgery. Now, Patrick can tie his shoes again, and he can fill a glass with water without dropping or breaking it.
www.readwriteweb.com/archives/code-free_augmented_reality_in_under_5_minutes_video.php Augmented reality guru Bruce Sterling shared a fascinating video on his Wired.com blog Beyond the Beyond today that shows a developer building an AR application without any programming language in just shy of five minutes. Using the Mac-based visual design app Quartz Composer and few additional plugins, the developer (apparently a Russian named Vladmir, according to his YouTube account) quickly assembles the application using Quartz’s visual Yahoo Pipes-like interface. The video embedded above is pretty easy to follow despite being a screencast of a complex design application. The experience itself is not the impressive thing – fans of AR have seen webcams place objects on black and white makers for a while now. This application is an innovative implementation of the ARToolKit, a free and open-source library for creating AR apps created in 1999.
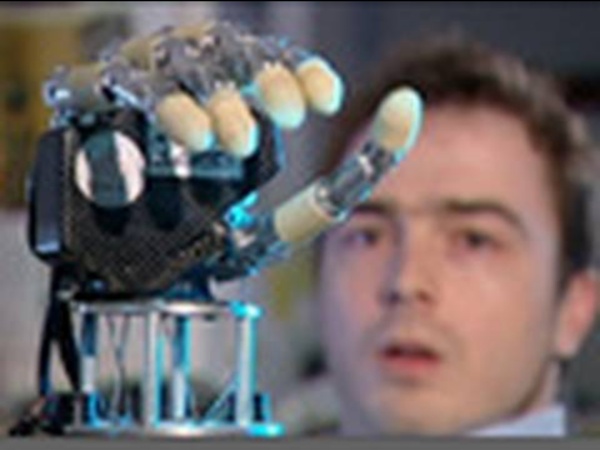
Custom Fit Bionic Fingers Work Like The Real Thing (Video Touch Bionics is moving forward with its prosthetic fingers. They have much of the same capability as the i-Limb, but customized to each amputee's unique physiology. In the world of prosthetics, there’s really no such thing as “one size fits all.” There’s been a ton of really exciting news about prosthetics this year. Typically a mechanized prosthesis can handle one kind of input: pressure sensitive pads, electrical signals measured from the skin, or wires directly connected to nerves. As each prosthesis is different, and each patient has a different amputation, getting Pro-Digits to respond to myo-electric control can take some calibration. One of the really remarkable features of Pro-Digits is that they can be cosmetically matched to the rest of your body. It took me a few seconds to recognize the i-Limb on the right. I guess the i-Limb is the one on top? [photo and video credit: Touch Bionics]
Que se passera-t-il le jour où les ordinateurs seront plus intelligents que les humains La lecture de la semaine, il s’agit d’un article extrait du numéro d’avril du magazine The Walrus, mensuel canadien de Toronto. On le doit à Alex Hutchinson et il s’intitule “Déficit d’intelligence : que se passera-t-il le jour où les ordinateurs seront plus intelligents que les humains ?” Un jour dans le siècle qui vient – et peut-être plus tôt que vous ne croyez, commence Hutchinson – des chercheurs arriveront sans doute à créer une intelligence artificielle plus performante que la nôtre. Image : La page d’accueil de la Lifeboat Fondation. L’auteur rappelle que Vernor Vinge, le mathématicien et informaticien américain, avait nommé ce moment de l’histoire la “Singularité technologique” et qu’il l’imaginait advenir avant 2030. C’est à ce dernier que s’intéresse particulièrement cet article, car Sawyer, non content d’être un auteur de science-fiction à succès, siège à la Fondation Lifeboat. Et on peut tout à fait voir là une menace pour l’humanité. 1. Xavier de la Porte
Custoprothetik The Law of Accelerating Returns An analysis of the history of technology shows that technological change is exponential, contrary to the common-sense “intuitive linear” view. So we won’t experience 100 years of progress in the 21st century — it will be more like 20,000 years of progress (at today’s rate). The “returns,” such as chip speed and cost-effectiveness, also increase exponentially. You will get $40 trillion just by reading this essay and understanding what it says. Now back to the future: it’s widely misunderstood. The Intuitive Linear View versus the Historical Exponential View Most long range forecasts of technical feasibility in future time periods dramatically underestimate the power of future technology because they are based on what I call the “intuitive linear” view of technological progress rather than the “historical exponential view.” When people think of a future period, they intuitively assume that the current rate of progress will continue for future periods. The Law of Accelerating Returns
Alan Turing Alan Turing en 1936. Alan Mathison Turing, né le 23 juin 1912 à Londres et mort le 7 juin 1954 à Wilmslow, est un mathématicien et cryptologue britannique, auteur de travaux qui fondent scientifiquement l'informatique. Il est aussi un des pionniers de l'Intelligence artificielle[1]. Pour résoudre le problème fondamental de la décidabilité en arithmétique, il présente en 1936 une expérience de pensée que l'on nommera ensuite machine de Turing et des concepts de programme et de programmation, qui prendront tout leur sens avec la diffusion des ordinateurs, dans la seconde moitié du XXe siècle. Poursuivi en justice en 1952 pour homosexualité, il choisit, pour éviter la prison, la castration chimique par prise d'œstrogènes. Biographie Enfance et jeunesse Ses parents l'inscrivent à l'école St. Études supérieures et travaux sur la calculabilité En 1928, l'Allemand David Hilbert énonce le problème de la décision — connu sous le nom allemand d'« Entscheidungsproblem ». Cryptanalyse Codage de la voix
CHERCHEURS, THEORICIENS A-G Page 1/3 créée le 17 août 1999 - mise à jour le 17 Avril 2004 - dernière mise à jour le 07 décembre 2005 BAHMANN Wolfram Secrétaire Européen de P.A.C.E. Il diffuse, entre autres textes, une compilation de 49 pages, faite à partir des présentations et réunions d’informations du Dr Harold Puthoff : " Recherche sur le ZPE, extraction d’énergie à partir de l’espace. En plus du secrétariat Européen de P.A.C.E., (visite de site recommandée sur ), Wolfram Bahmann assure le secrétariat de la DVS depuis le 22/11/97. BAILEY Patrick G. PO Box 201 Los Altos CA 94023-0201Président de INE P.O.Box 58639 Salt LAKE City, UT 84158-8639Tél :801-583-6232. Lors del’International Forum on New Science(1304 S College avenue Ft. Au congrès de Denver 94, il a présenté un panorama complet sur les appareils à Energie Libre et les preuves expérimentales relatives au ZPE faites par des chercheurs qui n’assistaient pas au congrès, mais dont il fournit les coordonnées. P. BARRETT Terence W
Cybernetique et psyche