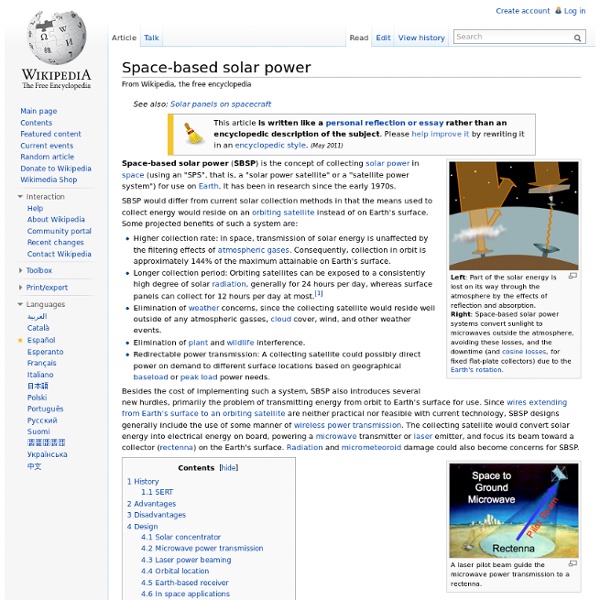
Space-based solar power
The Solar Project
Coordinates: Solar Two Power Tower Project The Solar Project consists of the Solar One, Solar Two and Solar Tres solar thermal power plants based in the Mojave Desert, USA and Andalucía, Spain. Solar Two was demolished in 2009.[1] Solar One[edit] Solar One was a pilot solar-thermal project built in the Mojave Desert just east of Barstow, CA, USA. Solar One's method of collecting energy was based on concentrating the sun's energy onto a common focal point to produce heat to run a steam turbine generator. In the late 1970s, a competition was held by DoE to obtain the best heliostat design for the project. The project produced 10 MW of electricity using 1,818 mirrors, each 40 m² (430 ft²) with a total area of 72,650 m² (782,000 ft²). WikiMiniAtlas During times of high winds, blowing dust is sometimes illuminated by the reflected sunbeams to create an unusual atmospheric phenomenon in the vicinity of the power tower. Solar Two[edit] Solar Tres[edit] Land use[edit] In popular culture[edit]
HIGH INTENSITY LASER POWER BEAMING RECEIVER FOR SPACE AND TERRESTRIAL APPLICATIONS
Abstract: Systems and methods are described that facilitate refueling a vehicle with electrical energy by targeting receiver thereon and pointing a high-intensity laser source at the receiver. Vertical multi-junction (VMJ) photocells receive the laser energy and convert the laser energy into electrical energy. Claims: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Description: [0001] This application claims priority to U.S. [0003] This invention relates to a method and apparatus for receiving high-intensity laser light and converting it into electrical energy for refueling a vehicle or a space craft. [0004] While the invention is particularly directed to the art of refueling aerial vehicles, and will be thus described with specific reference thereto, it will be appreciated that the invention has usefulness in other fields and applications. [0011] Further scope of the applicability of the invention will become apparent from the detailed description provided below.
DESERTEC Foundation: Start
SOLAR POWER SATELLITE SYSTEM FOR TRANSMITTING MICROWAVE ENERGY TO THE EARTH AND METHOD OF ARRANGING A SOLAR POWER SATELLITE SYSTEM ABOUT THE SUN FOR SAME
Abstract: Solar power satellite system for transmitting microwave energy to the earth and a method of arranging the solar power satellite system about the sun for same. The solar power satellite system comprises a space-based power generation unit disposed in a planetary orbit about the sun. A photovoltaic cell on the space-based power generation unit collects solar energy that is then converted to microwave energy to be beamed to the earth. A ground-based rectenna receives the microwave energy and converts the microwave energy to electricity that is transmitted to an end user. The solar power satellite system and method provides electrical power on earth day or night and regardless of atmospheric conditions. Claims: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Description: [0001] This invention generally relates to solar power satellites and more particularly relates to solar power satellite systems.
Related:
Related: