

Geology Entrance You might wish to start in the Cenozoic Era (65 million years ago to the present) and work back through time, or start with Hadean time (4.5 to 3.8 billion years ago) and journey forward to the present day. No matter "when" you start, don't forget to stop along the way to learn about the stratigraphy, ancient life, fossil localities, and tectonics of the various time periods. Here are three links that can help to speed your journey: 1) Get helpful hints on navigating the Geology Wing. 2) Read about the history of the geologic time scale, and find out more about how it is organized. 3) Jump to a specific time period using the UCMP Geological Time Machine. Last but not least, don't forget to visit our exhibit on Plate tectonics, an important geological concept in any time period!
From Pre History to Civilization From Pre History to Civilization The term pre-history refers to the period when written languages and records did not yet exist. How do we know about the pre-history period? Archeology-the study of the ways of life of early people by studying what they left behind (artifacts) Historians-study all evidence about the past, including archeology, written documents, pictures, films, etc. The stone age is divided into two parts. 1) Paleolithic (Old stone age) 2) Neolithic (New stone age) NOTE: Problems with the term “civilization” Historians and anthropologist have noted several problems with the term civilization. At its most basic element, civilization is based on the food supply. “Three meals a day area a highly advanced institution. People grubbed food from the earth with their bare hands, then used simple tools made from stones or animal bones. It was nature that finally taught man to save for tomorrow. This style of living is called Paleolithic. 1) limited population group 3) social equality
Stone tool Stone has been used to make a wide variety of different tools throughout history, including arrow heads, spearpoints and querns. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or chipped stone, and a person who creates tools out of the latter is known as a flintknapper. Chipped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert or flint, radiolarite, chalcedony, obsidian, basalt, and quartzite via a process known as lithic reduction. One simple form of reduction is to strike stone flakes from a nucleus (core) of material using a hammerstone or similar hard hammer fabricator. If the goal of the reduction strategy is to produce flakes, the remnant lithic core may be discarded once it has become too small to use. Evolution[edit] Clark's scheme was adopted enthusiastically by the archaeological community. Pre-Mode I[edit] Kenya Ethiopia Mode I: The Oldowan Industry[edit] A typical Oldowan simple chopping-tool. Mode II: The Acheulean Industry[edit] Neolithic industries[edit]
List of timelines From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of timelines currently on Wikipedia. §Types[edit] §General timelines[edit] §History[edit] §Arts[edit] §Biographical timelines[edit] §Crime[edit] §Events[edit] §Disasters[edit] §Economics[edit] §Entertainment[edit] §Environmental issues[edit] §Fiction[edit] §Geographical timelines[edit] Timeline of country and capital changes §Ancient civilizations[edit] §Extant civilizations[edit] §Supranational entities and regions, peoples[edit] §Sovereign states[edit] §Subnational regions and cities, narrow timelines[edit] §Law[edit] §Military[edit] §Military conflicts[edit] §Philosophy[edit] §Politics[edit] §Religion[edit] §Ayyavazhi[edit] Timeline of Ayyavazhi history (1809–present) §Buddhism[edit] Timeline of Buddhism (563 BCE – present) §Christianity[edit] §Islam[edit] §Jainism[edit] Timeline of Jainism §Judaism[edit] §Sikhism[edit] Sikh Gurus (1469–1666) §Science[edit] §Astronautics and planetary science[edit] §Astronomy, Astrophysics, and Cosmology[edit] §Biology[edit] §Sports[edit]
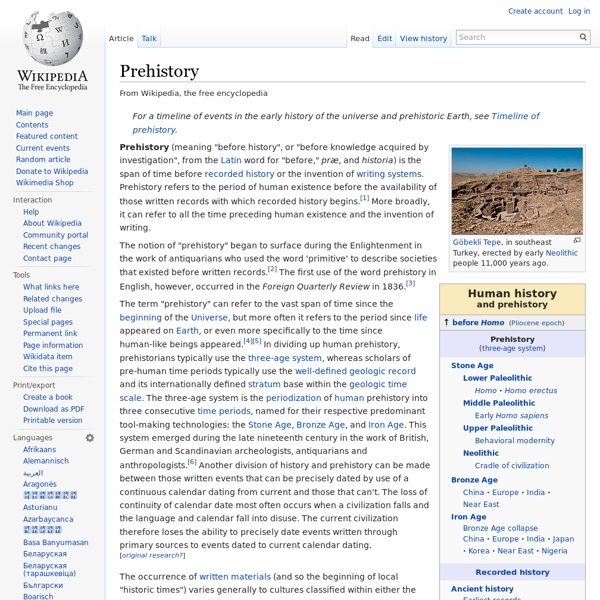
Geologic time scale The geologic time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological measurement that relates stratigraphy to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred throughout Earth's history. The table of geologic time spans presented here agrees with the nomenclature, dates and standard color codes set forth by the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Evidence from radiometric dating indicates that the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The geology or deep time of Earth's past has been organized into various units according to events which took place in each period. Different spans of time on the GTS are usually delimited by changes in the composition of strata which correspond to them, indicating major geological or paleontological events, such as mass extinctions. Terminology[edit] History and nomenclature of the time scale[edit] Graphical representation of Earth's history as a spiral
Paleo-Africans in America Several types of blacks entered the Americas including the Anu or negrito type and the Proto-Saharan variety of blacks. Up until recently it was believed that the first humans crossed the Bering Strait 12,000 B.P., to enter the North American continent.(Begley 1991, p.15) This view was never accepted by physical anthropologists who have found skeletal remains far older than 12,000 B.P. The last ice age in North America lasted between 110,000 and 17,000BP. The first Americans did not cross the Bearing Straits to enter the Americas.The earliest sites for Negroes date between 20,000 and 40000 years ago Old Crow Basin Canada(38,000BC) Pedra Furada (45,000BC) Brazil. Chile: Monteverde (12,500 years), Tierra del Fuego, Cueva de Fell, Tres Arroyos and some other places. There are older ones in the Argentinian Patagonia. Today archaeologists have found sites from Canada to Chile that range between 20,000 and 40,000 years old. P.S. Here we have a comparison of ancient skulls found in the Americas.
Stone Age Ġgantija temples in Gozo, Malta. Some of the world's oldest free-standing structures. Stone Age artifacts include tools used by modern humans and by their predecessor species in the genus Homo, and possibly by the earlier partly contemporaneous genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus. The Stone Age is the first of the three-age system of archaeology, which divides human technological prehistory into three periods: Historical significance[edit] Modern Awash River, Ethiopia, descendant of the Palaeo-Awash, source of the sediments in which the oldest Stone Age tools have been found The Stone Age is contemporaneous with the evolution of the genus Homo, the only exception possibly being at the very beginning, when species prior to Homo may have manufactured tools.[3] According to the age and location of the current evidence, the cradle of the genus is the East African Rift System, especially toward the north in Ethiopia, where it is bordered by grasslands. The Stone Age in archaeology[edit]
List of time periods - Wikipedia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The categorisation of the past into discrete, quantified named blocks of time is called periodization.[1] This is a list of such named time periods as defined in various fields of study. These can be divided broadly into prehistorical periods and historical periods (when written records began to be kept). In archaeology and anthropology, prehistory is subdivided around the three-age system, this list includes the use of the three-age system as well as a number of various designation used in reference to sub-ages within the traditional three. The dates for each age can vary by region. General periods[edit] Sociological periods[edit] Only for late modern contemporary history. Technological periods[edit] PrehistoryAncient history (The Bronze and Iron Ages are not part of prehistory for all regions and civilizations who had adopted or developed a writing system.) American periods[edit] Australian periods[edit] Southeast Asian periods[edit] Filipino periods[edit]
Geologic time scale Online exhibits Geologic time scale Take a journey back through the history of the Earth — jump to a specific time period using the time scale below and examine ancient life, climates, and geography. Ways to begin your exploration: Use the links in the "time machine" below and explore a specific period that interests you.Read more about the geologic time scale, its origins and its time divisions.Find out more about plate tectonics, an important geological concept in any time period! The Vanishing Evidence of Classical African Civilizations “A 2001 Update” Prof. Manu Ampim The “Vanishing Evidence” series is a general summary of years of detailed observation and research. I originally wrote "The Vanishing Evidence of Classical African Civilizations" series in The Gaither Reporter in 1995-1996. My initial goal was simply to follow the path of research outlined by the eminent scholar, Dr. My observations of the evidence are careful and are supported by photographic and video documentation. One of the most absurd invention of the conspirators is the forged statues of Ra-Hotep and Nofret in the Cairo Museum. One of the great forgeries of the 19th century which has already been proven is that of the famous Queen Tetisheri. Who are the conspirators responsible for these acts of destruction, alteration and invention is a basic question that must be answered. This brings us to the identification of a large group of conspirators, who are the handlers of the excavated artifacts. Prof. Prof.
Iron Chemical element, symbol Fe and atomic number 26 Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe (from Latin ferrum 'iron') and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching 1,500 °C (2,730 °F) or higher, about 500 °C (932 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. The body of an adult human contains about 4 grams (0.005% body weight) of iron, mostly in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Most notably, Iron is the highest atomic number element that could be created in exothermic nucleosynthesis. Characteristics Allotropes The first three forms are observed at ordinary pressures. The physical properties of iron at very high pressures and temperatures have also been studied extensively,[8][9] because of their relevance to theories about the cores of the Earth and other planets. Melting and boiling points Magnetic properties Isotopes Cosmogenesis Oceans
List of state leaders in the 8th century - Wikipedia State leaders in the 7th century – State leaders in the 9th century – State leaders by year This is a list of state leaders in the 8th century (701–800) AD. Africa[edit] Africa: Northeast[edit] Makuria (complete list) – Merkourios, King (696–710)Simeon, King (early 8th century)Abraham, King (early 8th century)Markos, King (mid-8th century)Kyriakos, King (c.747–768)Mikhael, King (c.785/794–804/813) Africa: Northcentral[edit] Ifriqiya (complete list) – Rustamid dynasty (complete list) – ʿAbdu r-Rahman ibn Bahram ibn Rūstam (Bānū-Bādūsyān), Imam (776–788)ʿAbdu l-Wahhab ibn Abd ar-Rahman, Imam (788–824) Africa: Northwest[edit] Barghawata (complete list) – Idrisid dynasty (complete list) – Idris I, King (788–791)Idris II, King (791–828) Kingdom of Nekor (complete list) – America: Mesoamerica[edit] Calakmul (complete list) – Yuknoom Took' K'awiil, King (c.702–731)Wamaw K'awiil, King (c.736)Ruler Y, King (c.741)Great Serpent, King (c.751)B'olon K'awiil, King (771–c.789) Copán (complete list) – Asia[edit] Turks
History of the Earth The history of the Earth concerns the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.[1][2] Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's past. The age of Earth is approximately one-third of the age of the universe. An immense amount of biological and geological change has occurred in that time span. The first life forms appeared between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years ago. Geological change has been constantly occurring on our planet since the time of its formation and biological change since the first appearance of life. Geological time, condensed in a diagram displaying the relative lengths of the eons of Earth's history Geologic time scale[edit] The history of the Earth is organized chronologically in a table known as the geologic time scale, which is split into intervals based on stratigraphic analysis.[2][6] A full-time scale can be found at the main article. Millions of Years Formation of the Moon[edit]