


Joseph Louis Lagrange Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Lodovico Lagrangia [1][2][3] (also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrangia [4]), 25 January 1736 in Turin, Piedmont; died 10 April 1813 in Paris) was an Italian Enlightenment Era mathematician and astronomer. He made significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics. In 1766, on the recommendation of Euler and d'Alembert, Lagrange succeeded Euler as the director of mathematics at the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, Prussia, where he stayed for over twenty years, producing volumes of work and winning several prizes of the French Academy of Sciences. In 1787, at age 51, he moved from Berlin to Paris and became a member of the French Academy. Scientific contribution[edit] Biography[edit] In appearance he was of medium height, and slightly formed, with pale blue eyes and a colourless complexion. W.W. Early years[edit] - Variational calculus[edit] - Miscellanea Taurinensia[edit] Berlin[edit]
Cercles et droites d'Euler 1.b. Relation d'Euler dans le triangle Dans un triangle équilatéral, le centre du cercle circonscrit, le centre de gravité et l'orthocentre sont confondus. Pour démontrer l'égalité vectorielle (relation d'Euler), faire un changement de point de vue en transformant l'exercice en « caractériser le point M tel que Caractérisation vectorielle de l'orthocentre Soit M le point tel que : , d'où Une relation de Chasles permet d'écrire : et si A’ est le milieu de [BC], la forme vectorielle du théorème de la médiane donne Le vecteur est colinéaire à . En remplaçant M par H on obtient la relation vectorielle et la relation d'Euler Quel est le nom de la droite qui joint le centre du cercle circonscrit, le centre de gravité et l'orthocentre d'un triangle ? La définition vectorielle du centre de gravité permet d'écrire 3 donc . Télécharger la figure GéoPlan dr_euler.g2w Voir : quatre relations d'Euler
Indicatrice d'Euler (totient) ChronoMath, une chronologie des MATHÉMATIQUES à l'usage des professeurs de mathématiques, des étudiants et des élèves des lycées & collèges Il s'agit de l'application, traditionnellement notée φ, qui à tout entier naturel n non nul associe le nombre d'entiers naturels inférieurs à n et premiers avec n : φ(n) = Card {k, k∈N, 1 ≤ k ≤ n - 1, pgcd(k,n) = 1} L'indicateur d'Euler joue un rôle important en arithmétique et tout particulièrement dans l'étude et la distribution des nombres premiers. En anglais, on parle de totient function, du latin totiens = tant de fois, proche de quotiens = combien de fois, mais d'usage interrogatif, qui a donné quotient en français et en anglais : chercher le quotient de n par p c'est chercher combien de fois "il y a p dans n". Il apparaît, et cela semble bien évident, que si n est premier, alors φ(n) = n - 1, sinon φ(n) < n - 1. Théorème 1 : Si n est premier, φ(np) = np-1(n - 1) pour tout entier naturel p ≥ 1. Théorème 2 : Remarque : Théorème 3 : Théorème 5 : Buffon
en.m.wikipedia English polymath (1642–1726) Sir Isaac Newton (; 4 January [O.S. 25 December] 1643 – 31 March [O.S. 20 March] 1727)[a] was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author.[5] Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed.[6] His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, achieved the first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics.[7][8] Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz.[9] He contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science.[11][12][13][15] Early life The King's School University of Cambridge Mid-life Calculus Historian of science A. Death
Srinivasa Ramanujan Srinivasa Ramanujan Iyengar FRS (pronunciation: i/sriː.ni.vaː.sə raː.maː.nʊ.dʒən/) (22 December 1887 – 26 April 1920) was an Indian mathematician and autodidact who, with almost no formal training in pure mathematics, made extraordinary contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions. Ramanujan initially developed his own mathematical research in isolation; it was quickly recognized by Indian mathematicians. When his skills became apparent to the wider mathematical community, centred in Europe at the time, he began a famous partnership with the English mathematician G. H. Hardy. Early life[edit] Ramanujan's home on Sarangapani Street, Kumbakonam Ramanujan was born on 22 December 1887 in Erode, Madras Presidency (now Pallipalayam, Erode, Tamil Nadu), at the residence of his maternal grandparents in a Brahmin family.[5] His father, K. Since Ramanujan's father was at work most of the day, his mother took care of him as a child. Mr. for all , and
Théorèmes et formules d'Euler Théorèmes et formules d'Euler Leonhard Paul Euler Leonhard Paul Euler (1707 -1783), mathématicien et physicien suisse, membre de l'Académie royale des sciences de Prusse à Berlin. Il est considéré comme un éminent mathématicien du XVIIIème siècle et l'un des plus grands et des plus prolifiques de tous les temps. Il a travaillé dans presque tous les domaines des mathématiques: La géométrie, le calcul infinitésimal, la trigonométrie, l'algèbre et la théorie des nombres. En notation mathématique: Euler a introduit et popularisé plusieurs conventions de notation par le biais de ses nombreux ouvrages largement diffusés. Enoncé 1 : Le petit théorème de Fermat "Si p est un nombre premier et si a est un entier quelconque, alors est un multiple de p.". Enoncé 2 : Le théorème des deux carrés de Fermat "Un entier est somme de deux carrés si et seulement si chacun de ses facteurs premiers de la forme 4k + 3 intervient à une puissance paire ". Enoncé 3 : Constante d'Euler-Mascheroni Enoncé 4 :
Leonhard Euler ChronoMath, une chronologie des MATHÉMATIQUES à l'usage des professeurs de mathématiques, des étudiants et des élèves des lycées & collèges Né à Bâle d'un père pasteur, Leonhard, esprit brillant étudia les lettres, la théologie et la médecine et semblait, à 17 ans, voué aux ordres religieux. Les Bernoulli étaient des amis de la famille et il fut l'élève de Jean Bernoulli qui persuada Euler père de laisser son fils s'orienter vers les mathématiques. A 18 ans, il se faisait connaître à l'Académie des sciences de Paris par divers mémoires comme ceux sur la théorie des marées et la propagation du son. Introduit par les Bernoulli, il s'installa à Saint-Pétersbourg (1727), alors capitale de l'empire russe, auprès de Pierre Ier le Grand et remplaça Daniel Bernoulli (1733) à l'Académie des sciences pour la physique et les mathématiques. Appelé à Berlin (1741) par Frédéric II, roi de Prusse, il y présida l'Académie des sciences jusqu'en 1766 (c'est Lagrange qui lui succédera). y = ax ⇔ x = loga y
en.m.wikipedia Imperial Standard of Napoleon I Napoléon Bonaparte (/nəˈpoʊliən, -ˈpoʊljən/;[2] French: [napɔleɔ̃ bɔnapaʁt], born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821) was a French military and political leader who rose to prominence during the latter stages of the French Revolution and its associated wars. As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon was born in Corsica to a relatively modest family of noble Italian ancestry that had settled on the island in the 16th century. Napoleon took power in 1799 and installed himself as First Consul with few restrictions on his control of France. To enforce the Continental blockade, he launched a large-scale invasion of Russia in 1812 that proved to be a major military failure. Origins and education Napoleon was born on 15 August 1769 to Carlo Maria di Buonaparte and Maria Letizia Ramolino in his family's ancestral home, Casa Buonaparte, in the town of Ajaccio, the capital of the island of Corsica.
Carl Friedrich Gauss Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (/ɡaʊs/; German: Gauß, pronounced [ɡaʊs]; Latin: Carolus Fridericus Gauss) (30 April 1777 – 23 February 1855) was a German mathematician who contributed significantly to many fields, including number theory, algebra, statistics, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, geophysics, mechanics, electrostatics, astronomy, matrix theory, and optics. Sometimes referred to as the Princeps mathematicorum[1] (Latin, "the Prince of Mathematicians" or "the foremost of mathematicians") and "greatest mathematician since antiquity," Gauss had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science and is ranked as one of history's most influential mathematicians.[2] Early years[edit] Gauss was a child prodigy. The year 1796 was most productive for both Gauss and number theory. Middle years[edit] Gauss, who was 24 at the time, heard about the problem and tackled it. One such method was the fast Fourier transform. Later years and death[edit] Religious views[edit]
La droite d'Euler La figure ci-dessous présente les 4 types de droites remarquables étudiées au collège. (voir définitions des droites et des points de concours en bas de page) Le centre de gravité G, l’orthocentre H et le centre O du cercle circonscrit sont alignés sur une droite appelée droite d’Euler du triangle. Cette découverte, connue avant Leonhard Euler (1707 ; 1783), est en fait due au mathématicien écossais Robert Simson (1687 ; 1768) à qui on n'a pas attribué le nom car il existe dejà une droite de Simson. Par une méthode algébrique, Euler propose cependant en 1765 une démonstration de cette propriété dans un ouvrage écrit en latin Solutions faciles de problèmes difficiles en géométrie. Télécharger la figure dynamique au format GeoGebra. MEDIANES Dans un triangle, une médiane est un segment qui joint un sommet au milieu du côté opposé. HAUTEURS Dans un triangle, une hauteur est une droite qui passe par un sommet et qui est perpendiculaire au côté opposé.
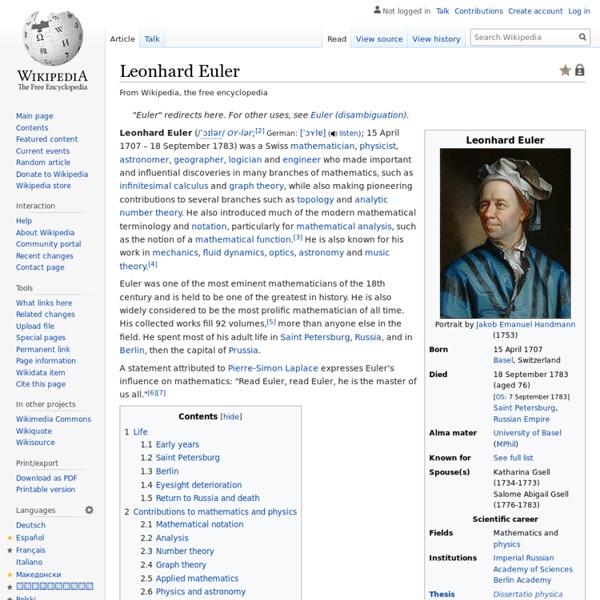
Leonhard Euler Portrait par Johann Georg Brucker (1756). Leonhard Euler (en allemand : [ˈleːɔnhaʁt ˈɔɪ̯lɐ] Écouter), né le 15 avril 1707 à Bâle (Suisse) et mort le 7 septembre 1783 (18 septembre dans le calendrier grégorien) à Saint-Pétersbourg (Empire russe)[1], est un mathématicien et physicien suisse, qui passa la plus grande partie de sa vie dans l'Empire russe et en Allemagne. Il était notamment membre de l'Académie royale des sciences de Prusse à Berlin. Euler est considéré comme un éminent mathématicien du XVIIIe siècle et l'un des plus grands et des plus prolifiques de tous les temps. À l'âge de treize ans, en 1720, Leonhard est inscrit à l'université de Bâle, et en 1723 obtient sa maîtrise de philosophie ou Magister Philosophiæ, grâce à une dissertation qui compare les idées maîtresses de Descartes à celles de Newton. Euler arrive dans la capitale russe le 17 mai 1727, le jour de la mort de Catherine Ire de Russie, veuve de Pierre le Grand. et celui de la fonction arc tangente. est