


Celtic mythology Overview[edit] Though the Celtic world at its apex covered much of western and central Europe, it was not politically unified nor was there any substantial central source of cultural influence or homogeneity; as a result, there was a great deal of variation in local practices of Celtic religion (although certain motifs, for example the god Lugh, appear to have diffused throughout the Celtic world). Inscriptions of more than three hundred deities, often equated with their Roman counterparts, have survived, but of these most appear to have been genii locorum, local or tribal gods, and few were widely worshipped. The nature and functions of these ancient gods can be deduced from their names, the location of their inscriptions, their iconography, the Roman gods they are equated with, and similar figures from later bodies of Celtic mythology. Celtic mythology is found in a number of distinct, if related, subgroups, largely corresponding to the branches of the Celtic languages: The Dagda[edit]
Chinese mythology Chinese mythology refers to those myths found in the historical geographic area of China: these include myths in Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other ethnic groups (of which fifty-six are officially recognized by the current administration of China).[1] Chinese mythology includes creation myths and legends, such as myths concerning the founding of Chinese culture and the Chinese state. As in many cultures' mythologies, Chinese mythology has in the past been believed to be, at least in part, a factual recording of history. Thus, in the study of historical Chinese culture, many of the stories that have been told regarding characters and events which have been written or told of the distant past have a double tradition: one which presents a more historicized and one which presents a more mythological version.[2] Historians have written evidence of Chinese mythological symbolism from the 12th century BC in the Oracle bone script. Major concepts[edit]
Epic of Gilgamesh The Epic of Gilgamesh, an epic poem from Mesopotamia, is considered the world's first truly great work of literature. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with five Sumerian poems about 'Bilgamesh' (Sumerian for 'Gilgamesh'), king of Uruk. These independent stories were used as source material for a combined epic. The first surviving version of this combined epic, known as the "Old Babylonian" version, dates to the 18th century BC and is titled after its incipit, Shūtur eli sharrī ("Surpassing All Other Kings"). The first half of the story discusses Gilgamesh, king of Uruk, and Enkidu, a wild man created by the gods to stop him oppressing the people of Uruk. In the second half of the epic, Gilgamesh's distress at Enkidu's death causes him to undertake a long and perilous journey to discover the secret of eternal life. History[edit] Versions of the epic[edit] Standard Akkadian version[edit] The 12th tablet is a sequel to the original 11, and was probably added at a later date.
Fengshen Yanyi Fengshen Yanyi, also known as Fengshen Bang, or translated as The Investiture of the Gods, is a 16th-century Chinese novel and one of the major vernacular Chinese works in the shenmo genre written during the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644).[1] Consisting of 100 chapters, it was first published in book form around the 1550s.[1] Plot[edit] The novel is a romanticised retelling of the overthrow of King Zhou, the last ruler of the Shang Dynasty, by King Wu, who would establish the Zhou Dynasty in place of Shang. The story integrates oral and written tales of many Chinese mythological figures who are involved in the struggle as well. Bewitched by his concubine Daji, who is actually a vixen spirit in disguise as a beautiful woman, King Zhou of Shang oppresses his people and persecutes those who oppose him, including his own subjects who dare to speak up to him. Some well-known anecdotes[edit] Nüwa and King Zhou[edit] King Zhou visits the temple of the ancient Chinese goddess Nüwa to worship her.
Gilgamesh Gilgamesh (/ˈɡɪl.ɡə.mɛʃ/; Akkadian cuneiform: 𒄑𒂆𒈦 [𒄑𒂆𒈦], Gilgameš, often given the epithet of the King, also known as Bilgamesh in the Sumerian texts)[1] was the fifth king of Uruk, modern day Iraq (Early Dynastic II, first dynasty of Uruk), placing his reign ca. 2500 BC. According to the Sumerian King List he reigned for 126 years. In the Tummal Inscription,[2] Gilgamesh, and his son Urlugal, rebuilt the sanctuary of the goddess Ninlil, in Tummal, a sacred quarter in her city of Nippur. Gilgamesh is the central character in the Epic of Gilgamesh, the greatest surviving work of early Mesopotamian literature. In the epic his father was Lugalbanda and his mother was Ninsun (whom some call Rimat Ninsun), a goddess. In Mesopotamian mythology, Gilgamesh is a demigod of superhuman strength who built the city walls of Uruk to defend his people from external threats, and travelled to meet the sage Utnapishtim, who had survived the Great Deluge. Cuneiform references[edit] See also[edit]
Marduk Marduk (Sumerian spelling in Akkadian: AMAR.UTU 𒀫𒌓 "solar calf"; perhaps from MERI.DUG; Biblical Hebrew מְרֹדַךְ Merodach; Greek Μαρδοχαῖος,[1] Mardochaios) was the Babylonian name of a late-generation god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon, who, when Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of Hammurabi (18th century BCE), started to slowly rise to the position of the head of the Babylonian pantheon, a position he fully acquired by the second half of the second millennium BCE. In the city of Babylon, he resided in the temple Esagila.[2] According to The Encyclopedia of Religion, the name Marduk was probably pronounced Marutuk. In the perfected system of astrology, the planet Jupiter was associated with Marduk by the Hammurabi period.[4] Mythology[edit] Marduk and his dragon Mušḫuššu, from a Babylonian cylinder seal Babylonian[edit] In the case of Ea, the transfer proceeded pacifically and without effacing the older god.
Mesopotamian religion The god Marduk and his dragon Mušḫuššu Mesopotamian religion refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Sumerian and East Semitic Akkadian, Assyrian, Babylonian and later migrant Arameans and Chaldeans, living in Mesopotamia (a region encompassing modern Iraq, Kuwait, southeast Turkey and northeast Syria) that dominated the region for a period of 4200 years from the fourth millennium BCE throughout Mesopotamia to approximately the 10th century CE in Assyria.[1] Mesopotamian polytheism was the only religion in ancient Mesopotamia for thousands of years before entering a period of gradual decline beginning between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE. Reconstruction[edit] As with most dead religions, many aspects of the common practices and intricacies of the doctrine have been lost and forgotten over time. History[edit] Overview map of ancient Mesopotamia. Akkadian names first appear in king lists of these states circa 2800 BCE. Religion in the Neo-Assyrian Empire[edit] "Enlil!
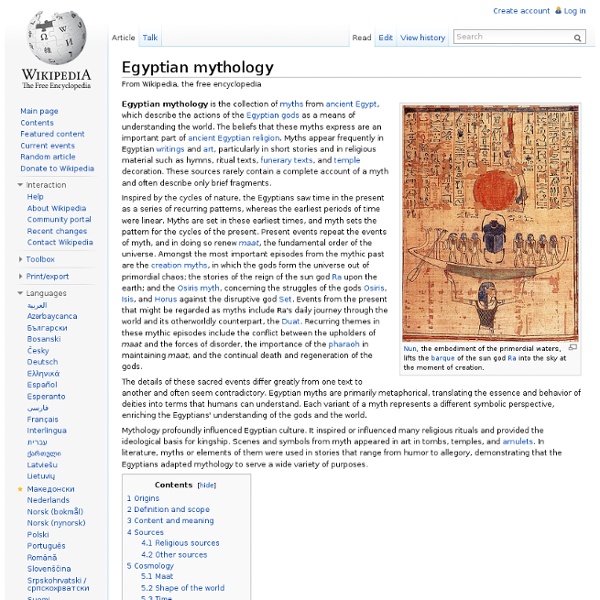
Myth of Osiris and Isis From right to left: Isis, her husband Osiris, and their son Horus, the protagonists of the Osiris myth, in a Twenty-second Dynasty statuette The Osiris myth reached its basic form in or before the 24th century BCE. Many of its elements originated in religious ideas, but the conflict between Horus and Set may have been partly inspired by a regional struggle in Egypt's early history or prehistory. Scholars have tried to discern the exact nature of the events that gave rise to the story, but they have reached no definitive conclusions. Parts of the myth appear in a wide variety of Egyptian texts, from funerary texts and magical spells to short stories. Sources[edit] The same elements from the myth that appear in the Pyramid Texts recur in funerary texts written in later times, such as the Coffin Texts from the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BCE) and the Book of the Dead from the New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BCE). Rituals in honor of Osiris are another major source of information. Synopsis[edit]
Mythology Some (recent) approaches have rejected a conflict between the value of myth and rational thought, often viewing myths, rather than being merely inaccurate historical accounts, as expressions for understanding general psychological, cultural or societal truths. Etymology[edit] The English term mythology predates the word myth by centuries.[5] It appeared in the 15th century,[7] borrowed whole from Middle French mythologie. The word mythology "exposition of myths" comes from Middle French mythologie, from Late Latin mythologia, from Greek μυθολογία mythologia "legendary lore, a telling of mythic legends; a legend, story, tale," from μῦθος mythos "myth" and -λογία -logia "study Terminology[edit] Origins[edit] Euhemerism[edit] Allegory[edit] Some theories propose that myths began as allegories. Personification[edit] Some thinkers believe that myths resulted from the personification of inanimate objects and forces. Myth-ritual theory[edit] Functions of myth[edit] There are two pathologies. General
Nuada Airgetlám In Irish mythology, Nuada or Nuadu (modern spelling: Nuadha), known by the epithet Airgetlám (modern spelling: Airgeadlámh, meaning "silver hand/arm"), was the first king of the Tuatha Dé Danann. He is cognate with the Gaulish and British god Nodens. His Welsh equivalent is Nudd or Lludd Llaw Eraint. Description[edit] Nuada was king of the Tuatha Dé Danann for seven years before they came to Ireland. They made contact with the Fir Bolg, the then-inhabitants of the island, and Nuada sought from them half of the island for the Tuatha Dé, which their king rejected. Bres, aided by the Fomorian Balor of the Evil Eye, attempted to retake the kingship by force, and war and continued oppression followed. Nuada's great sword was one of the Four Treasures of the Tuatha Dé Danann, brought from one of their four great cities.[5] Legacy[edit] Mythological parallels[edit] Etymology[edit] The name Nuada probably derives from a Celtic stem *noudont- or *noudent-, which J. References[edit]
The Dagda Description[edit] Despite his great power and prestige, the Dagda is sometimes depicted as oafish and crude, even comical, wearing a short, rough tunic that barely covers his rump, dragging his great penis on the ground.[1] Such features are thought to be the additions of Christian redactors for comedic purposes. Tellingly, the Middle Irish language Coir Anmann (The Fitness of Names) paints a less clownish picture: "He was a beautiful god of the heathens, for the Tuatha Dé Danann worshipped him: for he was an earth-god to them because of the greatness of his (magical) power. The Dagda had an affair with Bóand, wife of Elcmar. Whilst Aengus was away the Dagda shared out his land among his children, but Aengus returned to discover that nothing had been saved for him. The Dagda was also the father of Bodb Dearg, Cermait, Midir, Aine, and Brigit. Etymology[edit] See also[edit] References[edit] Further reading[edit] Bergin, Osborn (1927).